A proximal phalanx fracture in children is a common type of injury that occurs in the finger bones of the hand. These fractures can happen due to falls, sports injuries, or other accidents that put direct pressure on the finger. The proximal phalanx is the bone that connects the finger to the hand, and a fracture in this area can cause pain, swelling, and difficulty moving the affected finger.
Treatment for a proximal phalanx fracture in children typically involves immobilizing the finger with a splint or cast to allow the bone to heal properly. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to realign the bone and ensure proper healing. Physical therapy may also be recommended to help restore strength and range of motion in the finger after the fracture has healed.
It is important for parents and caregivers to seek prompt medical attention if they suspect a proximal phalanx fracture in a child. Delaying treatment can lead to complications such as improper healing, deformity, or long-term issues with the affected finger. With proper care and management, most children with proximal phalanx fractures can expect a full recovery and return to normal function in their fingers.
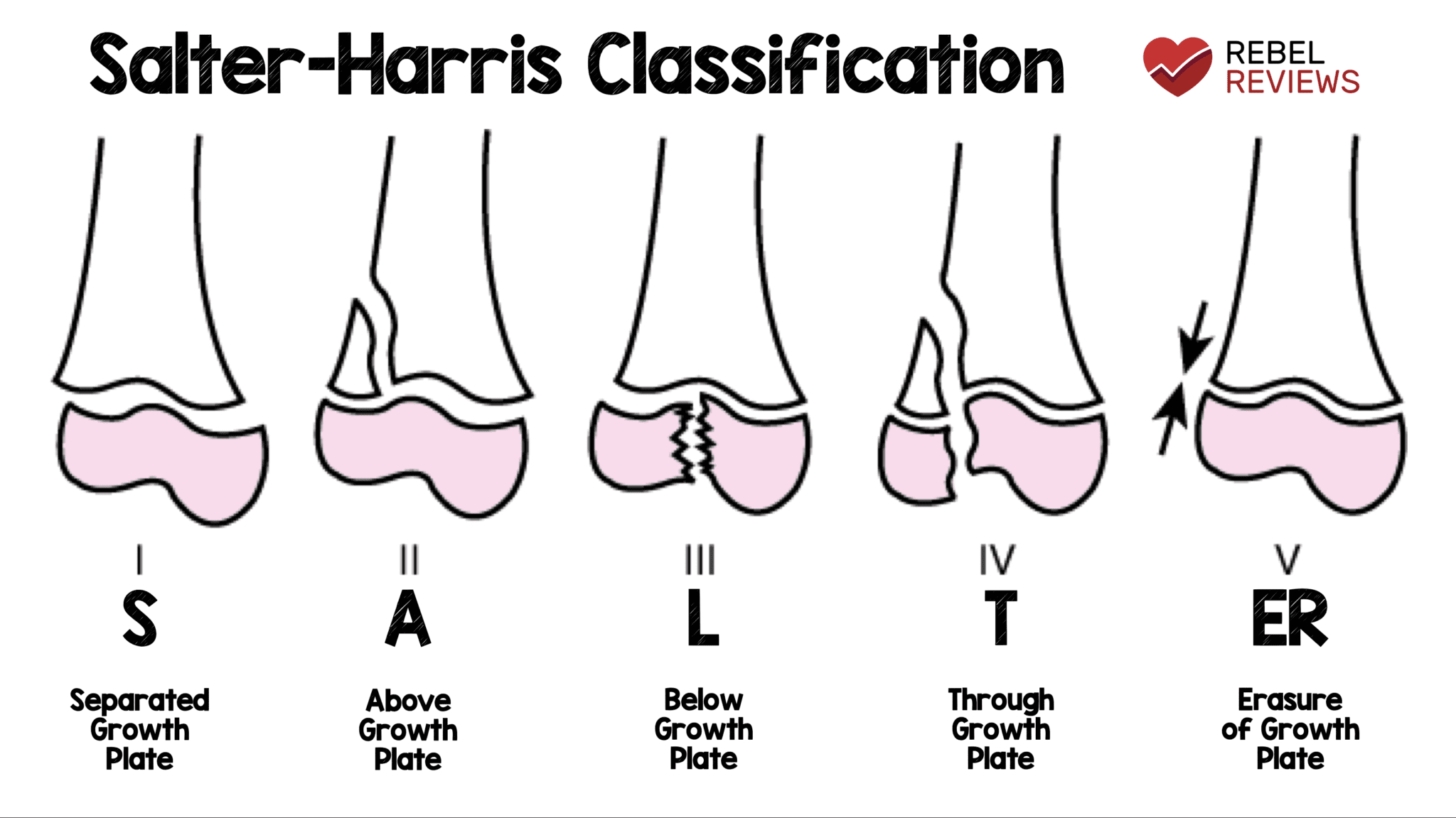
What is a Salter-Harris proximal phalanx fracture?
Salter-Harris type II fractures of the proximal phalanx are the most common type of finger fracture. An unmineralized physis is biomechanically weaker compared with the surrounding ligamentous structures and mature bone, which makes fractures about the physis likely.
What is the most common hand fracture in children?
Phalangeal fractures constitute approximately 65% of pediatric hand fractures. MetacarpalMetacarpalIn human anatomy, the metacarpal bones or metacarpus, also known as the “palm bones”, are the appendicular bones that form the intermediate part of the hand between the phalanges (fingers) and the carpal bones (wrist bones), which articulate with the forearm.https://en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Metacarpal_bonesMetacarpal bones – Wikipedia fractures account for approximately 35% of pediatric and adolescent hand fractures, with 100 of every 100,000 children sustaining a fracture of the metacarpals.
How serious is a Salter-Harris fracture?
If a Salter-Harris fracture is not diagnosed and treated quickly, it can lead to permanent growth arrest, during which the bone stops growing entirely.
How is a phalanx fracture treated in children?
Nondisplaced phalanx fractures are managed with splint immobilization. Stable, reduced phalanx fractures are immobilized but require close monitoring to ensure maintenance of fracture reduction.


