The following article provides an overview of the symptoms associated with L3-L4 nerve damage. Nerves play a crucial role in transmitting signals from the brain to different parts of the body. When the L3-L4 nerves, which are located in the lower back, sustain damage, various symptoms can arise.
One common symptom of L3-L4 nerve damage is back pain. This pain can be localized around the lower back and may radiate towards the thighs and buttocks. The intensity of the pain can vary and may increase with movement or specific activities. Additionally, the affected individual may experience numbness or a tingling sensation in the lower back and legs. This discomfort can hinder one’s mobility and overall quality of life.
Nerve damage at the L3-L4 level can also cause muscle weakness. The muscles in the lower back, thighs, and hips may feel weaker or fatigued, affecting daily activities such as walking, standing, or lifting objects. Loss of strength in these areas can lead to a decrease in overall mobility.
In some cases, L3-L4 nerve damage can cause difficulties with bladder and bowel control. This occurs due to the disruption of nerve signals responsible for coordinating these functions. Incontinence, urinary retention, or difficulty passing stool can all be potential symptoms.
Other possible symptoms include changes in reflexes, such as a diminished knee-jerk reflex, and altered sensations in the affected areas. These sensory changes can vary from person to person and may include decreased sensitivity to touch or temperature.
It is important to note that each individual may experience a unique combination of symptoms, and the severity can vary depending on the extent of nerve damage. Prompt medical evaluation and diagnosis are crucial to determine the underlying cause of the nerve damage and establish an appropriate treatment plan. Rehabilitation exercises, pain management techniques, and, in severe cases, surgical interventions, can be employed to alleviate symptoms and promote recovery.
Where is L4-L5 and S1 located?
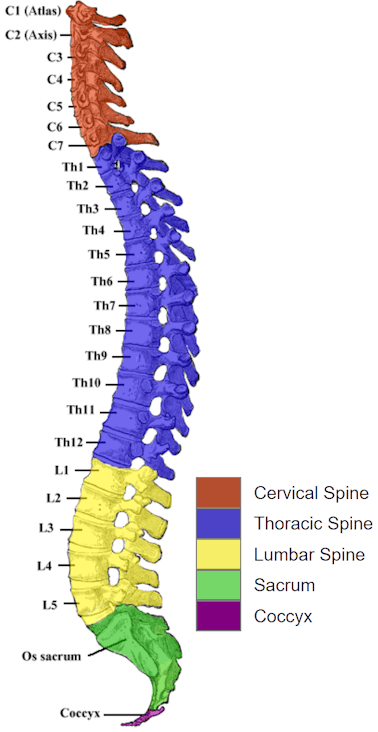
The L4-L5 disc in the low back is between the L4 vertebrae and L5 vertebrae which make up the L4-L5 spinal segment. The L5-S1 disc at the bottom of the spine lies between the L5 vertebra and the first bony segment at the top of the sacrum, which is sacral segment 1 (or S1).
What parts of the body are affected by L4-L5?
The L5 nerve root exits the spine at the level of the L4-L5 vertebrae and innervates (supplies sensation to) the muscles of the thigh and knee, as well as the skin over the front and side of the thigh. A herniated disc at this level can cause pain, numbness, or weakness in the thigh, knee, and leg.
How do you fix L3 and L4 spine?
– Medication. …
– Immobilization. …
– Physical therapy. …
– Chiropractic manipulation. …
– Injection.

Where is L1 and L2 located in your back?
Known as the lumbar vertebrae, or “lumbar spine” (from L1 to L5 on your spinal column), they are located below the 12 chest (thoracic) vertebrae and above the five fused bones composing your triangular sacrum bone.Oct 2, 2023
How do you get rid of upper back pain between shoulder blades?
– Heat or Cold Therapy. Applying a cold pack or hot compress to the affected area can provide relief from upper back pain. …
– Gentle Stretching Exercises. …
– Correcting Posture. …
– Over-the-Counter Pain Relief Medications. …
– Massage.
What is a red flag for upper back pain?
Red flag symptoms may include: Constant back pain. Unexplained continuous fever. Swelling or other structural deformity.

What stretches help upper back pain?
– Downward facing dog. Start in a plank position with your shoulders over your wrists. …
– Modified downward facing dog. …
– Child’s pose. …
– Cat-cow. …
– Thread the needle. …
– Cross body shoulder stretch. …
– Chin to chest stretch. …
– Standing side reach.
Why does my upper back ache so much?
Many cases of upper and middle back pain are caused by external forces that can stress the muscles, ligaments, and discs, such as: Muscle stress and strain. Discomfort may result from poor posture, not lifting correctly, or muscle overuse.