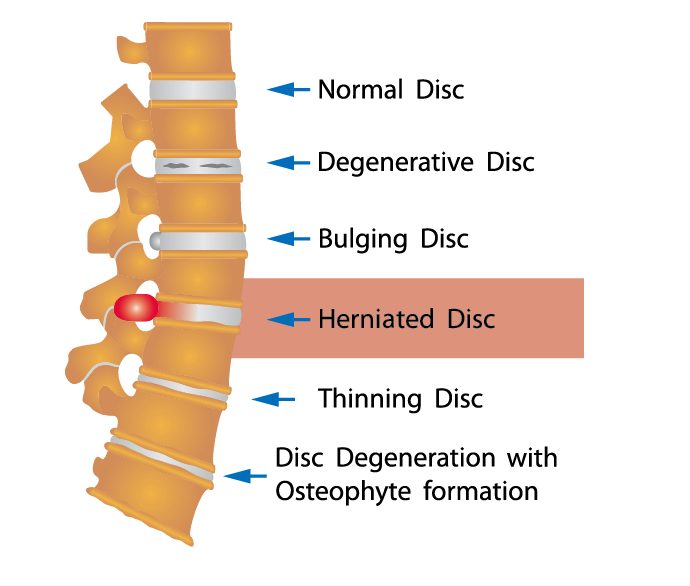
A herniated disc, also known as a slipped or ruptured disc, occurs when the jelly-like material inside a spinal disc pushes through a crack or tear in the disc’s tough exterior. This condition commonly affects individuals between the ages of 30 and 50, with a slightly higher prevalence in men.
There are several risk factors that can increase the likelihood of developing a herniated disc. One of the most significant factors is age. As we age, the discs in our spine lose some of their water content, making them less flexible and more prone to injury. Additionally, certain occupations that require heavy lifting, bending, or twisting motions can increase the risk of disc herniation. Jobs in construction, transportation, and healthcare are often associated with a higher incidence of this condition.
A sedentary lifestyle can also contribute to the development of a herniated disc. Lack of physical activity weakens the muscles that support the spine, making it more susceptible to injury. Obesity is another risk factor, as excess body weight puts added stress and pressure on the spinal discs.
Genetics may also play a role in determining who is more likely to experience a herniated disc. Some individuals may inherit weaker discs that are more prone to herniation.
The symptoms of a herniated disc vary depending on the location and extent of the herniation. Common signs include localized pain in the neck or lower back, radiating pain down the arm or leg, numbness, tingling, and muscle weakness. Treatment options range from conservative measures such as rest, physical therapy, and pain medications, to more invasive procedures like epidural injections or surgery.
In conclusion, individuals between the ages of 30 and 50, particularly men, are at a higher risk of developing a herniated disc. Factors such as age, occupation, sedentary lifestyle, obesity, and genetic predisposition can contribute to the likelihood of experiencing this condition. It is important to remain physically active, maintain a healthy weight, and practice proper lifting techniques to reduce the risk of disc herniation.
At what age do herniated discs start?
People ages 30 to 50 are most likely to get a herniated disk. The problem affects men twice as often as women.Jul 1, 2021
What makes a herniated disc worse?
The pain from a herniated disc usually is worse when you are active and gets better when you are resting. Coughing, sneezing, sitting, driving, and bending forward may make the pain worse. The pain gets worse when you make these movements because there is more pressure on the nerve.
What triggers a herniated disc?
Sometimes, using the back muscles instead of the leg and thigh muscles to lift heavy objects can lead to a herniated disk. Twisting and turning while lifting also can cause a herniated disk. Rarely, a traumatic event such as a fall or a blow to the back is the cause.
What is the most common cause of disc herniation?
The most common cause of disc herniation is a degenerative process in which, as humans age, the nucleus pulposus becomes less hydrated and weakens. This process will lead to a progressive disc herniation that can cause symptoms. The second most common cause of disc herniation is trauma.
What is the difference between a urogynecologist and a urologist?
Urology is a more general field of medicine than Urogynecology. For example, urologists treat women, men, and children. Urogynecologists, on the other hand, deal only with matters of a woman’s pelvic floor.
How is a urogynecologist different from a gynecologist?
A urogynecologist is a physician who specializes in disorders of the pelvic floor. It combines knowledge of both urology and gynecology to help diagnose and treat symptoms. Often, a urogynecologist works to restore the pelvic floor anatomy that has weakened.
What is urological gynaecology?
A urogynecologist is a specialist who has completed training extra training in both gynecology and urology. Since urogynecologists have training in both specialties (women’s health and urology), they are particularly trained to help women with conditions like these: Incontinence (bladder problems) Stress incontinence.
Should I see a urologist or an urogynecologist?
It usually depends on who you see first. In general, if you have a dropped uterus or a very weak pelvic floor, I think a urogynecologist is the most appropriate person for you to see first. If you have either a complex urinary issue, or even straightforward urinary problems, a urologist is probably your best bet.
Why would you see a urogynecologist?
“You should be evaluated or referred to a urogynecologist when you have problems of pelvic organ prolapse, urinary incontinence unresponsive to medications, problems with emptying the bladder or rectum, or the need for special expertise in surgical options to treat these conditions,” he said.