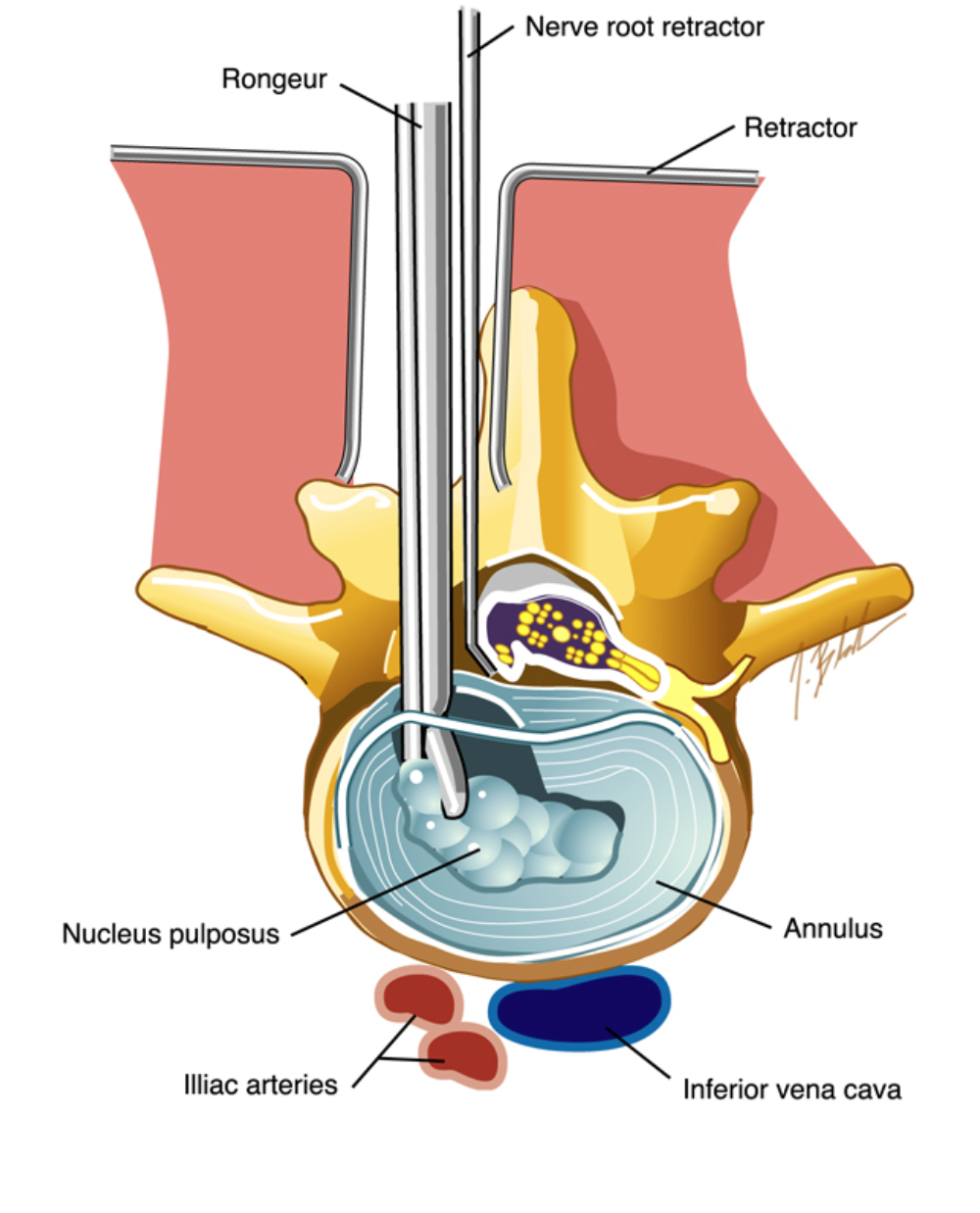
The CPT code for minimally invasive lumbar discectomy is 63030. This procedure is a commonly performed surgery to alleviate symptoms caused by herniated spinal discs in the lower back. The aim of minimally invasive lumbar discectomy is to remove the portion of the disc that is pressing on the nerve roots and causing pain and discomfort.
During the procedure, the surgeon makes a small incision in the patient’s back and uses specialized instruments to access the affected disc. The surgeon uses a microscope or endoscope to visualize the area and carefully remove the herniated disc material. This approach is considered minimally invasive because it causes less damage to the surrounding muscles and tissues compared to traditional open surgery.
Minimally invasive lumbar discectomy offers several advantages. Firstly, the smaller incision size leads to less scarring and post-operative pain. It also reduces the risk of complications and infection. Moreover, patients who undergo this procedure generally experience a faster recovery and return to normal activities sooner than those who have traditional open surgery.
Postoperatively, patients are advised to follow a rehabilitation program that includes physical therapy and specific exercises to strengthen the back muscles and improve mobility. The surgeon may also recommend pain medications and lifestyle modifications to support the healing process.
In summary, the CPT code for minimally invasive lumbar discectomy is 63030. This procedure is a safe and effective option for patients suffering from herniated discs in the lower back. It offers many benefits, such as smaller incisions, reduced scarring, faster recovery, and improved outcomes. By understanding the CPT code and the procedure itself, healthcare professionals can accurately document and bill for this minimally invasive surgery.
What is CPT code 63030 for Microdiscectomy?
