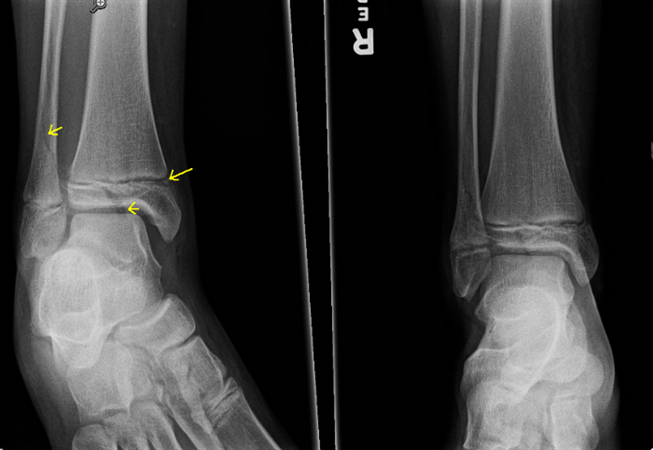
A triplane fracture is a type of fracture typically seen in pediatric patients, specifically involving the distal tibia. It is characterized by a fracture line that extends through the epiphyseal plate, metaphysis, and cortex of the bone, resulting in a three-part fracture.
This type of fracture is usually caused by trauma, such as a direct blow to the bone or a twisting injury. The triplane fracture is commonly seen in adolescents, especially during periods of rapid growth when the epiphyseal plate is still open and vulnerable to injury.
Diagnosis of a triplane fracture is typically made based on physical examination and imaging studies, such as X-rays and CT scans. Treatment of a triplane fracture usually involves immobilization of the affected limb with a cast or splint to allow the bone to heal properly. In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to realign the bone fragments and stabilize the fracture.
Complications of a triplane fracture include growth plate disturbances, malunion, and potential long-term issues with the affected limb. Therefore, it is important for patients with a triplane fracture to receive appropriate medical care and follow-up to prevent any complications and ensure proper healing.
What are the complications of a triplane fracture?
– Tibial length growth retardation or deformity around the ankle secondary to epiphyseal growth plate injury.
– Posttraumatic arthritis.
– Postoperative infection.
– Osteomyelitis.
– Pressure injuries from the cast.
– Fracture blisters.
– Compartment syndrome.
What is a closed triplane fracture of right ankle?
Triplane ankle fractures are complex traumatic Salter-HarrisSalter-HarrisSalter-Harris fractures (physeal fractures) refer to fractures through a growth plate (physis) and are, therefore, specifically applied to bone fractures in children.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov › books › NBK430688Salter-Harris Fracture – StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf IV fractures involving the metaphysismetaphysisThe metaphysis ( pl. : metaphyses) is the neck portion of a long bone between the epiphysis and the diaphysis. It contains the growth plate, the part of the bone that grows during childhood, and as it grows it ossifies near the diaphysis and the epiphyses.https://en.wikipedia.org › wiki › MetaphysisMetaphysis – Wikipedia, physis, and epiphysis. The term “triplane” refers to the different orientations of the fracture lines in the distal tibia and represents a frequent diagnostic challenge.
Does a triplane fracture need surgery?
For displaced fractures, closed reduction is attempted. Surgical fixation of a triplane fracture should be undertaken if the residual fracture gap is 2 mm or greater after attempted closed reduction and casting. Malunited fractures with more than 2 mm of intra-articular displacement are associated with poor outcomes.
Is a triplane fracture open or closed?
Tillaux fracturesTillaux fracturesTillaux fractures are intraarticular fractures involving the physis and epiphysis of the distal tibia and are seen in children and adolescents. These fractures are classified as Salter-Harris type III.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov › books › NBK482332Tillaux Fracture – StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf and triplane fractures are the most common ankle joint fractures in adolescents with closure of the epiphyseal plate according to the mechanism of injury.Feb 4, 2010
What is the schedule for Pediarix vaccine?
