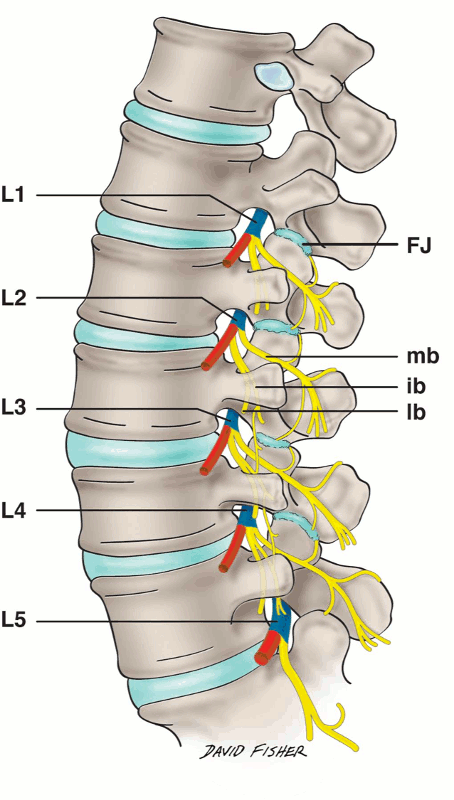
The lumbar nerves are a crucial part of the nervous system as they play a vital role in transmitting sensory and motor signals to and from the lower back and lower extremities. Understanding the roots of these nerves is of utmost importance in diagnosing and treating various conditions related to the lumbar region.
The lumbar nerves are formed by the fusion of the anterior and posterior roots of the spinal cord, which are situated within the lumbar vertebrae. There are five pairs of lumbar nerves, numbered L1 to L5, each with an anterior and posterior root. These roots emerge from the intervertebral foramina, small openings between adjacent vertebrae that allow the nerves to exit the spinal column.
The anterior roots of the lumbar nerves primarily consist of motor fibers that carry signals from the spinal cord to the muscles of the lower extremities. These signals are responsible for controlling movement and actions such as walking, running, and performing daily activities. The posterior roots, on the other hand, are predominantly composed of sensory fibers that transmit sensory information, such as pain, touch, temperature, and proprioception, from the lower back and lower extremities to the spinal cord and brain.
Each pair of lumbar nerves has specific areas of innervation within the lower back and lower extremities. For example, the L1 nerve root mainly innervates the inguinal region, while the L2 to L4 roots supply the anterior and medial aspects of the thigh. The L4 and L5 roots extend into the leg and foot, providing motor and sensory signals to these areas. Additionally, the L5 and S1 roots are responsible for innervating the muscles and skin of the posterior thigh, calf, and sole of the foot.
In conclusion, the roots of lumbar nerves originate from the spinal cord within the lumbar vertebrae and exit the spinal column through the intervertebral foramina. These nerves play a vital role in motor and sensory signaling to and from the lower back and lower extremities. Understanding the specific areas of innervation associated with each lumbar nerve root is crucial in diagnosing and treating conditions affecting the lumbar region.
What do L4 and L5 nerve roots control?
L2, L3 and L4 spinal nerves provide sensation to the front part of your thigh and inner side of your lower leg. These nerves also control hip and knee muscle movements. L5 spinal nerve provides sensation to the outer side of your lower leg, the upper part of your foot and the space between your first and second toe.