The Current Procedural Terminology (CPT®) code 63030 as maintained by American Medical Association, is a medical procedural code under the range – Posterior Extradural Laminotomy or LaminectomyLaminectomyA laminectomy is a surgical procedure that removes a portion of a vertebra called the lamina, which is the roof of the spinal canal. It is a major spine operation with residual scar tissue and may result in postlaminectomy syndrome.https://en.wikipedia.org › wiki › LaminectomyLaminectomy – Wikipedia for Exploration/ Decompression of Neural Elements or Excision of Herniated Intervertebral Disks Procedures.
How can I test myself for a herniated disc?
One way to determine if you have a herniated disc is by doing a simple test. Lie down on your back with your knees bent and feet flat on the floor. Place one hand behind your head and gently tilt your head to the opposite side. If you feel pain in your neck when you do this, it may be indicative of a herniated disc.
What confirms a herniated disc?
MRI . Radio waves and a strong magnetic field are used to create images of the body’s inner structures. This test can be used to confirm the location of the herniated disk and to see which nerves are affected.
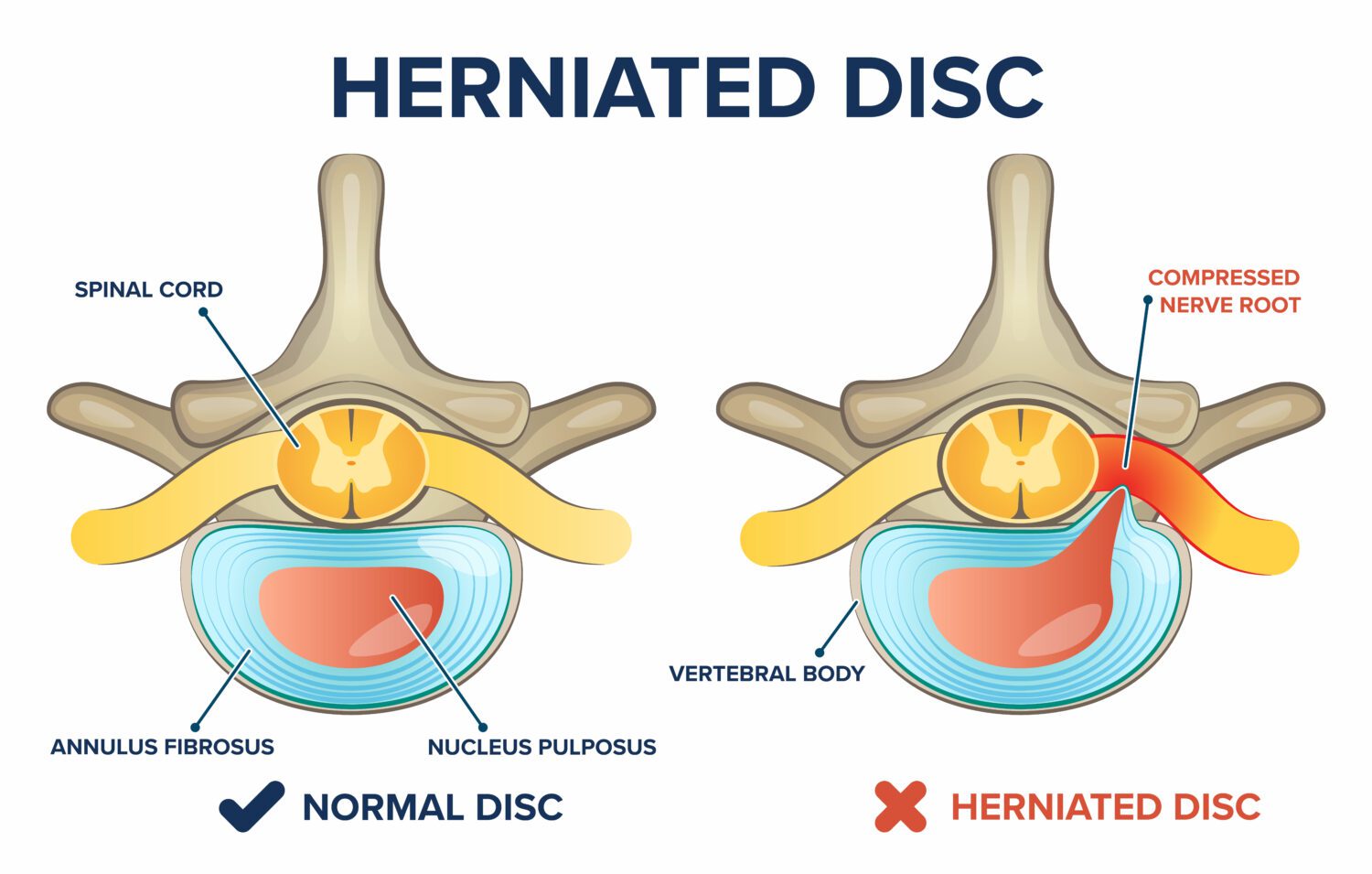
Can you see a herniated disc on an xray?
Often, if a disc slips out of place, the space between vertebrae may shrink or the vertebrae may become unstable without the disc to act as a cushion. X-rays can show a change in the height of the disc space or a shift in a vertebra’s position but cannot show a herniation itself.
What can be mistaken for a herniated disc?
Tumors of the spinal cord or near the sciatic or femoral plexus can cause neural compression and clinical signs similar to those of disc herniation. Such tumors are usually misdiagnosed as discal herniation and appropriate treatment is delayed.
Is MRI or xray better for herniated disc?
The MRI is best for evaluating the soft tissue in the spine and neck and is therefore the best way to find the slipped disk.