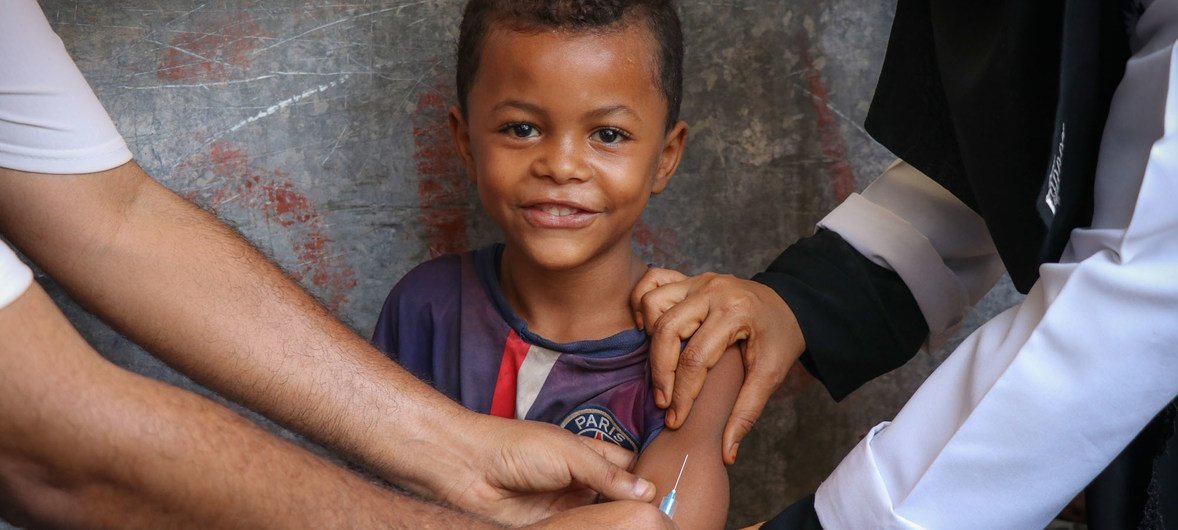
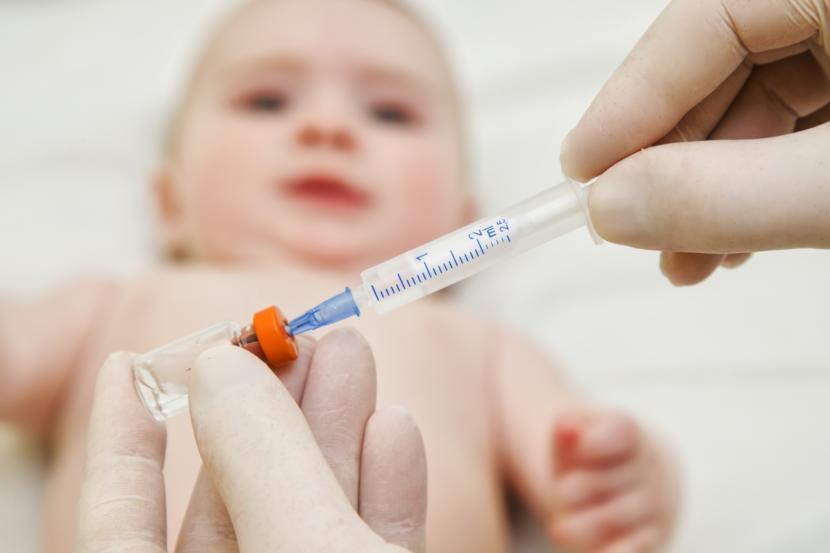
Immunization is a crucial aspect of children’s health care, as it helps protect them from potentially deadly diseases. However, like any medical intervention, there are risks associated with immunization. One of the main risks is adverse reactions to the vaccines themselves. These reactions can range from mild symptoms like fever and soreness at the injection site to more serious side effects such as allergic reactions or seizures. While these reactions are generally rare, they can occur and should be monitored closely.
Another risk of immunization is the potential for vaccine-preventable diseases to still occur despite vaccination. This can happen if a child’s immune system does not respond adequately to the vaccine, or if the vaccine is not fully effective for that particular individual. In these cases, the child may still be at risk of developing the disease, even after being vaccinated.
It is important for parents to weigh the risks and benefits of immunization for their children. Overall, the benefits of vaccination in preventing serious illnesses far outweigh the risks of potential adverse reactions. However, it is crucial to work with healthcare providers to ensure that children receive the appropriate vaccines at the recommended ages and to monitor for any potential side effects. By staying informed and proactive about vaccination, parents can help protect their children from dangerous diseases.
