https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ro3GzqJO1-k
Childhood vaccination is an essential part of ensuring the health and well-being of children around the world. The most common childhood vaccines protect against diseases such as measles, mumps, rubella, polio, and hepatitis B.
The measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine is typically given in two doses, with the first dose administered at 12-15 months and the second dose at 4-6 years. This vaccine is highly effective at preventing these highly contagious diseases.
The polio vaccine is usually given in four doses, starting at 2 months of age and followed by doses at 4 months, 6-18 months, and a final dose between 4-6 years. Polio can cause paralysis and even death, so vaccination is crucial for preventing its spread.
Hepatitis B is a viral infection that can cause liver damage and even liver cancer. The vaccine is typically given in three doses, with the first dose administered shortly after birth and subsequent doses given at 1-2 months and 6-18 months.
Overall, childhood vaccines are an important tool in protecting children from serious and potentially life-threatening diseases. It is essential for parents to ensure that their children receive all recommended vaccinations on schedule to keep them healthy and safe.
Which of the following is a common childhood immunization?
Common vaccines given in childhood include: Influenza. Diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis vaccine (DTaP) Hepatitis A and B.
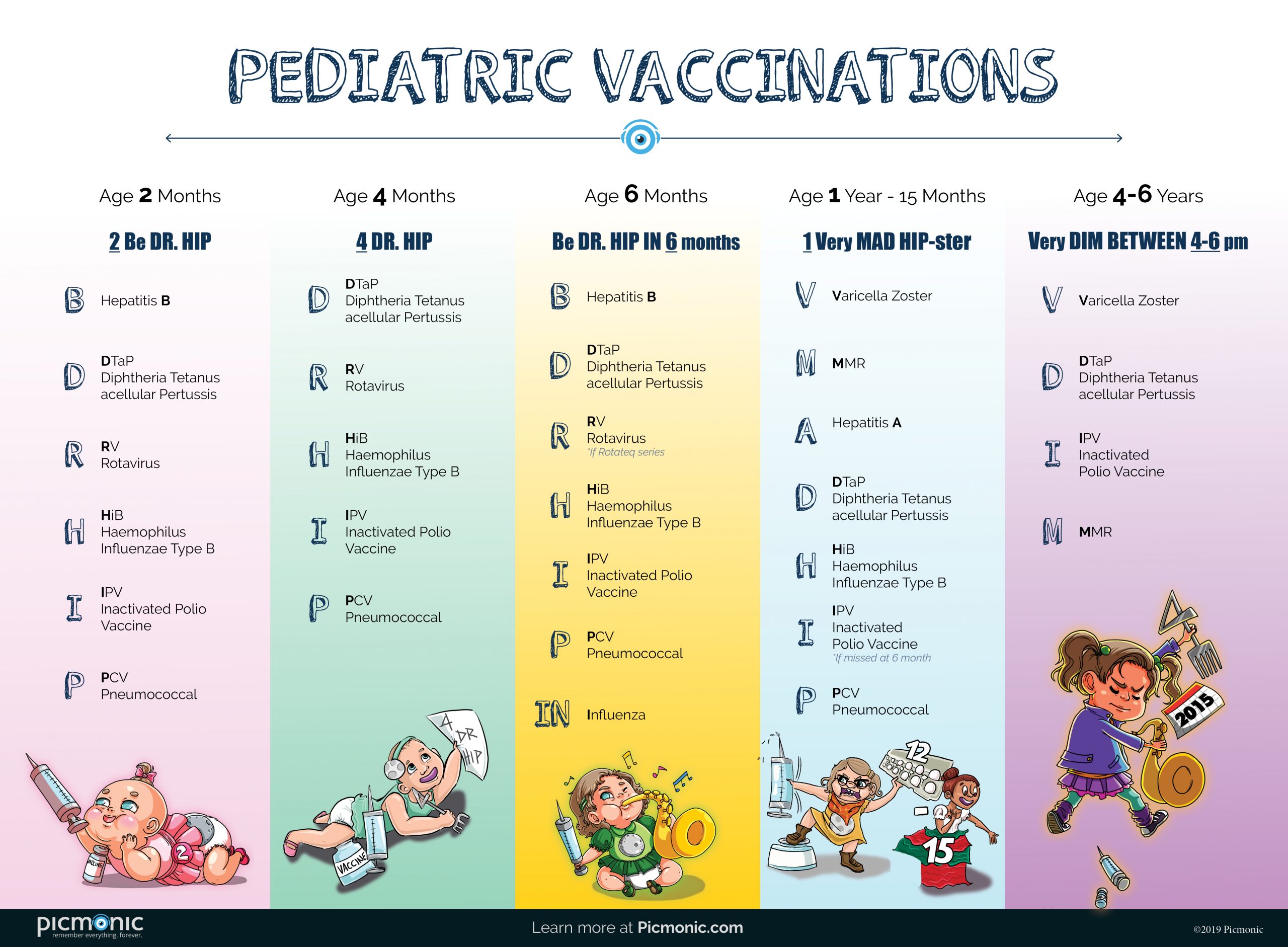
What are the normal childhood immunizations include?
