Paralysis refers to the loss of muscle function and sensation in certain parts of the body and is a potential risk associated with discectomy, a surgical procedure performed to treat herniated or degenerative discs in the spine. This article aims to summarize the chances of paralysis after a discectomy.
Recent studies indicate that the risk of paralysis after discectomy is extremely low. The incidence of paralysis ranges from 0.1% to 1%, depending on various factors such as the location and severity of the disc herniation, the skill of the surgeon, and the overall health of the patient. However, it is important to note that these statistics may vary from case to case.
One of the main causes of paralysis after discectomy is nerve root injury or damage during the procedure. This can occur when a surgeon accidentally disrupts or damages the nerve roots, leading to the impairment of muscle function and sensation. However, advancements in surgical techniques and the availability of intraoperative monitoring devices have significantly reduced the risk of nerve damage.
In addition, surgeons utilize preoperative imaging techniques such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT) scans to identify the exact location and condition of the herniated disc. This allows them to carefully plan the surgical approach and minimize the risk of complications.
Postoperative care also plays a crucial role in preventing paralysis. Patients are usually advised to engage in physical therapy and follow strict postoperative instructions to promote muscle strength, flexibility, and proper healing. Following these instructions can further decrease the chances of paralysis after discectomy.
It is important for patients to consult with their healthcare provider to understand the potential risks and benefits associated with any surgical procedure, including discectomy. They should also ensure that they are receiving care from an experienced and qualified surgeon to minimize the likelihood of complications.
In conclusion, while the chances of paralysis after discectomy are relatively low, it is still a possibility. However, with advancements in surgical techniques, careful planning, and postoperative care, the risk of paralysis can be significantly minimized. It is essential for patients to have detailed discussions with their healthcare providers to make informed decisions about their treatment options.
Is a Microdiscectomy a major or minor surgery?
Even though microdiscectomy recovery times are generally much faster than more invasive spinal surgeries, they’re still major procedures that involve general anesthetic. As such, they require careful oversight prior to medical personnel releasing you to return home. You can expect several specific things to happen.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-983383674-99be5704a7ee41d0a1f51df6c08a5d16.jpg)
Is lumbar discectomy considered as major surgery?
It’s increasingly common today for spine-related procedures to involve minimally invasive techniques. This is one of the reasons a discectomy isn’t necessarily “major” surgery in the traditional sense. Still, any spine-related procedure should be taken seriously, especially when it comes to recovery.Feb 4, 2022

What is the success rate of a discectomy?
Operative procedure. LDH is a common disease and lumbar discectomy is the most common surgical procedure carried out for patients with low back pain and leg symptoms. Although most researchers are focusing on surgical techniques during operation. The success rate of lumbar discectomy is about 70% to 90%.
Is discectomy a high risk surgery?
Diskectomy is considered safe. But as with any surgery, diskectomy carries a risk of complications. Potential complications include: Bleeding.Jul 1, 2022
How easy is it to herniate a disc after Microdiscectomy?
How Common is Reherniation After Microdiscectomy? Over 200,000 lumbar discectomies are performed in the United States each year, most of which are microdiscectomies. Based on follow-up studies, recurrent lumbar disc herniation only occurs in roughly 10% of all microdiscectomy patients.
