Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is a minimally invasive procedure commonly used to treat various medical conditions, including liver, lung, and kidney tumors. The most common complication associated with RFA is pain, which can occur during or after the procedure. Post-procedural pain is usually mild to moderate and can be managed with over-the-counter pain medications. However, in some cases, patients may experience more severe pain that requires prescription painkillers.
Other potential complications of RFA include infection, bleeding, and damage to surrounding tissues or organs. Infection is a rare but serious complication that can occur if bacteria enter the body through the skin during the procedure. Bleeding is also relatively uncommon but can occur if a blood vessel is damaged during the ablation. Damage to surrounding tissues or organs is another potential complication, especially if the tumor is located close to vital structures.
Overall, the risk of complications with RFA is low, particularly when the procedure is performed by an experienced medical team. Patients should discuss any concerns or potential complications with their healthcare provider before undergoing radiofrequency ablation. Early detection and prompt treatment of complications can help ensure successful outcomes and minimize the risk of long-term adverse effects.
What are the risks of nerve ablation?
The risk of complications from RFA is very low. On occasion, permanent nerve damage or pain can occur. In some people, their original pain may get worse. Other complications, including infection and bleeding at the needle insertion site, are uncommon.

How long does nerve ablation last?
The damage to your nerves blocks them from sending pain signals to your brain. But the nerve often tries to grow back. If it does, the results are only temporary and usually last for around 6 to 9 months.
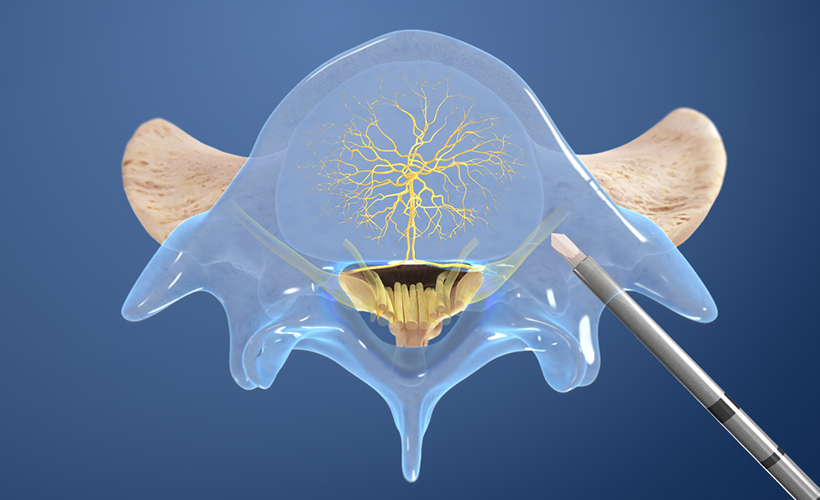
Who is a candidate for nerve ablation?
Who Is a Candidate for Radiofrequency Ablation? Our skilled specialists may recommend radiofrequency ablation to treat many types of chronic pain including: Injuries such as whiplash. Neuropathic pain conditions like complex regional pain syndrome or peripheral nerve entrapment syndromes.
What are the negative side effects of nerve ablation?
The risk of complications from RFA is very low. On occasion, permanent nerve damage or pain can occur. In some people, their original pain may get worse. Other complications, including infection and bleeding at the needle insertion site, are uncommon.
What are the cardinal signs of osteomyelitis?
Localized bone pain, erythema and drainage around the affected area are frequently present. The cardinal signs of subacute and chronic osteomyelitis include draining sinus tracts, deformity, instability and local signs of impaired vascularity, range of motion and neurologic status.
When should I be concerned about osteomyelitis?
See your doctor if you experience worsening bone pain along with fever. If you’re at risk of infection because of a medical condition or recent surgery or injury, see your doctor right away if you notice signs and symptoms of an infection.Nov 8, 2022

What is the hallmark of osteomyelitis?
Signs and symptoms of osteomyelitis include: Fever. Swelling, warmth and redness over the area of the infection. Pain in the area of the infection.Nov 8, 2022
What is the triad of osteomyelitis?
Indeed, it should be kept in mind that the absence of fever does not rule out osteomyelitis, and that the classic triad of fever, pain and increased markers of inflammation is not always present.
What are the red flags of osteomyelitis?
Symptoms of osteomyelitis swelling of the affected area. a feeling of warmth on the affected area. redness of the skin in the affected area, which may be harder to see on black or brown skin. a limp (more common in children)