A pathological fracture of the hip is a type of fracture that occurs in the hip bone as a result of an underlying disease or condition weakening the bone structure. Unlike traumatic fractures that occur due to a sudden injury or accident, pathological fractures happen when the bone is already weakened and unable to withstand normal stress or strain.
There are several underlying conditions that can lead to pathological fractures of the hip. These include bone tumors, such as osteosarcoma or metastatic tumors that spread from other parts of the body to the hip bone. Other causes include bone diseases like osteoporosis, which gradually weakens the bones over time, and osteomyelitis, a bone infection that can cause bone deterioration.
The signs and symptoms of a pathological fracture of the hip are similar to those of a traumatic fracture and may include severe pain, swelling, bruising, deformity, and difficulty in moving the affected leg. However, in the case of a pathological fracture, the patient may not have experienced any recent trauma or injury.
To diagnose a pathological fracture of the hip, doctors typically perform imaging tests such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans to assess the extent of the fracture and identify any underlying conditions. Additionally, a bone biopsy may be performed to determine the exact cause of the fracture.
Treatment for a pathological fracture of the hip depends on the underlying cause and the severity of the fracture. Options may include surgical intervention to stabilize the bone, radiation therapy or chemotherapy to treat underlying tumors, or antibiotics to combat bone infections. Physical therapy may also be prescribed to aid in rehabilitation and restore mobility.
In conclusion, a pathological fracture of the hip is a fracture that occurs in the hip bone due to an underlying disease or condition weakening the bone structure. Prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment are crucial to prevent further complications and restore normal hip function.
What is the life expectancy of a pathological fracture?
Pathological fractures have significant implications for patient morbidity and mortality and are often considered a marker of end-stage cancer. The literature suggests a 1-year survival rate in the range of 30–40% [6–9].Sep 6, 2018

How does a hip fracture happen?
A severe impact, such as a car crash, can cause hip fractures in people of all ages. In older adults, a hip fracture is most often a result of a fall from a standing height. In people with very weak bones, a hip fracture can occur simply by standing on the leg and twisting.

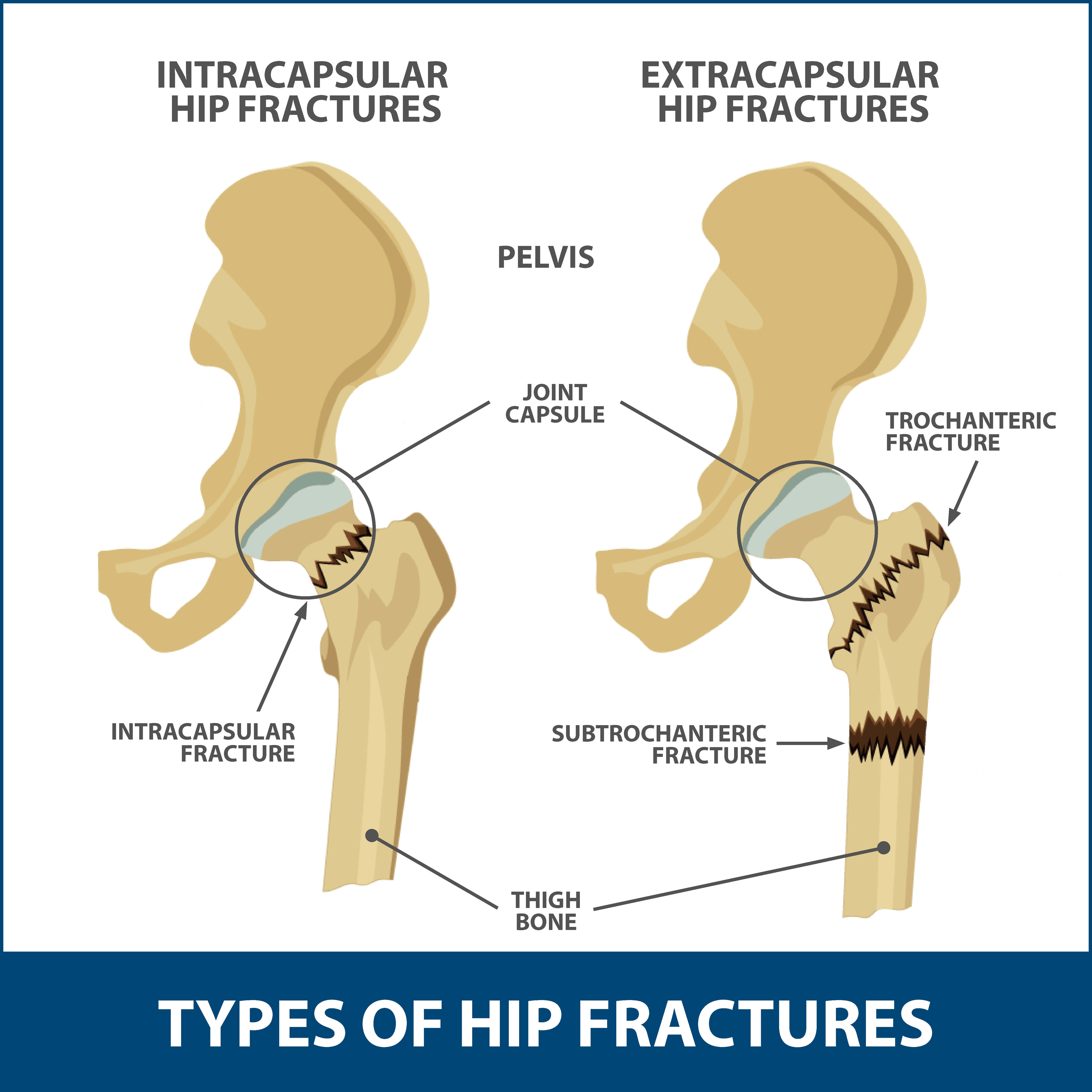
Where is a hip fracture most likely to occur?
Most hip fractures occur in one of two locations on the long bone that extends from the pelvis to your knee (femur): The femoral neckfemoral neckThe femoral neck (femur neck or neck of the femur) is a flattened pyramidal process of bone, connecting the femoral head with the femoral shaft, and forming with the latter a wide angle opening medialward.https://en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Femoral_neckFemoral neck – Wikipedia. This area is situated in the upper portion of your femur, just below the ball part (femoral head) of the ball-and-socket joint. The intertrochanteric region.