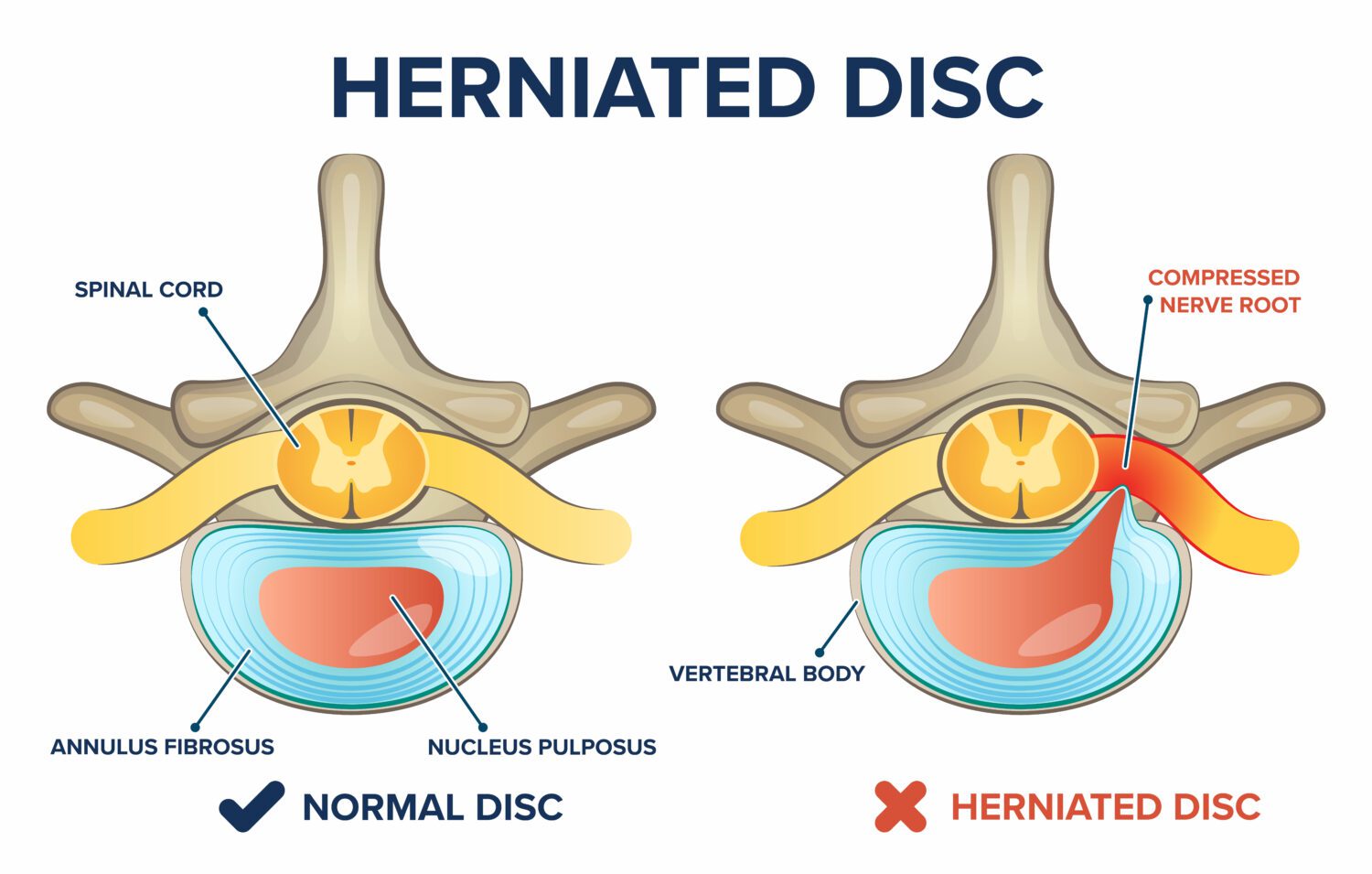
How do I know if my Microdiscectomy failed?
The most obvious sign of failed back surgery syndrome is persistent, dull, and aching pain involving the back or legs not associated with the healing process. Other symptoms include: New pain at a level different from the location treated. Inability to recuperate.
What not to do after lumbar discectomy?
—Do NOT bend or twist at the waist. Always bend with your knees! —Limit your sitting to 20-30 minute intervals at a time to avoid muscular discomfort. —During the healing process in the first few weeks after surgery, you will likely tire more easily and will need to rest between activities.

What happens after a failed Microdiscectomy?
If the bone doesn’t actually knit together, the screws and rods will predictably work themselves loose over time, or even break. Once this happens, patients may develop either new back pain or recurrent leg symptoms. The other big category is that of continued degeneration at a level next to a previous surgery.Sep 5, 2018
Why does my back still hurt after discectomy?
Recurrent pain after lumbar discectomy may be due to a variety of causes, including recurrent disc herniation involving the operated level, a new disc herniation at other spinal levels, epidural fibrosis or scarring, or other anatomical changes involving the spinal canal aside from the intervertebral disc1.


