https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=
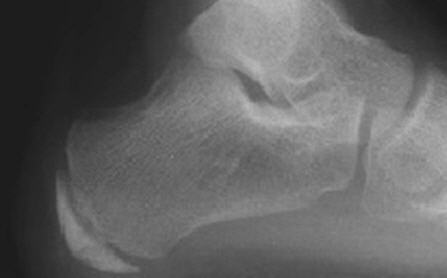
The calcaneal apophysis is a bony prominence located at the back of the heel, where the Achilles tendon attaches to the calcaneus bone. It serves as an attachment point for the Achilles tendon, which is crucial for the movement of the foot and ankle. The apophysis is made up of cartilage during childhood and gradually ossifies as a person grows older. The growth plate at the apophysis is known as the apophyseal line, and it is the last growth plate in the human body to close, typically around the age of 14-15 in girls and 15-17 in boys.
The calcaneal apophysis can be subject to overuse injuries, particularly in physically active individuals such as athletes. Sever’s disease, also known as calcaneal apophysitis, is a common condition that occurs when the apophysis becomes inflamed due to repetitive stress. This can result in pain and tenderness at the back of the heel, especially with physical activity.
Understanding the anatomy of the calcaneal apophysis is important for diagnosing and treating conditions such as Sever’s disease. Proper management typically involves rest, ice, stretching, and strengthening exercises to help alleviate symptoms and prevent further injury to the apophysis. In severe cases, medical intervention may be necessary to address the underlying issues and promote healing of the affected area.
How do you treat Sever’s syndrome?
– Put ice or a cold pack on the heel every 1–2 hours, for 15 minutes at a time. …
– Give medicine for pain such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin, or store brand) or acetaminophen (Tylenol or store brand). …
– Use heel gel cups or supportive shoe inserts to lower the stress on the heel.

