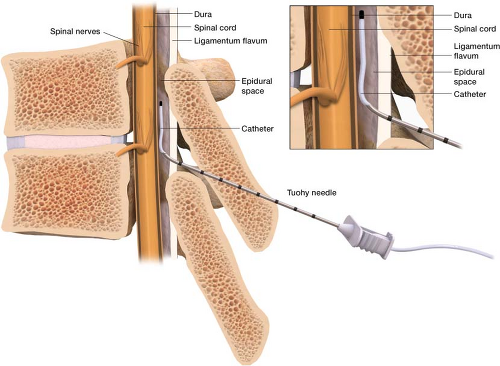
The placement of an epidural catheter is a common practice during certain medical procedures and surgeries to provide pain relief. However, sometimes the catheter is left in place after the procedure for a number of reasons. One main reason is to continue providing pain relief post-operatively without the need for additional injections. This can be especially beneficial for patients who have undergone extensive surgeries or who have chronic pain conditions.
Another reason for leaving the catheter in place is to allow for easy access to administer additional medication if needed. This can be helpful in case the patient experiences an increase in pain levels or if there are complications during recovery. Additionally, leaving the catheter in place can also minimize the risk of infection that may occur with repeated insertions of needles for injections.
In some cases, the catheter may be left in place for an extended period of time for continuous pain management, such as in labor and delivery or for certain types of chronic pain conditions. Overall, leaving the epidural catheter in place can provide ongoing pain relief and improve patient comfort during the recovery process.
Do they leave the epidural needle in?
A needle is used to insert a fine plastic tube called an epidural catheter into your back (spine) near the nerves that carry pain messages to your brain. The needle is then removed, leaving just the catheter in your spine. You may feel mild discomfort when the epidural needle is positioned and the catheter is inserted.
Does the epidural catheter stay in you?
How long will the epidural stay in? The tube will stay in your back until your pain is under control and you can take pain pills. Sometimes this can be up to seven days. If you are pregnant, the tube will be taken out after the baby is born.May 1, 2017
How long does an epidural catheter stay in?
The pain relief should last as long as your labor lasts, and the dose can be adjusted if you experience breakthrough pain. The epidural catheter typically stays in for the duration of your labor up until the time of your transfer from the labor and delivery floor to your discharge to a postpartum room.

Does the epidural tube stay in your back during labor?
An epidural is a numbing medicine given by inserting a needle and a catheter (a small, flexible tube) into the lower part of a woman’s back. The needle is removed, but the catheter remains to deliver pain medication as needed throughout labor.

What is the downside of epidural steroid injection?
An epidural steroid injection can have serious consequences if it’s not administered correctly, or the patient isn’t suitable for the procedure. Known adverse effects of epidural steroid injections include: Neurological symptoms, including an inability to swallow, vertigo, and worsening neck pain [4-5].
What is the dark side of epidural steroid injection?
Although rare, risks and complications that apply to lumbar ESI injections include: Low blood pressure, which can make you feel lightheaded. Severe headache caused by spinal fluid leakage. Infection from the epidural procedure, such as an epidural abscess, discitis, osteomyelitis or meningitis.
How successful are epidural shots for back pain?
Treatment with epidural steroid injections in the lower spine is not effective for reducing pain and disability. The injections may be more effective than placebo at short-term follow-up, but the effects are not clinically meaningful.
Why not to get a epidural steroid injection?
The dark side of epidural injections is that, in extremely rare cases, they can result in convulsions, serious infection, permanent nerve damage, severe breathing difficulties, and even death. Permanent nerve damage results from spinal cord damage or severe infection caused by an epidural injection.
What are the side effects of L4 l5 epidural steroid injection?
– “Steroid flush,” or flushing of the face and chest, with warmth and an increase in temperature for several days.
– Sleeping problems.
– Anxiety.
– Menstrual changes.
– Water retention.
– In rare instances, pain that actually increases for several days after the procedure.