What are the risk factors of immunization?
Vaccines do have some risk for adverse reaction, the most common being redness and soreness at the injection site or fever and allergic reactions.
What if I refuse to vaccinate my child?
Children who are not vaccinated can transmit vaccine- preventable diseases at schools and in the community. Unvaccinated children can infect babies who are too young to be fully immunized. Unvaccinated children can infect people of any age who can’t be immunized for medical reasons.
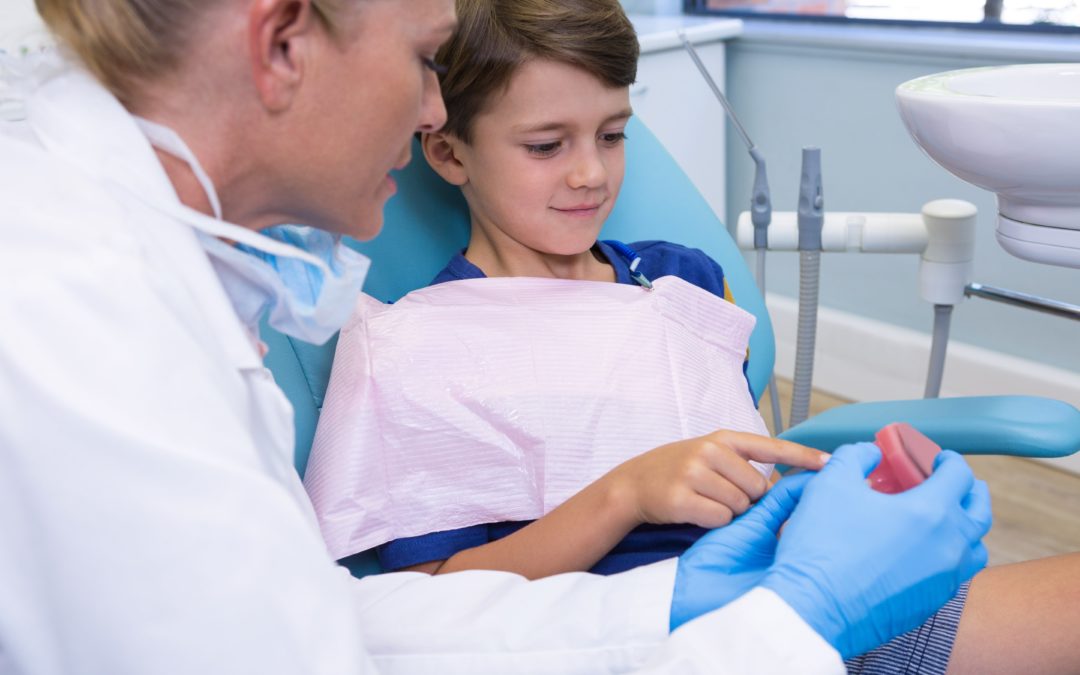
At what age should a child go to the dentist?
The first visit The first dental visit is recommended by 12 months of age, or within 6 months of the first tooth coming in. The first visit often lasts 30 to 45 minutes. Depending on your child’s age, the visit may include a full exam of the teeth, jaws, bite, gums, and oral tissues to check growth and development.
When should I start dental care for my baby?
Schedule your child’s first dental appointment. Your child should have an exam by a dentist before his/her first birthday or within 6 months after the first tooth comes in. If your drinking water is not fluoridated, talk to your pediatrician about infant fluoride supplements.
Is it common for a 2 year old to have cavities?
Dental caries (cavities) are common in baby teeth. In fact, experts share that some 20 percent of kids ages 2 to 5 may have untreated cavities. While your child will eventually lose their primary (baby) teeth, taking care of those teeth is important because they hold space for adult teeth.
Should a 2 year old go to the dentist?
The first dental visit is recommended by 12 months of age, or within 6 months of the first tooth coming in. The first visit often lasts 30 to 45 minutes. Depending on your child’s age, the visit may include a full exam of the teeth, jaws, bite, gums, and oral tissues to check growth and development.
What age should a child first visit the dentist?
The first dental visit is recommended by 12 months of age, or within 6 months of the first tooth coming in. The first visit often lasts 30 to 45 minutes. Depending on your child’s age, the visit may include a full exam of the teeth, jaws, bite, gums, and oral tissues to check growth and development.