Lower back pain is a common issue experienced by females who engage in exercise. The causes of this discomfort can vary, but they are typically related to specific factors that impact the muscles, ligaments, and joints in the lower back area.
One of the main causes of lower back pain in females exercising is poor posture. When participants do not maintain proper alignment during physical activities, excessive stress is placed on the lower back muscles, leading to discomfort and potential injury. This is particularly true for exercises that involve repetitive movements or heavy lifting.
Another contributing factor is weak core muscles. The core muscles, including the abdominal and back muscles, provide support and stability to the spine. If these muscles are weak, the lower back becomes more susceptible to strain and injury. Insufficient core strength can result from a sedentary lifestyle or neglecting core-specific exercises in a workout routine.
Types of exercises can also play a role in lower back pain. High-impact activities, such as running or jumping, can generate excessive force on the lumbar spine, leading to discomfort. Similarly, exercises that involve repetitive bending or twisting motions can strain the lower back muscles and contribute to pain.
Furthermore, hormonal changes during the menstrual cycle can influence lower back pain in females exercising. Fluctuations in estrogen and progesterone levels can lead to ligament laxity, making the pelvic region less stable and potentially increasing the risk of lower back pain during exercise.
To prevent lower back pain, females should focus on maintaining proper posture during physical activities and engage in strengthening exercises that target the core muscles. Additionally, incorporating low-impact exercises into their routine, such as swimming or biking, can help reduce strain on the lower back. Consulting with a healthcare professional or a certified trainer may provide personalized guidance and exercises to address and prevent lower back pain in females exercising.
What are the red flags for low back pain?
“Red flags” include pain that lasts more than 6 weeks; pain in persons younger than 18 years or older than 50 years; pain that radiates below the knee; a history of major trauma; constitutional symptoms; atypical pain (eg, that which occurs at night or that is unrelenting); the presence of a severe or rapidly …

What diseases start with lower back pain?
