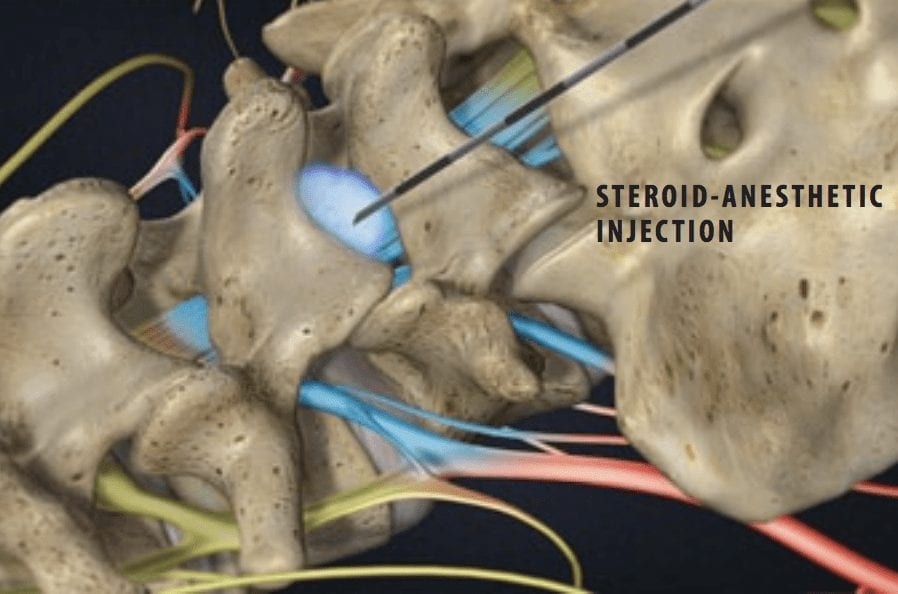
Epidural steroid injections are a common treatment option for patients suffering from back pain or sciatica. However, there are some potential downsides to this treatment that patients should be aware of. One of the main risks associated with epidural steroid injections is the possibility of infection at the injection site. While rare, this can lead to serious complications and may require further medical intervention. Additionally, some patients may experience a temporary increase in pain after the injection, although this usually subsides within a few days. Other potential side effects include headaches, nausea, and dizziness. In some cases, patients may also experience a temporary decrease in immunity, which can increase the risk of infections. It is important for patients to discuss the potential risks and benefits of epidural steroid injections with their healthcare provider before proceeding with this treatment.
Can you walk after a lumbar epidural steroid injection?
If your injection had local anesthetic and a steroid, your legs may feel heavy or numb right after. You will probably be able to walk. But you may need to be extra careful. Take care not to lose your balance, and be sure to follow your doctor’s instructions.
How successful are epidural shots for back pain?
Treatment with epidural steroid injections in the lower spine is not effective for reducing pain and disability. The injections may be more effective than placebo at short-term follow-up, but the effects are not clinically meaningful.
How long after spinal epidural can you walk?
It is recommended that you lie down and rest at home for at least 2 hours immediately after the procedure. Plan to rest and relax for the first 24 hours after the injection in a reclined position. Limit walking or sitting to 10-20 minutes at a time. You may resume all medications as previously prescribed.

How long should you rest after a lumbar epidural steroid injection?
Don’t exercise or conduct any rigorous activity for at least 24 hours after the epidural. You can evaluate when you feel okay to exercise. Don’t apply heat to the injection site for at least 72 hours (three days) after the epidural. This includes direct heat like a heat pack.
What is the most likely source of blood in a patient with an epidural hemorrhage?
An epidural hematoma (EDH) is usually caused by a head injury. A skull fracture occurs in 75% of the cases. A skull fracture that tears the middle meningeal artery is the most common source of bleeding.
What is the difference between a subdural hemorrhage and an epidural hemorrhage?
Epidural bleeding occurs between the skull and dura; whereas subdural bleeding occurs between the dura and arachnoid. Skull fracture from blunt trauma causes laceration of arterial vessels, most commonly the middle meningeal artery. Fracture occurs most commonly in the region of the temporal bone.

What is the difference between a subdural hemorrhage and an EDH?
Extradural haematoma (EDH) is a blood clot that forms on the outside of the natural covering of the brain (‘dura materdura materIn neuroanatomy, dura mater is a thick membrane made of dense irregular connective tissue that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. It is the outermost of the three layers of membrane called the meninges that protect the central nervous system.https://en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Dura_materDura mater – Wikipedia’), while acute subdural haematoma (ASDH) refers to a blood clot on the inner surface of the dura that appears within the first few days of head injury.
What is the difference between extradural and subdural haemorrhage presentation?
Extradural haematoma (EDH) is a blood clot that forms on the outside of the natural covering of the brain (‘dura materdura materIn neuroanatomy, dura mater is a thick membrane made of dense irregular connective tissue that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. It is the outermost of the three layers of membrane called the meninges that protect the central nervous system.https://en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Dura_materDura mater – Wikipedia’), while acute subdural haematoma (ASDH) refers to a blood clot on the inner surface of the dura that appears within the first few days of head injury.
What causes an epidural hemorrhage?
An epidural hematoma (EDH) occurs when blood accumulates between the skull and the dura mater, the thick membrane covering the brain. They typically occur when a skull fracture tears an underlying blood vessel. EDHs are about half as common as a subdural hematomas and usually occur in young adults.