The recommended dosing schedule for immunization with PEDIARIX consists of 3 doses at 2, 4, and 6 months of age (at intervals of 6 to 8 weeks, preferably 8 weeks).
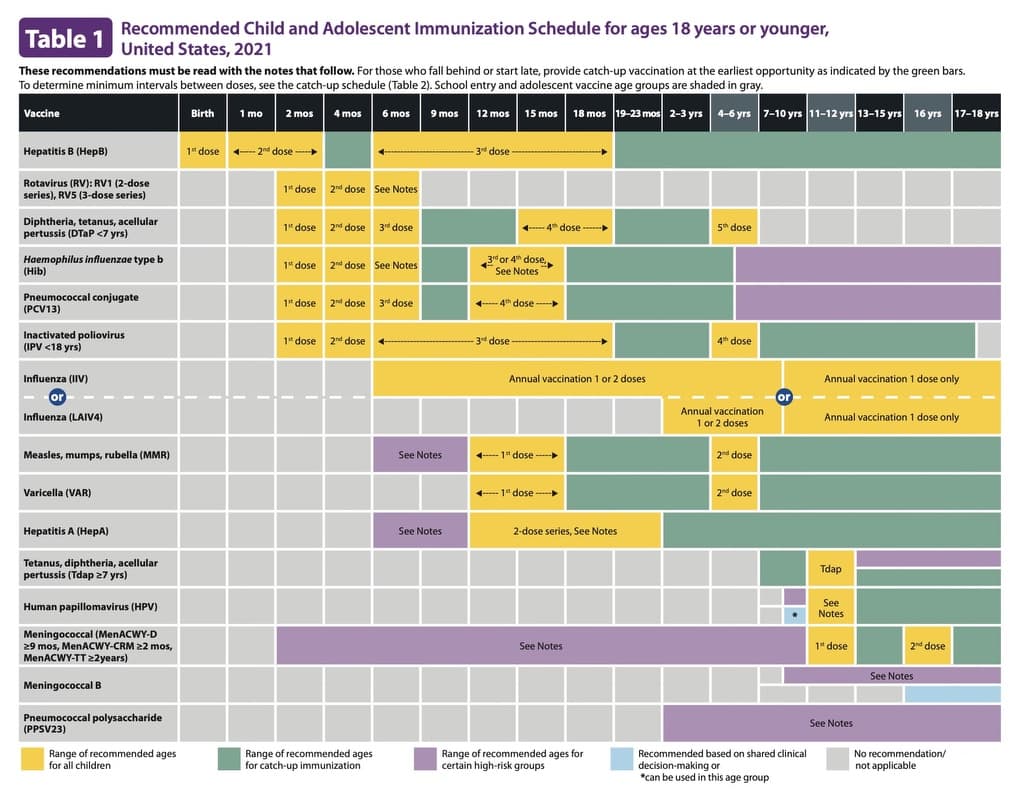
What are the childhood vaccine combos?
Combination vaccines have been in use in the United States since the mid-1940s. Examples of combination vaccines are: DTap (diphtheria-tetanus-pertussis), trivalent IPV (three strains of inactivated polio vaccine), MMR (measles-mumps-rubella).
What if I refuse to vaccinate my child?
Children who are not vaccinated can transmit vaccine- preventable diseases at schools and in the community. Unvaccinated children can infect babies who are too young to be fully immunized. Unvaccinated children can infect people of any age who can’t be immunized for medical reasons.
What vaccines are mandatory for school in NY?
– Diphtheria and Tetanus toxoid-containing vaccine and Pertussis vaccine (DTaP or Tdap)
– Hepatitis B vaccine.
– Measles, Mumps and Rubella vaccine (MMR)
– Polio vaccine.
– Varicella (Chickenpox) vaccine.
What are the 5 most important vaccines for children’s?
– Diphtheria, tetanus and whooping cough (pertussis) (DTaP)
– Polio (IPV)
– Measles, mumps and rubella (MMR)
– Chickenpox (varicella)
– Influenza (flu) every year.