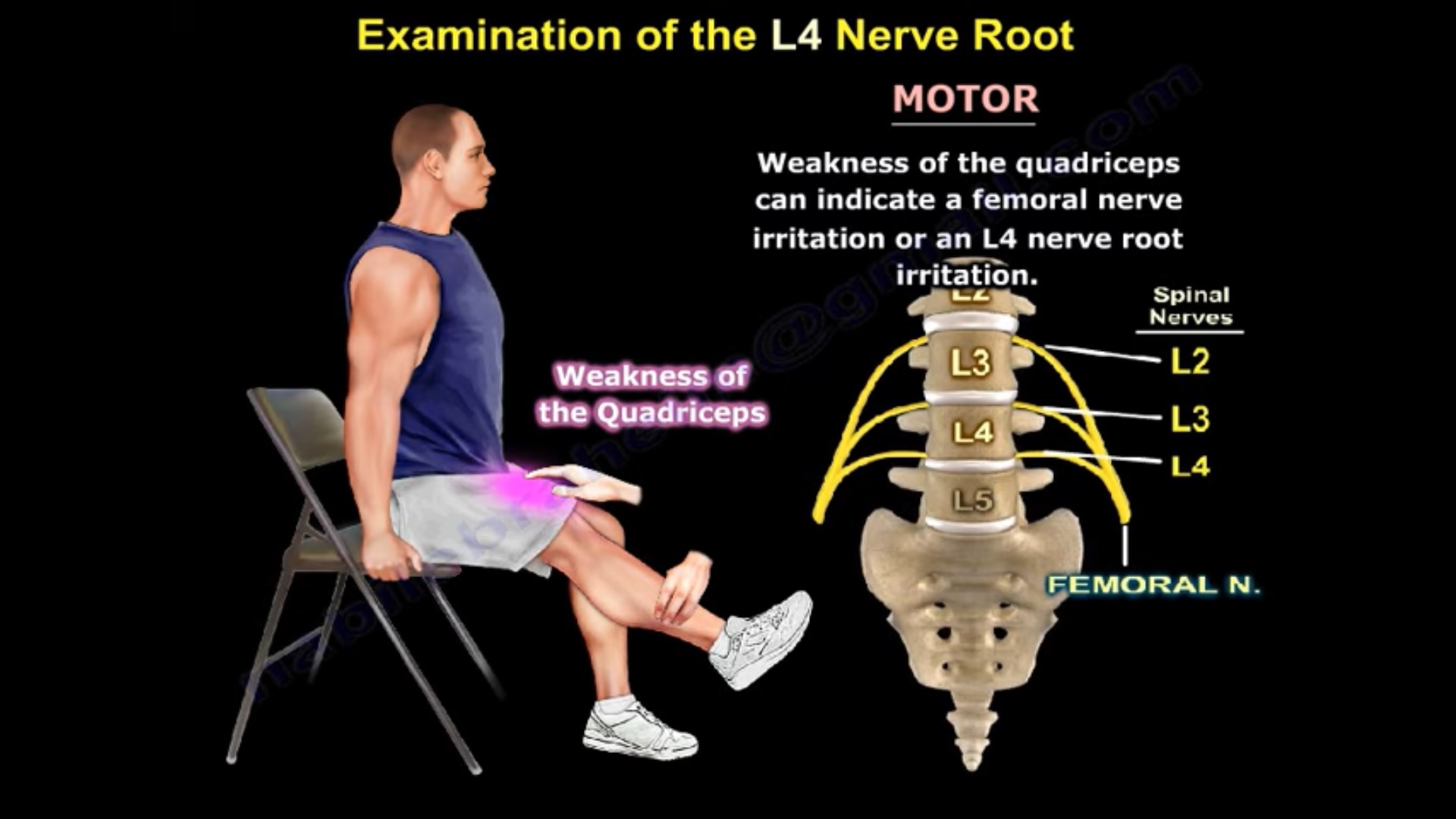
What are the symptoms of L4-L5 nerve damage?
This condition is caused by damage to the discs between the fourth and fifth lumbar vertebrae in your spine. Symptoms of a L4-L5 disc herniation can include pain, numbness, tingling, and weakness in the lower back and legs.
What is the best treatment for L4-L5?
The most common conventional treatments for spinal stenosis at L4 and L5 include: Physical therapy, which may involve strengthening and flexibility exercises, stabilization, joint mobilization, heat or ice therapy, and massage.Oct 6, 2022
What is the ICD-10 code for S72 22XA?
2024 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code S72. 22XA: Displaced subtrochanteric fracture of left femur, initial encounter for closed fracture.
What is the ICD-10 code for fracture of hip and pelvis?
ICD-10-CM S32. 9XXA is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group(s) (MS-DRG v41.0): 535 Fractures of hip and pelvis with mcc. 536 Fractures of hip and pelvis without mcc.
What is diagnosis code S72 92XA?
2024 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code S72. 92XA: Unspecified fracture of left femur, initial encounter for closed fracture.
What is S72 8X2A ICD-10?
Other fracture of left femur, initial encounter for closed fracture. S72. 8X2A is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the ICD-10 code for S72 92XA?
2024 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code S72. 92XA: Unspecified fracture of left femur, initial encounter for closed fracture.