The indication for CT lumbar spine is to evaluate the bones, joints, and soft tissues in the lower back region for a variety of conditions. CT scans, or computed tomography, use a combination of x-rays and computer technology to create detailed cross-sectional images of the spine.
One common reason for ordering a CT scan of the lumbar spine is to investigate back pain. Chronic lower back pain can be caused by various factors such as disc degeneration, herniated discs, spinal stenosis, or fractures. The CT scan provides valuable information about the spine’s bony structures, including any fractures or abnormalities that may be contributing to the pain.
Additionally, CT scans can also help diagnose and assess the progression of conditions such as degenerative disc disease or spondylolisthesis. These conditions occur when the discs between the vertebrae wear down or when one vertebra slips forward or backward. The detailed images obtained from a CT scan enable doctors to accurately diagnose and plan appropriate treatment options.
CT lumbar spine scans are also useful in evaluating spinal tumors, infections, or inflammations. The images obtained provide valuable insights into the nature and extent of these conditions, aiding in the development of a suitable management plan.
Overall, CT lumbar spine scans are an essential tool in diagnosing and managing various lower back conditions. The detailed images obtained help identify the cause of back pain and guide healthcare professionals in developing appropriate treatment plans. By effectively assessing the bones, joints, and soft tissues in the lumbar spine, CT scans prove to be an invaluable tool in providing accurate and comprehensive evaluations of lower back conditions.
Which CT scans need contrast?
In general, oral contrast is used for most abdominal and pelvic CT scans unless there is no suspicion of bowel pathology (e.g., noncontrast CT to detect kidney stones) or when administration would delay a diagnosis in the trauma setting.Sep 1, 2013
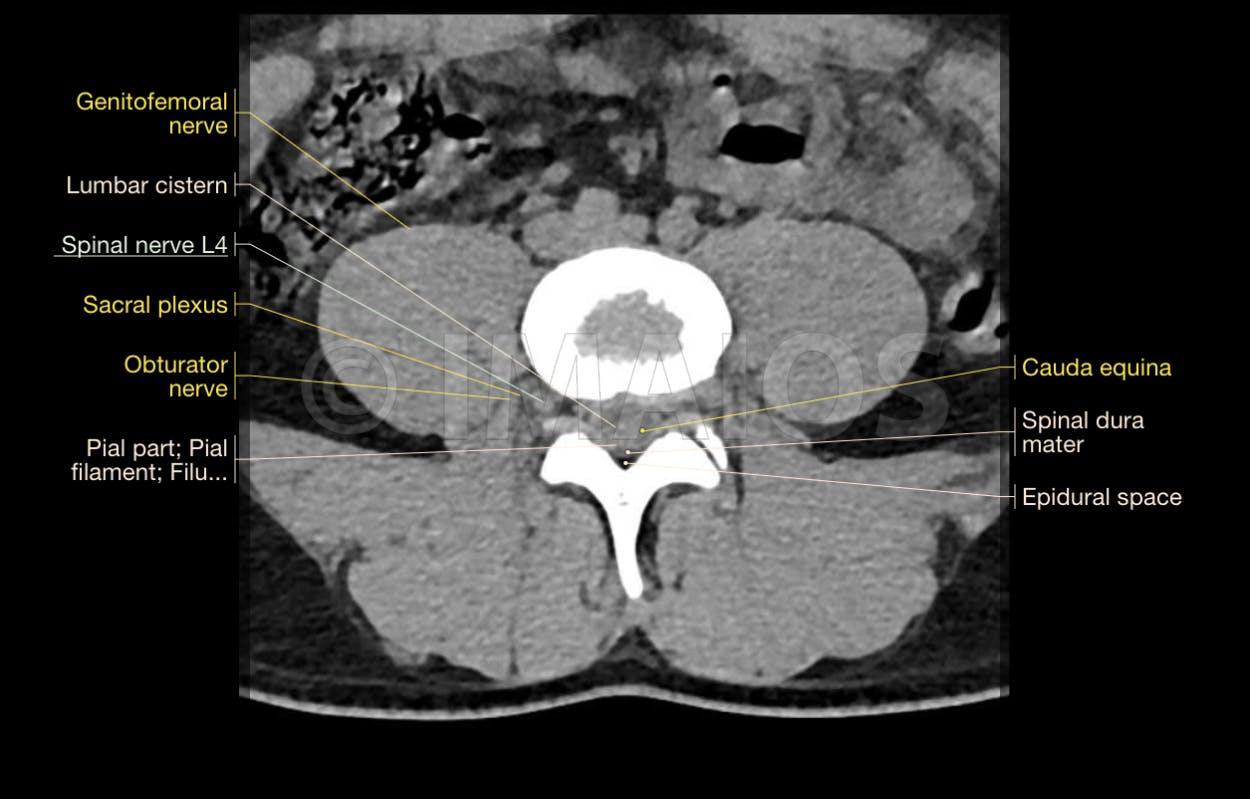
What does a CT scan of the lumbar spine show?
A CT scan of the spine may be performed to assess the spine for a herniated disk, tumors and other lesions, the extent of injuries, structural anomalies such as spina bifida (a type of congenital defect of the spine), blood vessel malformations, or other conditions, particularly when another type of examination, such …
Does CT lumbar spine need contrast?
The CT lumbar spine or L-spine protocol serves as an examination for the assessment of the lumbar spine. As a separate examination, it is most often performed as a non-contrast study. It might be combined or simultaneously acquired with a CT abdomen.Jun 1, 2021

What are the indications for lumbar spine with contrast?
Indications: pain, numbness, trauma, fracture, postop, neoplasm, stenosis.
How do doctors know if you have nerve damage?
Electromyography (EMG) is used to record the electrical activity in muscle. It can identify abnormalities in the muscles or nerves resulting from peripheral neuropathy, nerve degeneration or damage to the protective covering (myelin sheath) that surrounds the nerves in your brain or spinal cord.
Does a lumbar MRI show inflammation?
Some of the inconsistencies that a lumbar spine MRI may show include compression or inflammation of the spinal cord and adjacent nerves, degeneration of joints such as vertebral facet joints, disc herniation, infection of the discs, spinal cord and vertebrae, trauma to the tissues, and tumors.
Can you see nerve damage on an MRI?
An MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) scan is an effective way to diagnose a pinched nerve, providing clear, detailed images of the spine to help identify any abnormalities. While a neurological examination can diagnose nerve damage, an MRI scan can pinpoint it more specifically.Jan 9, 2023
What does an MRI of the lumbar spine show?
A lumbar spine MRI can detect a variety of conditions in the lower back, including problems with the bones (vertebrae), soft tissues (such as the spinal cord), nerves, and disks.
How do they check for nerve damage?
A nerve conduction velocitynerve conduction velocityLargely generalized, normal conduction velocities for any given nerve will be in the range of 50–60 m/s.https://en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Nerve_conduction_velocityNerve conduction velocity – Wikipedia (NCV) test — also called a nerve conduction study (NCS) — measures how fast an electrical impulse moves through your nerve. NCV can identify nerve damage. During the test, your nerve is stimulated, usually with electrode patches attached to your skin.