What does apophysis mean in anatomy?
The apophysis is a site of tendon or ligament attachment, as compared to the epiphysisepiphysisAn epiphysis (from Ancient Greek ἐπί (epí) ‘on top of’, and φύσις (phúsis) ‘growth’; pl. : epiphyses) is one of the rounded ends or tips of a long bone that ossify from a secondary center of ossification.https://en.wikipedia.org › wiki › EpiphysisEpiphysis – Wikipedia which contributes to a joint, and for that reason, it is also called ‘traction epiphysis’. When unfused, apophyses can easily be mistaken for fractures.
What is sclerosis of the calcaneal apophysitis?
What is Sever’s disease? Sever’s disease (calcaneal apophysitis) is an inflammatory condition that affects the heel bone (calcaneus) causing heel pain. It happens frequently in young athletes between the ages of 10 and 13, causing pain in one or both heels when walking. Tenderness and swelling may also be present.
What is triplane fracture?
Triplane ankle fracturesankle fracturesAnkle fractures can be caused by various modes of trauma, e.g., twisting, impact, and crush injuries. Falling, tripping, or sports activities may cause twisting forces through the ankle. Impact injuries may result from falling from a height with impaction of the distal tibia and fibula against the talus.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov › books › NBK542324Ankle Fractures – StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf are complex traumatic Salter-HarrisSalter-HarrisSalter-Harris fractures (physeal fractures) refer to fractures through a growth plate (physis) and are, therefore, specifically applied to bone fractures in children.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov › books › NBK430688Salter-Harris Fracture – StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf IV fractures involving the metaphysismetaphysisThe metaphysis ( pl. : metaphyses) is the neck portion of a long bone between the epiphysis and the diaphysis. It contains the growth plate, the part of the bone that grows during childhood, and as it grows it ossifies near the diaphysis and the epiphyses.https://en.wikipedia.org › wiki › MetaphysisMetaphysis – Wikipedia, physis, and epiphysis. The term “triplane” refers to the different orientations of the fracture lines in the distal tibia and represents a frequent diagnostic challenge.
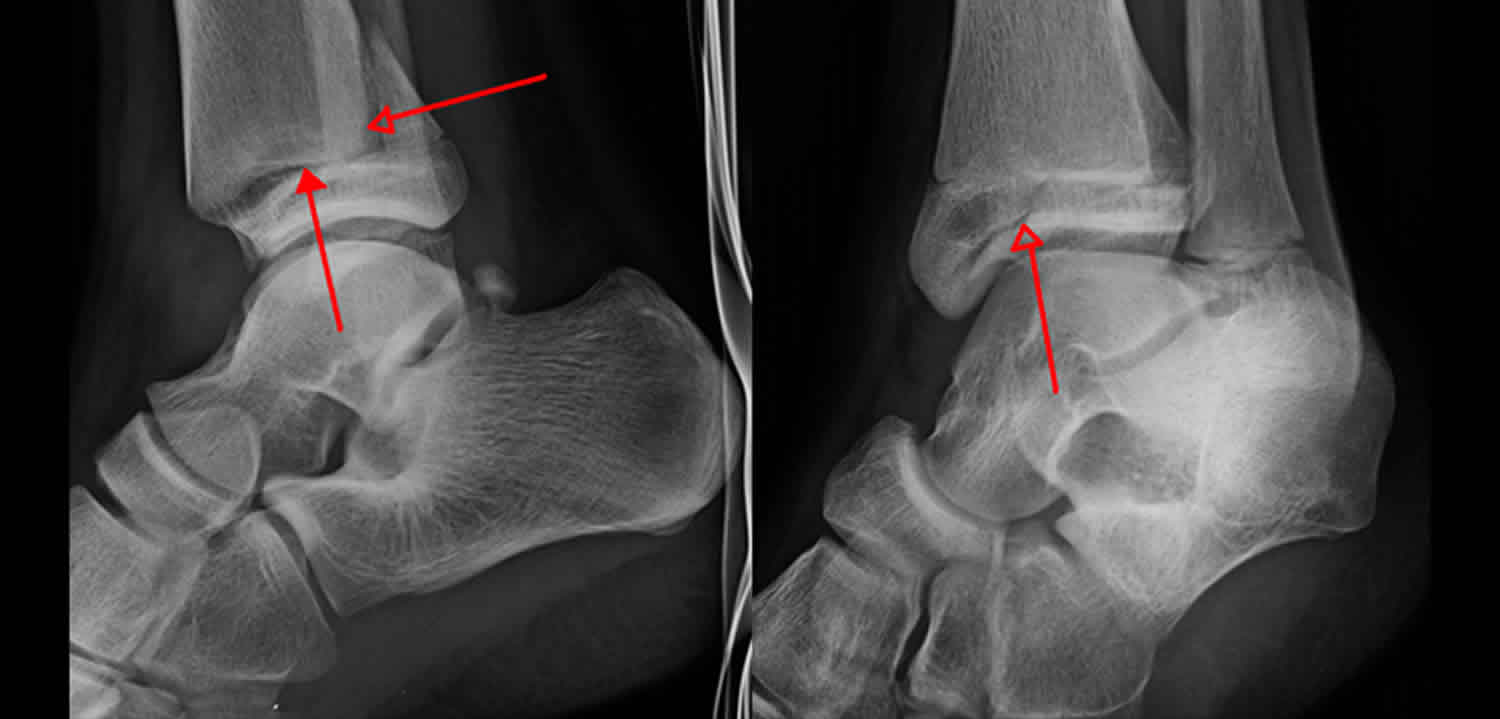
What are the complications of a Tillaux fracture?
Tillaux fractures can cause pain or stiffness for up to 2 years after the injury, with joint incongruity resulting in degenerative arthritis, varus deformity, rotational deformity (rare), tibiotalar slant, nonunion, delayed union (rare), and leg-length inequality (extremely rare).

What is the surgical approach for a triplane fracture?
Open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) is performed for a triplane fracture demonstrating 2 mm or more of displacement after attempted closed reduction. The surgical approach depends on the fracture planes and can be anterolateral for lateral fractures or anteromedial for medial fractures.
How is a triplane ankle fracture treated?
Treatment is closed reduction or surgical fixation depending on the degree of fracture displacement and articular step-off. The prognosis is excellent, given the triplane ankle fracture is identified and appropriately treated.

Does a Tillaux fracture require surgery?
This study showed that Tillaux-Chaput fractures could be safely and efficiently treated with mini-open surgery. We recommend mini-open surgery, complete anatomical reduction, and internal fixation for successful results. Keywords: Adolescent; AOFAS; Chaput; mini-open surgery; surgical procedures; Tillaux.