The Gardner classification system, developed by American psychologist Howard Gardner in 1983, is a theory of multiple intelligences that challenges traditional views of intelligence as a single, unitary concept. Gardner proposed that there are eight different types of intelligence, each representing a different way of processing information and solving problems. These types include linguistic, logical-mathematical, spatial, musical, bodily-kinesthetic, interpersonal, intrapersonal, and naturalistic intelligences.
According to Gardner, individuals may excel in one or more of these intelligences, and the education system should be tailored to accommodate and nurture all types of intelligence, rather than privileging linguistic and logical-mathematical abilities as traditionally done. This theory has had a significant impact on education, as it has led to a greater emphasis on personalized and differentiated instruction to cater to the diverse strengths and abilities of students.
Critics of the Gardner classification system argue that there is not enough empirical evidence to support the existence of distinct intelligences, and that the theory is too broad and vague to be useful in practical applications. Despite these criticisms, Gardner’s theory continues to influence educational practices around the world, encouraging educators to adopt a more holistic and inclusive approach to teaching and learning.
What is the garden system classification?
The Garden classification incorporates displacement, fracture completeness, and relationship of bony trabeculae in the femoral head and neck. Gardens’ originally reviewed 80 patients with femoral neckfemoral neckThe femoral neck (femur neck or neck of the femur) is a flattened pyramidal process of bone, connecting the femoral head with the femoral shaft, and forming with the latter a wide angle opening medialward. Femoral neck. Upper extremity of right femur viewed from behind and above.https://en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Femoral_neckFemoral neck – Wikipedia fractures, which he classified in Types I to IV, and he followed these patients for at least 12 months postoperatively.
What is a femoral neck fracture Garden Type 3?
Garden Types III and IV femoral neck fractures are displaced. Fixation options for displaced femoral neck fractures include hemiarthroplasty, THA, and internal fixation. Arthroplasty often is used for displaced femoral neck fractures in the elderly while internal fixation is still favored in younger patients.
What is the Pipkin classification system?
Pipkin classified fractures by their location in the femoral headfemoral headThe femoral head is the most proximal portion of the femur and is supported by the femoral neck. It articulates with the acetabulum of the pelvis. The femoral head is nearly spherical (two-thirds) but has a medial depression known as the fovea capitis femoris that serves as an attachment point for the ligamentum teres.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov › books › NBK519005Anatomy, Bony Pelvis and Lower Limb, Fovea Capitis Femoris – NCBI and the presence of any associated fractures as one of four types: type I is defined as fracture inferior to the capitis femoris; type II is defined as fracture extended superior to the capitis femoris; type III is a type I or type IIfracture associated …
What is Pipkin classification based on?
Pipkin classified fractures by their location in the femoral headfemoral headThe femoral head is the most proximal portion of the femur and is supported by the femoral neck. It articulates with the acetabulum of the pelvis. The femoral head is nearly spherical (two-thirds) but has a medial depression known as the fovea capitis femoris that serves as an attachment point for the ligamentum teres.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov › books › NBK519005Anatomy, Bony Pelvis and Lower Limb, Fovea Capitis Femoris – NCBI and the presence of any associated fractures as one of four types: type I is defined as fracture inferior to the capitis femoris; type II is defined as fracture extended superior to the capitis femoris; type III is a type I or type IIfracture associated …
How bad does a nerve ablation hurt?
Most people experience some pain and discomfort after radiofrequency ablation. There may be swelling, numbness, or soreness where the needle was inserted, or it may feel like a sunburn. Typical post-procedure pain should not be severe.
What is the procedure for burning the spinal nerve?
Rhizotomy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure to remove sensation from a painful nerve by killing nerve fibers responsible for sending pain signals to the brain. The nerve fibers can be destroyed by severing them with a surgical instrument or burning them with a chemical or electrical current.
