A herniated disc is often mistaken for other conditions due to the similarity in symptoms. One common misdiagnosis is a muscle strain or sprain in the back, as both conditions can cause pain, stiffness, and limited range of motion. Additionally, a herniated disc can be confused with sciatica, which is pain that radiates down the leg due to compression of the sciatic nerve. This is because a herniated disc in the lower back can also put pressure on the sciatic nerve, causing similar symptoms. Spinal stenosis, a condition where the spinal canal narrows and puts pressure on the spinal cord, can also be misdiagnosed as a herniated disc. Both conditions can cause back pain, numbness, and weakness in the legs. Finally, a herniated disc can sometimes be mistaken for a vertebral fracture, especially in older individuals with osteoporosis. It is important for healthcare providers to conduct a thorough physical exam and imaging tests to accurately diagnose a herniated disc and differentiate it from other conditions with similar symptoms. Proper diagnosis is crucial for determining the most effective treatment plan and preventing further complications.
How to tell the difference between spinal stenosis and herniated disc?
The main difference between spinal stenosis and disc herniations is that forward bending is relieving for spinal stenosis and disc herniations are generally more painful when you bend forward.
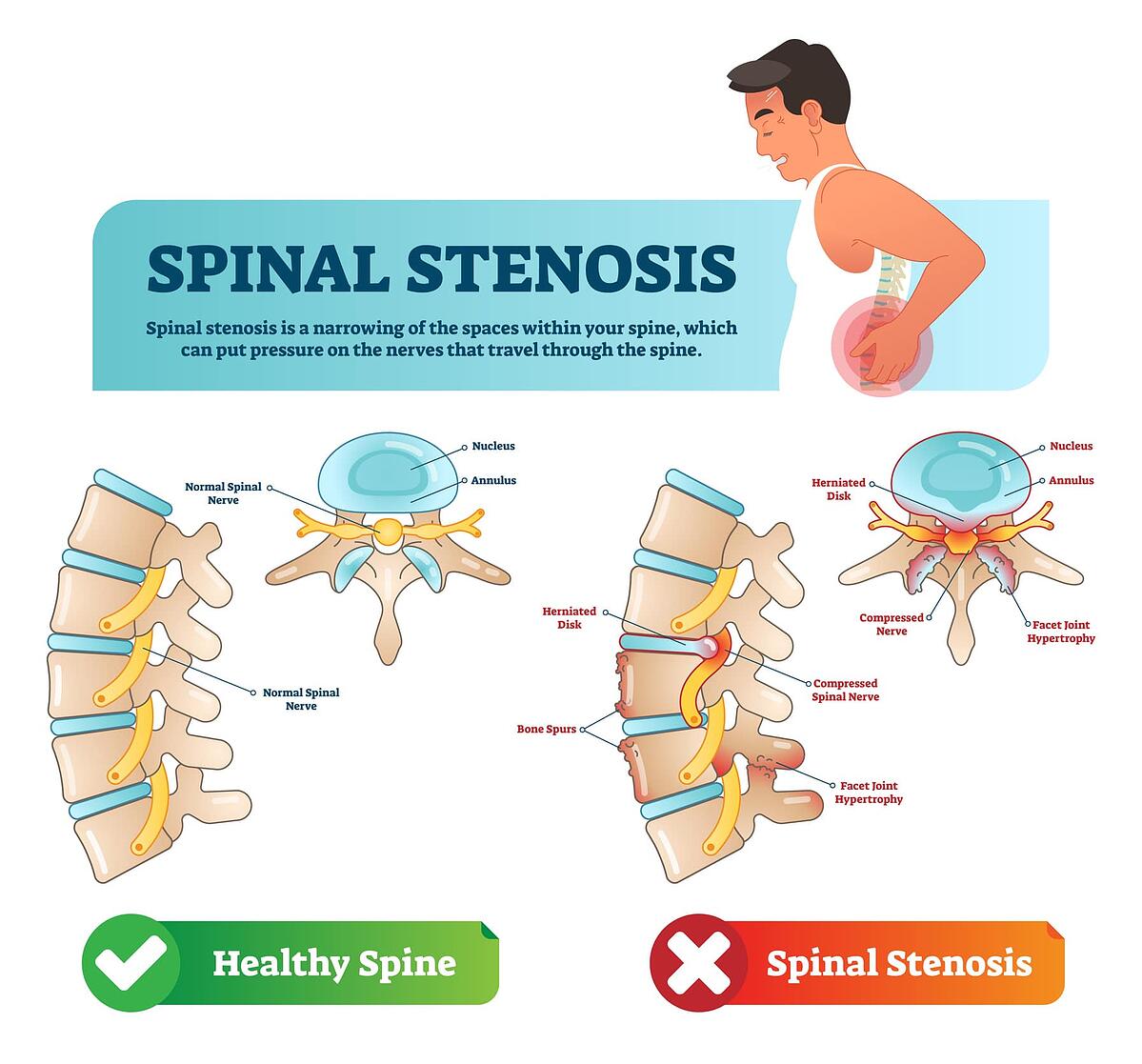
When should you suspect spinal stenosis?
If you have any of these symptoms, you need to get medical attention right away: Loss of bowel or bladder control. Severe or increasing numbness between your legs, inner thighs, and back of the legs. Severe pain and weakness that spreads into one or both legs.
What can be mistaken for a slipped disc?
Yes. A misdiagnosed herniated disc is one of the most common reasons patients endure chronic neck or back pain. Herniated discs are often misdiagnosed as piriformis syndrome, a muscular disorder in the buttocks, mild sciatica, degenerative disc disease, and osteoarthritis.

What else could be a herniated disc?
Herniated disks are also called ruptured disks or slipped disks, although the whole disk does not rupture or slip. Only the small area of the crack is affected. Compared with a bulging disk, a herniated disk is more likely to cause pain because it generally protrudes farther and is more likely to irritate nerve roots.
Can kyphoplasty be redone?
Due to technical constraints, placing an additional kyphoplasty after one has already been accomplished may be technically dangerous and a simpler less costly vertebroplasty technique may be beneficial.
How long does a kyphoplasty last?
The entire procedure usually takes less than an hour. If more than one vertebra requires treatment, the procedure may take longer.
What can I do after kyphoplasty?
Go ahead and resume your normal daily activities, unless, of course, that involves heavy lifting or strenuous exercise. Hold off on those things for about six weeks post kyphoplasty.
Why does my back still hurt after kyphoplasty?
The findings revealed that 7.8% of the 809 people included in the study still had back pain after the kyphoplasty. Independent risk factors for the continued pain included: having a cavity inside a fractured vertebra. swelling due to fluid being trapped behind the membrane covering the back muscles.
Can kyphoplasty cause another fracture?
Conclusion: This study demonstrated a higher rate of subsequent fracture after kyphoplasty compared with natural history data for untreated fractures. Most of these occurred at an adjacent level within 2 months of the index procedure.
