Title: Major Concerns After Spinal Fusion: An Overview
Introduction:
Spinal fusion is a surgical procedure commonly performed to treat various spinal conditions such as degenerative disc disease, spinal fractures, or scoliosis. While this procedure aims to provide stability and pain relief, there are certain post-surgical concerns that patients need to be aware of. This article provides a brief overview of the major concerns following a spinal fusion procedure.
Body:
One of the primary concerns after spinal fusion surgery is the possibility of complications and their subsequent impact on the patient’s recovery. Complications can range from surgical site infections and blood clots to nerve damage or insufficient bone fusion. These complications can prolong the recovery process, increase pain levels, and potentially require additional intervention.
Another significant concern after spinal fusion is the development of adjacent segment disease (ASD). This refers to the degeneration or abnormal stress on the spinal segments adjacent to the fused area. ASD can potentially lead to the need for additional surgeries or interventions in the future.
Post-operative pain management is another crucial aspect. While pain is expected following surgery, some individuals may experience chronic or severe pain that requires specialized pain management techniques. This may include a combination of medication, physical therapy, or even alternative therapies such as acupuncture or yoga.
Maintaining spine mobility and flexibility is also a concern after spinal fusion. While the procedure aims to provide stability, it can limit the range of motion in the fused segment of the spine. Patients are often advised to engage in specific rehabilitation exercises to improve strength and flexibility in the surrounding spinal segments.
Psychological factors, such as anxiety and depression, are common concerns following spinal fusion surgery. The recovery process can be challenging, and patients may experience emotional distress. It is essential for healthcare providers to address these concerns and provide necessary support to improve the patient’s overall well-being.
Conclusion:
While spinal fusion surgery can offer significant benefits, it is essential to acknowledge and address the major concerns that can occur post-operatively. Recognizing and effectively managing complications, preventing the development of adjacent segment disease, providing adequate pain management, focusing on maintaining spinal mobility and addressing psychological factors are all crucial aspects of a successful recovery process. By understanding these concerns, patients can make informed decisions, and healthcare providers can optimize patient care.
What is the downside of spinal fusion?
Stress above or below fusion: A potential side effect to consider is that the adjacent vertebrae may become irritated following spinal fusion surgery. Some patients may experience strain or discomfort on the vertebrae directly above or below the fusion site.
Why spinal fusion is not recommended?
We don’t like to recommend spinal fusion because it does not, in many cases, correct the underlying problems of lumbar spinal instability as many people would think it would. In fact, spinal fusion surgery may increase spinal instability and degeneration.
Why should you avoid spinal fusion?
The risks of spinal fusion surgery are: AOften invasive with a recovery time of 6+ months. BSacrifices all movement from that level of the spine. CIncreased stress on adjoining spine levels, with higher chance for new damage, requiring ongoing fusion extension over time.
How long does a lumbar discectomy last?
What Is the Number of Years a Discectomy Typically Lasts? For some patients, results from a discectomy or a less invasive microdiscectomy last indefinitely. Others may experience renewed discomfort several months or even years after surgery, which may be a sign of reherniation of the same spinal disc.

What age should a female see a gynecologist?
What is the right age to take this step? The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) recommends that girls first see a gynecologist when they’re between the ages of 13 and 15. Most girls will not need a pelvic exam during this first visit, though.

Is there a difference between OB GYN and gynecologist?
Physicians who focus on gynecology do not deliver babies or treat pregnant women. They conduct cancer screenings, treat urinary tract issues, and more. Physicians who focus on obstetrics do not treat health issues outside pregnancy. OB/GYNs focus on both areas.
At what age should a woman get a Pap smear?
If you are at least age 21, you should start cervical cancer screening, even if you are not yet sexually active. If you are younger than 30, you can likely be tested for cervical cancer every other year instead of yearly.
What age do you get your first Pap smear?
Gynecologists recommend a Pap smear starting at age 21, and then every 3 years for women in their 20s. In this test, the doctor gently scrapes cells from the cervix using a small brush or spatula. The sample is checked in a lab for cell changes and cervical cancer.