– Chickenpox (Varicella)
– Diphtheria, tetanus, and whooping cough (pertussis) (DTaP)
– Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib)
– Measles, mumps, rubella (MMR)
– Polio (IPV) (between 6 through 18 months)
– Pneumococcal (PCV)
– Hepatitis A (HepA)
– Hepatitis B (HepB)
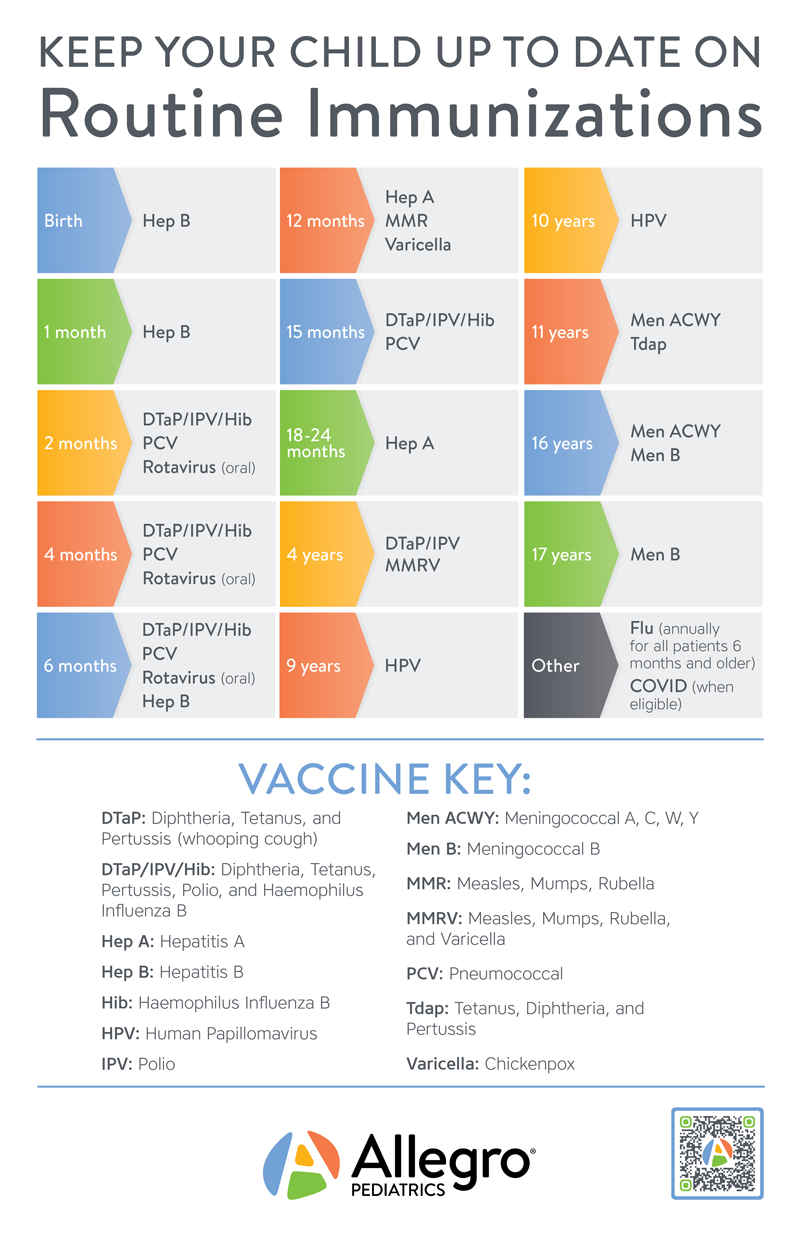
What childhood diseases are immunized?
– Chickenpox. Diphtheria. Flu.
– Hepatitis A. Hepatitis B. Hib.
– HPV. Measles. Meningococcal.
– Mumps. Polio. Pneumococcal.
– Rotavirus. RSV. Rubella.
– Tetanus. Whooping Cough.