Which part of the hip region that is most likely to be fractured?
Most hip fractures occur in one of two locations on the long bone that extends from the pelvis to your knee (femur): The femoral neckfemoral neckThe femoral neck (femur neck or neck of the femur) is a flattened pyramidal process of bone, connecting the femoral head with the femoral shaft, and forming with the latter a wide angle opening medialward.https://en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Femoral_neckFemoral neck – Wikipedia. This area is situated in the upper portion of your femur, just below the ball part (femoral head) of the ball-and-socket joint. The intertrochanteric region.
Which person is at highest risk for hip fractures?
Each year over 300,000 older people—those 65 and older—are hospitalized for hip fractures. More than 95% of hip fractures are caused by fallingfallingAbout 36 million falls are reported among older adults each year—resulting in more than 32,000 deaths. Each year, about 3 million older adults are treated in emergency departments for a fall injury. One out of every five falls causes an injury, such as broken bones or a head injury.https://www.cdc.gov › injury › features › older-adult-fallsKeep on Your Feet—Preventing Older Adult Falls | Features | Injury Center,2 usually by falling sideways. Women experience three-quarters of all hip fractures. Women fall more often than men.
What is the prognosis for hip fractures in the elderly?
Experts estimate that some 18 to 33 percent of all older adults who have suffered hip fractures will die within a year, with even higher rates of death among people who have dementia or who live in a nursing home.Jul 8, 2019
What is life expectancy after hip fracture?
According to a 2019 study in Acta Orthopaedica, the one-year mortality after a hip fracture is 21% for those whose fracture is surgically repaired. If the fracture is not repaired, the one-year mortality is about 70%.
What is the biggest risk factor for hip fracture?
Osteoporosis is the leading cause of hip fracture. Age is also a major risk factor. Other possible risk factors for hip fracture may include, but are not limited to, the following: Excessive alcohol and caffeine consumption.

What is the most common cause of death in a hip fracture?
During recovery, a hip stress fracture can immobilize a patient for a long amount of time, potentially leading to blood clots and decreased muscle mass. Post-surgical complications, like infections and pulmonary embolism, may also contribute to high death rates.