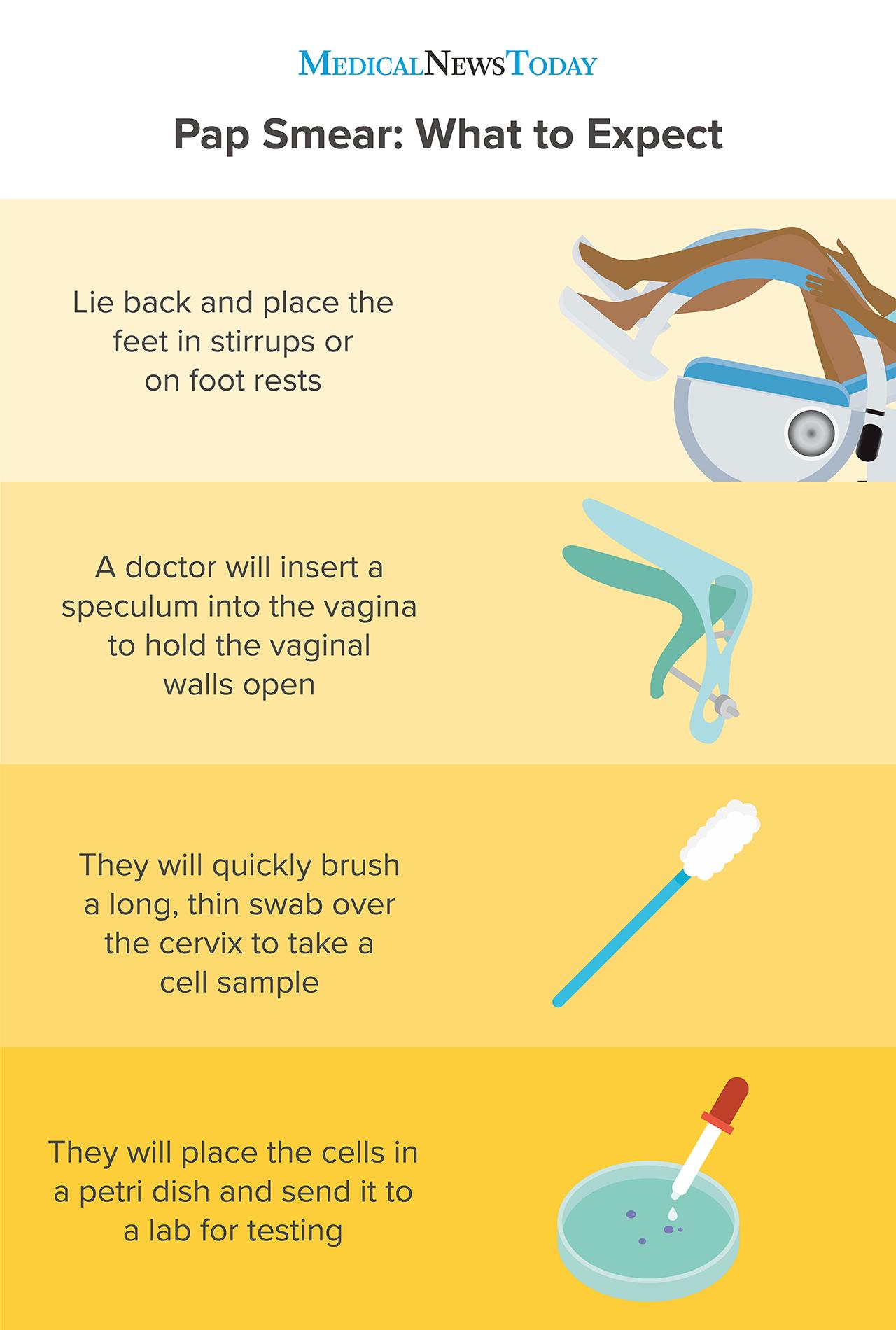
When should a girl start going to a gynecologist?
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) recommends that girls first see a gynecologist when they’re between the ages of 13 and 15. Most girls will not need a pelvic exam during this first visit, though.


