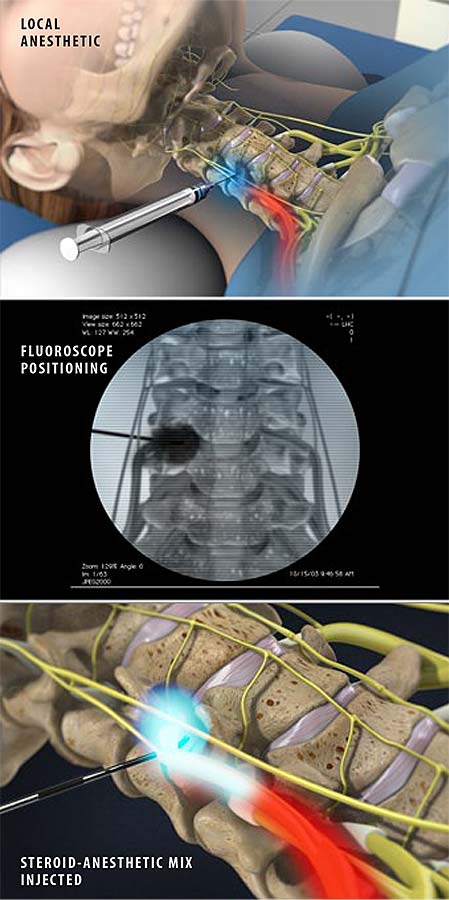
An epidural and a transforaminal epidural are both types of anesthesia procedures used to relieve pain during childbirth, surgery, or other medical procedures. However, there are key differences between the two techniques.
An epidural involves injecting medication into the epidural space, which is a space around the spinal cord. This medication numbs the lower part of the body, providing pain relief without affecting consciousness. It is commonly used during childbirth to help manage labor pain.
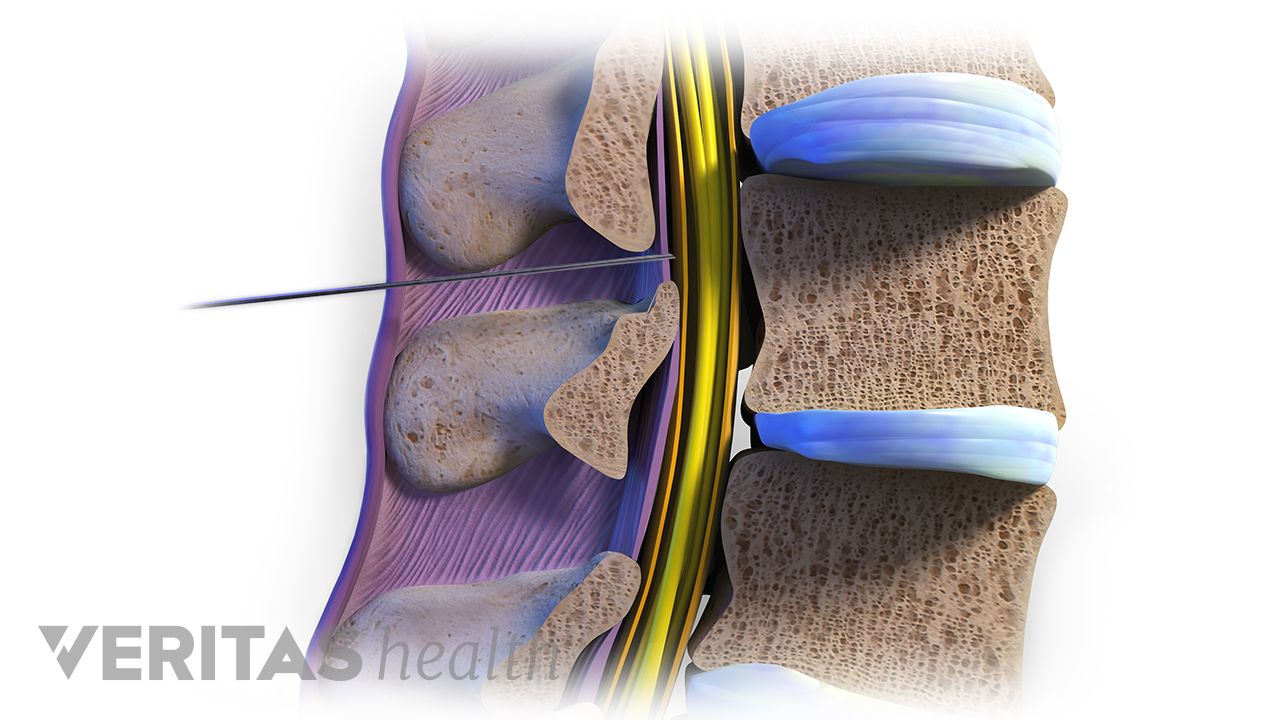
On the other hand, a transforaminal epidural involves injecting medication into the foraminal space, which is an opening in the spine where nerve roots exit. This technique targets a specific nerve root that may be causing pain, such as in cases of sciatica or spinal stenosis. By delivering the medication directly to the affected nerve, a transforaminal epidural can provide more targeted pain relief compared to a traditional epidural.
In summary, while both epidurals and transforaminal epidurals are effective methods for pain management, the main difference lies in the location of the medication injection and the specific target of pain relief. Patients should consult with their healthcare provider to determine which technique is most appropriate for their individual needs.
How often can you get a transforaminal epidural steroid injection?
Typically, a person may receive 3–4 transforaminal epidural steroid injections per year.
What is the success rate of transforaminal epidural steroid injections?
Treatment Success
—————— —————–
Sex Female
Male 43.5%
Level of injection S1 foramen
L5-S1 48.4%
What is the success rate of transforaminal epidural steroid injection?
The success rate in the transforaminal injection group was 84%, compared with 48% in the saline group. Botwin and colleagues demonstrated the efficacy of the transforaminal epidural injection in their retrospective cohort study in patients with sciatica (caused by lumbar spinal stenosis).
What are the side effects of transforaminal epidural steroid injection?
– “Steroid flush,” or flushing of the face and chest, with warmth and an increase in temperature for several days.
– Sleeping problems.
– Anxiety.
– Menstrual changes.
– Water retention.
– In rare instances, pain that actually increases for several days after the procedure.
What are the benefits of not having an epidural?
– Added freedom during labor. Getting an epidural during labor may ease your pain. …
– Labor may be faster. …
– Breastfeeding can be easier. …
– Faster recovery for mom. …
– Lower risk of medical interventions. …
– Can be safer for baby. …
– Stimulates feelings of connection and empowerment.

How bad does giving birth hurt without an epidural?
The most common description of the level of pain experienced was extreme menstrual cramps (45 percent), while 16 percent said it was like bad back pain and 15 percent compared it to a broken bone.May 6, 2018
Is it better to get an epidural or not?
For most women, this is a personal decision that depends on two things: how worried you are about having pain and how important natural childbirth (labour without pain medicine) is to you. An epidural is considered the most effective and easily adjustable type of pain relief for childbirth. Epidurals are very common.
Is it better to go natural or get an epidural?
The potential for a quicker labor, delivery and recovery – For some people, a natural birth may go more quickly. While it depends on several different factors, like how relaxed you may be, in some cases medications can interfere with contractions and prolong labor.
Why is it better to not get an epidural?
Epidurals are safe, but as with any medical procedure, there are small risks of side effects and complications. Serious risks—including blood clots inside the spine, infection (around the spine or brain), and nerve damage—are very rare. Other possible complications include low blood pressure, itchy skin, and headaches.