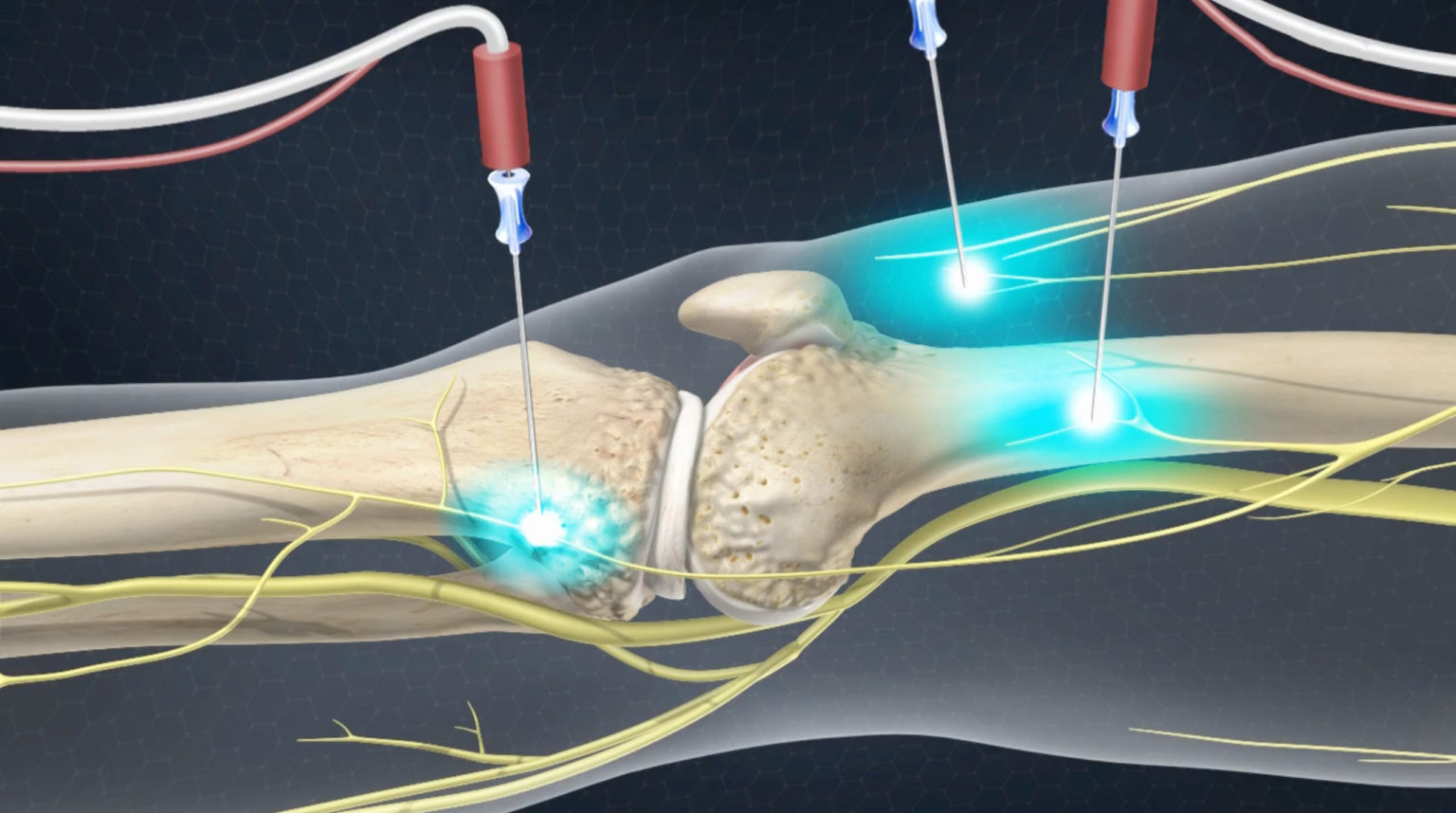
How painful is back nerve ablation?
The patient experiences minimal discomfort throughout the procedure. The patient remains awake and aware during the procedure to provide feedback to the physician. A light sedative can be used during the procedure. The technique for nerve ablation is similar to that used for diagnostic blocks.
