Laminectomy is a surgical procedure commonly performed to alleviate pressure on the spinal cord or nerves in the spine. While it is considered a relatively safe and effective treatment option, there are several potential downsides and risks associated with it.
One of the main drawbacks of laminectomy is the possibility of complications during or after the surgery. These can include infections, blood clots, damage to surrounding nerves or tissues, and spinal fluid leakage. These complications may require additional surgeries or prolonged hospital stays, which can significantly impact the patient’s recovery process.
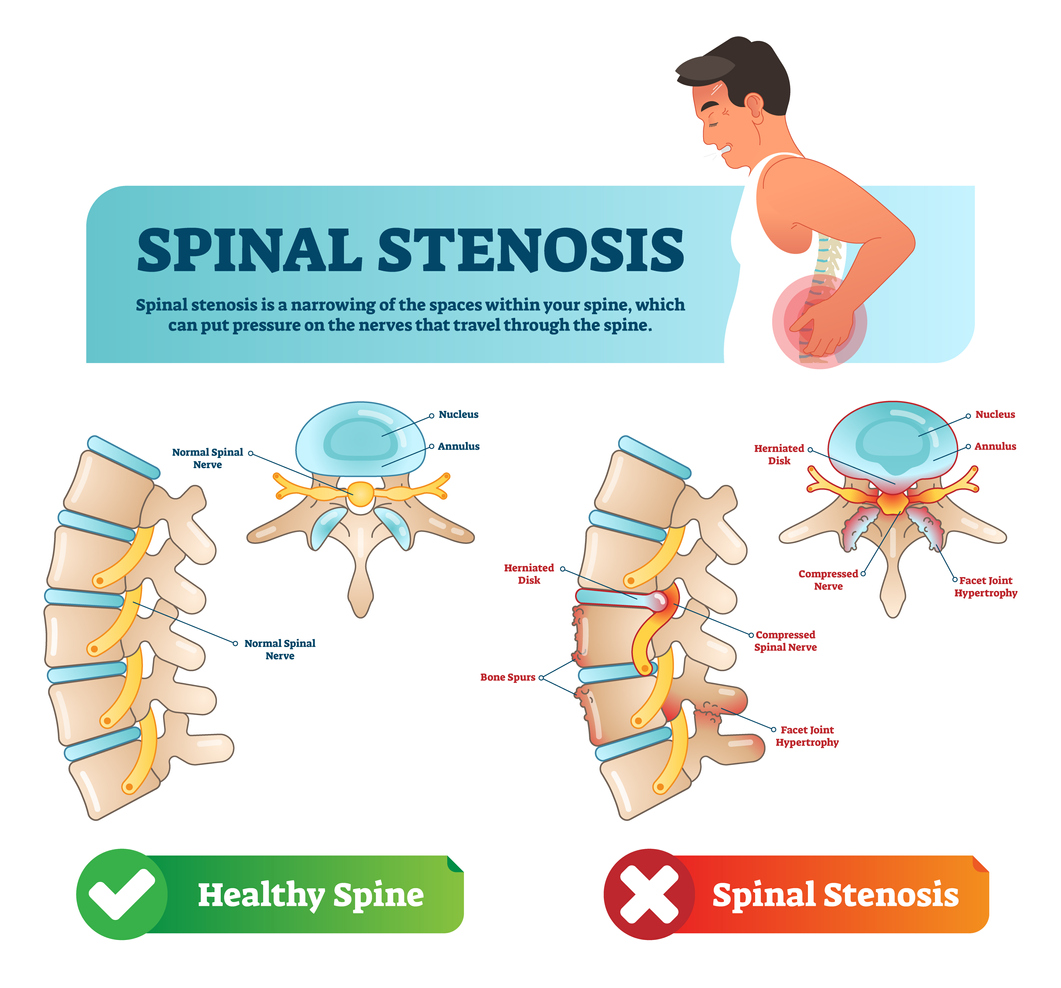
Furthermore, laminectomy may also result in long-term effects such as spinal instability. Removing a portion of the spinal bone, known as the lamina, can weaken the structural integrity of the spine, potentially leading to instability or spinal deformities. In such cases, additional spinal fusion surgeries may be necessary to stabilize the spine.
Another downside of laminectomy is the risk of postoperative complications, such as persistent pain or numbness. While the procedure aims to alleviate symptoms, some patients may experience ongoing or new symptoms following the surgery. This can be due to incomplete decompression, nerve damage, or scar tissue formation.
Additionally, laminectomy is not suitable for everyone and may not effectively address underlying spinal conditions in some cases. It is important for patients to undergo a thorough evaluation and consider alternative treatment options before undergoing the procedure.
In conclusion, although laminectomy can provide relief for individuals suffering from spinal cord or nerve compression, it is essential to be aware of the potential downsides and risks associated with this procedure. It is crucial for patients to have realistic expectations and make informed decisions in consultation with their healthcare providers to ensure the best possible outcomes.
What are the long term problems after a laminectomy?
Years after decompression (lumbar laminectomy), lumbar stenosis can come back (the bone can grow back) at the same level, or a new level can become stenotic and cause back pain or leg pain. Pain that is relieved right after surgery but then returns abruptly is often due to a recurrent lumbar disc herniation.
What is the recovery time for a laminectomy?
Your recovery time varies based on what your surgeon needs to do during surgery. You may recover fully within four to six weeks after a minimally invasive laminectomy. If you underwent a laminectomy with spinal fusion, it could take six months to heal completely.
Is laminectomy major surgery?
Removing the lamina allows the surgeon to create more room for the spinal cord and reduces compression against the vertebrae. Laminectomy is considered a major surgery.

How successful is laminectomy for spinal stenosis?
The success rate of a lumbar laminectomy to alleviate leg pain from spinal stenosis is generally favorable. Research suggests: 85% to 90% of lumbar central spinal stenosis patients find relief from leg pain after an open laminectomy surgery.
What is the difference between a pediatrician and a family doctor in Ontario?
Pediatricians solely specialize in the treatment of children, while family medicine doctors specialize in treating patients of all ages.
At what age do you stop seeing a pediatrician?
At what age do most people switch, and how? There’s no set age for switching from a pediatrician to an adult doctor — it can be whenever a person feels ready. Most pediatricians stop seeing patients who are between the ages of 18 and 21, so you’ll need to make the switch eventually.
What is the difference between a pediatrician and a family doctor in Toronto?
Pediatricians solely specialize in the treatment of children, while family medicine doctors specialize in treating patients of all ages.

Is a primary care physician the same as a pediatrician?
Pediatricians are primary care doctors who specialize in children’s health, including physical, mental, and social health. To be a pediatrician, doctors attend 4 years of medical school and spend 3 years as medical residents in pediatrics.
Do I need a pediatrician for my baby Ontario?
NOTE: each doctor’s availability may change throughout the year. In Ontario, the majority of healthy babies are cared for by family physicians. We encourage you to find a physician as soon as possible to ensure the baby’s first check-up takes place within 1-3 days of discharge from hospital.