– kidney and bladder problems, including kidney infections.
– pregnancy.
– endometriosis.
– ovarian cysts.
– uterine fibroids.
– spinal cord misalignment.
– spinal infections.
– cancer, such as cancer of the spinal cord.
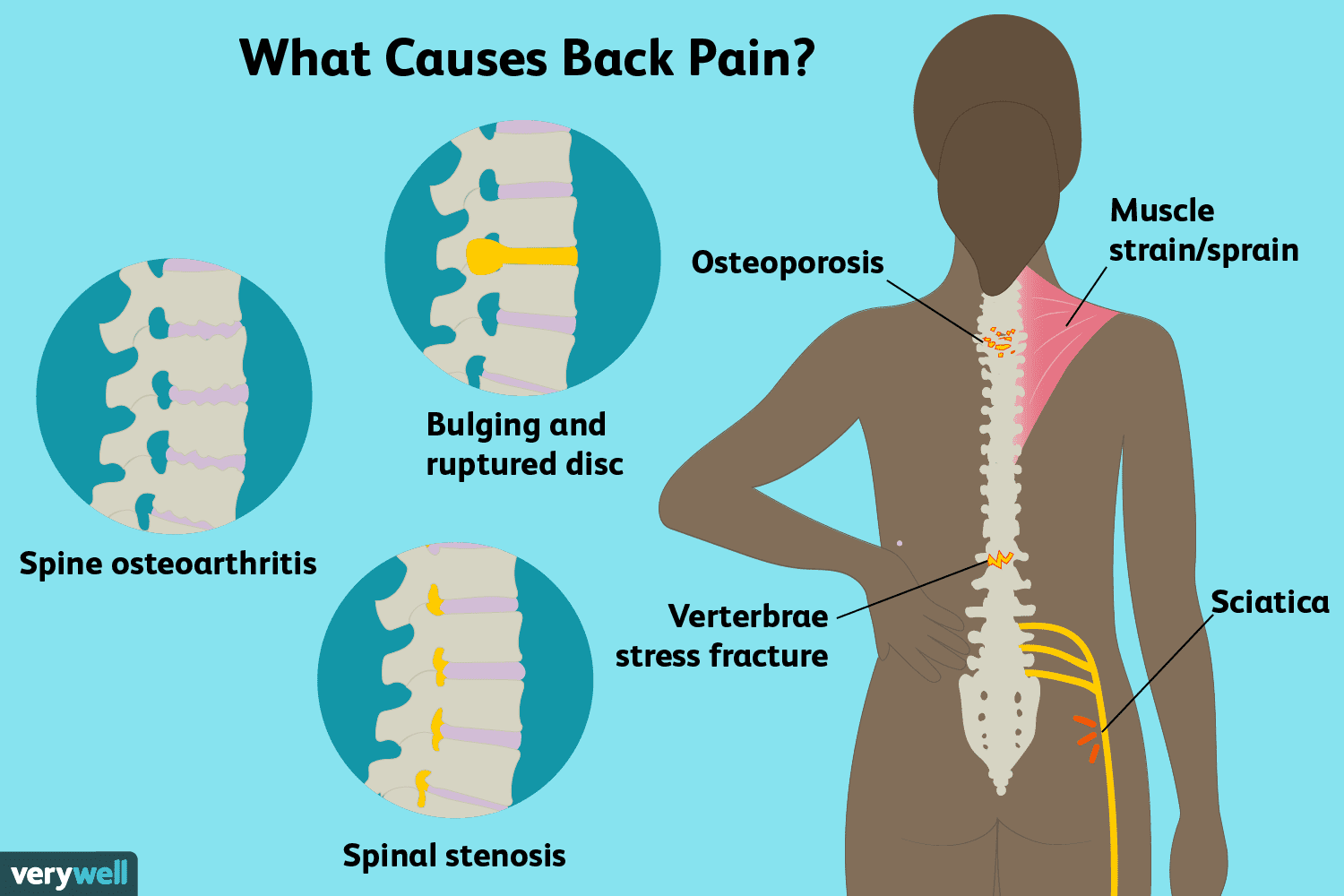
What are 3 causes of lower back pain?
– Sprains & Strains.
– Traumatic Injury.
– Fracture.
– Herniated Disc.
– Sciatica.
– Lumbar Spinal Stenosis.
– Osteoarthritis.
– Scoliosis.
What underlying diseases cause back pain?
– Ankylosing spondylitis.
– Endometriosis.
– Fibromyalgia.
– Herniated disk.
– Kidney infection (also called pyelonephritis)
– Kidney stones (Hard buildups of minerals and salt that form inside the kidneys.)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/backpainfinal-01-5c3ba0bf46e0fb0001b5b300.png)
When should I worry about left lower back pain?
In many cases lower back pain stops on its own. But if it doesn’t, here are some guidelines on when you may want to start seeking professional help: If the pain lasts four weeks or longer. If the pain keeps getting worse as time goes by.
What are the red flags for low back pain?
“Red flags” include pain that lasts more than 6 weeks; pain in persons younger than 18 years or older than 50 years; pain that radiates below the knee; a history of major trauma; constitutional symptoms; atypical pain (eg, that which occurs at night or that is unrelenting); the presence of a severe or rapidly …
What symptoms associated with back pain should prompt you to see a doctor?
– Is constant or intense, especially at night or when lying down.
– Spreads down one or both legs, especially if the pain extends below the knee.
– Causes weakness, numbness or tingling in one or both legs.
– Occurs with unintended weight loss.
– Occurs with swelling or redness on the back.
When is lower left back pain serious?
As a general guideline, seeing a doctor for lower left back pain is recommended if the pain follows an accident or injury, if it does not get better on its own, worsens, or interferes with daily functions such as standing, walking, or sleeping, or if it is accompanied by other troublesome or progressing symptoms.

How do I know if my lower back pain is serious?
If your back pain wakes you up in the middle of the night or appears when you’re in certain positions, such as lying down, then this could be a sign of a more serious problem. It could be a sign of a more systematic problem such as an infection, fracture, severe nerve compression or even cancer.