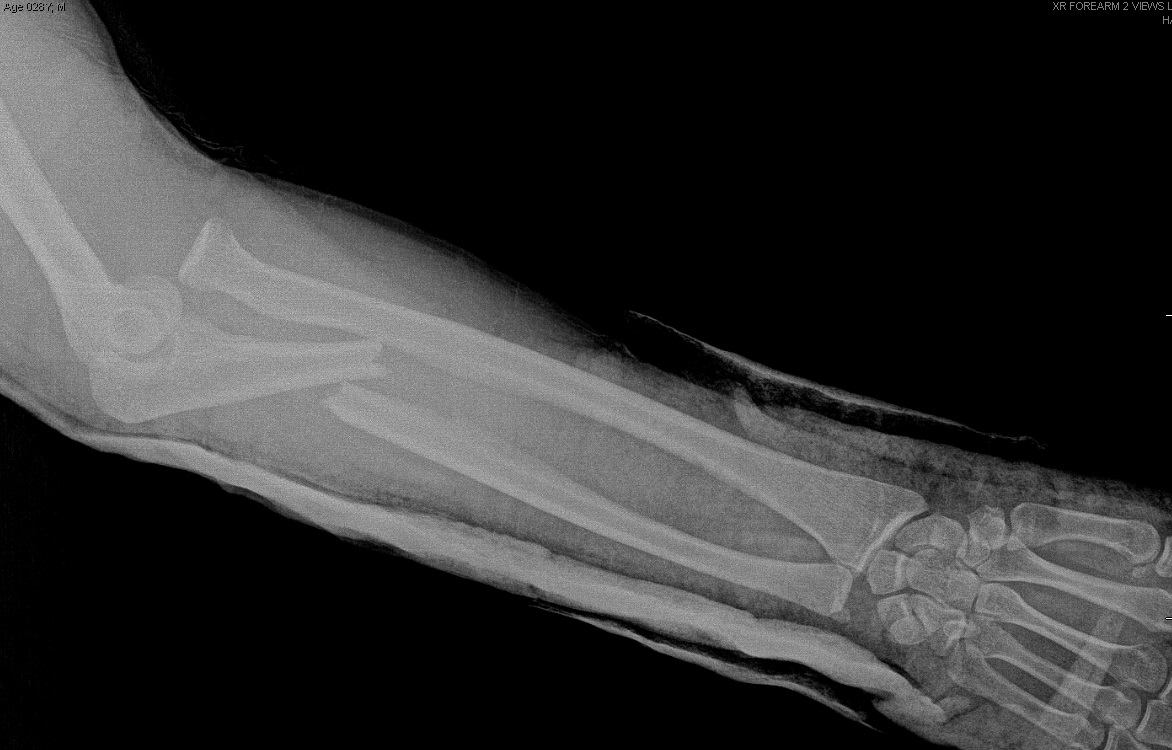
Monteggia and Galeazzi fractures are both types of forearm injuries that involve a fracture and dislocation of the bones in the arm. The Monteggia fracture is characterized by a fracture of the ulna bone in the forearm along with a dislocation of the radial head. On the other hand, the Galeazzi fracture involves a fracture of the radius bone in the forearm along with a dislocation of the distal radioulnar joint.
Both Monteggia and Galeazzi fractures are usually the result of high-energy trauma such as a fall from a height or a car accident. These injuries can be painful and debilitating, and may require surgical intervention to restore proper alignment of the bones.
It is important for healthcare providers to accurately diagnose Monteggia and Galeazzi fractures in order to provide appropriate treatment and prevent long-term complications such as chronic pain, stiffness, and loss of function in the arm. Treatment typically involves immobilization of the affected arm, followed by physical therapy to regain strength and mobility. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to repair the fracture and restore normal anatomy. With prompt and proper treatment, most patients can achieve a good recovery and return to their normal activities.
What is the cause of Monteggia?
Most common type in children accounting for 70% of cases, 15% of cases in adults. Mechanism of Injury: (1) direct blow to posterior elbow, (2) hyper-pronated force on an outstretched arm, (3) contracted biceps resists forearm extension causing dislocation and followed by impact leading to ulna fractureulna fractureAn isolated fracture of the ulnar shaft is defined as a nightstick fracture. The injury derives its name from the idea that a suspect struck with a police nightstick would hold his forearm above his face in a defensive posture when struck with a police baton, resulting in a fracture to the ulna.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov › books › NBK555951Nightstick Fracture – StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf.
What is a Galeazzi fracture criteria?
The Galeazzi fracture is a fracture of the middle to distal one-third of the radius associated with dislocation or subluxation of the distal radioulnar jointdistal radioulnar jointThe DRUJ is an incongruent diarthrodial, synovial articulation between the distal radius and ulna ( Fig. 1 ). It provides a pivot for pronation–supination of the distal forearm.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov › pmc › articles › PMC8440053Distal Radioulnar Joint Instability and Associated Injuries – NCBI (DRUJ). Advances in radiography and fracture research have helped define, classify, and guide operative management.
How do you reduce Monteggia?
– posterior Monteggia frx is reduced by applying traction to forearm w/ the forearm in full extension; – immobilization is continued until there is union of the ulna; – this ordinarily requires 6-10 wks depending on the age of pt; – ref: Repair of Bado II Monteggia Fracture: Case Presentation and Surgical Technique.
What is Monteggia equivalent?
Monteggia equivalent lesion represents a series of combined elbow and forearm injuries that resemble typical Monteggia fracture either in presentation or mechanism. The term has gradually evolved since its introduction, as sporadic case reports continued to complement it.May 6, 2020
Will my doctor know if I go to another doctor?
even if I don’t tell them or want to? Unlikely. Most of the time, you have to sign a consent form for your doctor to get medical records from another hospital or clinic. If you happened to have care at an affiliated clinic or hospital in the past, your labs or reports might show up.

What to do if you haven’t been to doctor in years?
– Find the right primary care model for you. If you haven’t been to a doctor in years, you should know that things in the primary care world have evolved. …
– Find a primary care physician you trust. …
– Get caught up on clinical care. …
– Then, take action outside the office.
/make-sure-you-have-a-trusting-relationship-with-your-doctor-picture-id689956326 (1).jpg?width=2048&name=make-sure-you-have-a-trusting-relationship-with-your-doctor-picture-id689956326 (1).jpg)
Is it OK to switch doctors within a practice?
Can I Change Doctors Within a Practice? It is in your right to see any provider you choose as long as they are willing to take you as a patient and you have insurance or other means to pay. However, you would be well served to advise the old provider of your intention to switch to someone else in the practice.
What to do if you can’t go to the doctor?
– Call Your Health Care Plan.
– Explore Telemedicine Options.
– Ask for a Referral to Another Provider.
– Consider a Nurse Practitioner.
– Utilize Urgent Care Clinics.
– Book Your Next Appointment Before You Leave Your Appointment.
– Be Flexible.
Is it okay to go to another doctor?
Your doctor is usually comfortable with your decision to get a second opinion. Getting a second opinion is a good idea when you have a medical issue. In fact, you might find that your general doctor will refer you to a specialist or encourage you to see another doctor before you even ask.