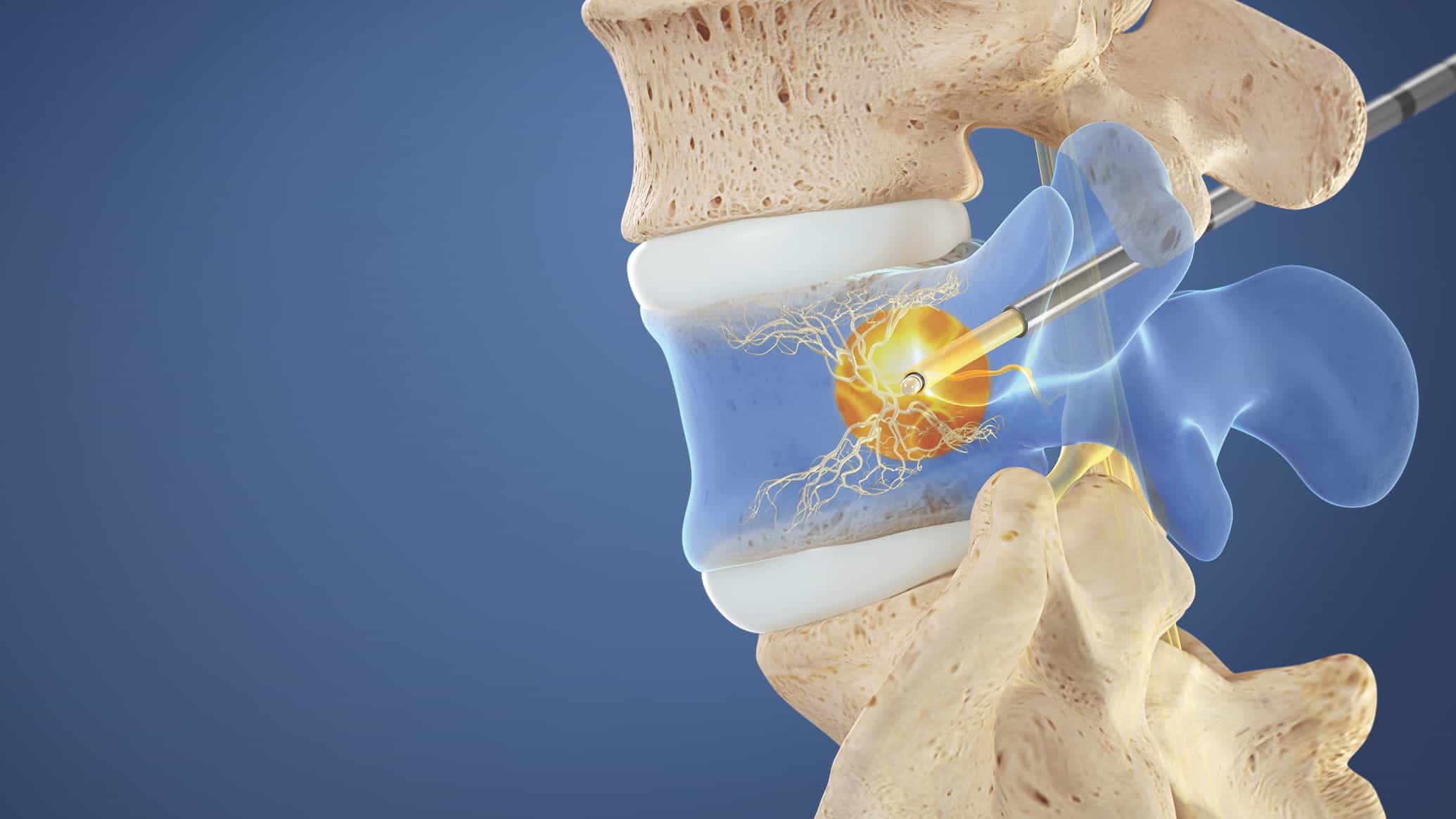
What is the recovery time for a back ablation?
Strenuous activities should be avoided for a couple days at least, but most people can resume normal work activities in two to three days. As said earlier, it may take up to 3 weeks for the ablated nerve to stop causing pain completely, and if the pain is too much then analgesics can be prescribed in the mean time.
What are the restrictions after back nerve ablation?
Rest when you get home. Don’t drive or do anything strenuous for 24 hours after the procedure. After a day or two, you can return to your normal activities, including bathing or showering. You may still feel soreness, pain or muscle spasms at the treatment site for a few days.


