Immunization is a crucial aspect of public health that helps protect individuals and communities from serious diseases. Key facts about immunization include its effectiveness in preventing diseases such as measles, polio, and influenza. Immunization works by stimulating the body’s immune system to produce antibodies, providing immunity against specific diseases.
Immunization is safe and has been extensively tested to ensure its effectiveness and minimal side effects. The benefits of immunization far outweigh the risks, as it can prevent suffering, disability, and even death from vaccine-preventable diseases.
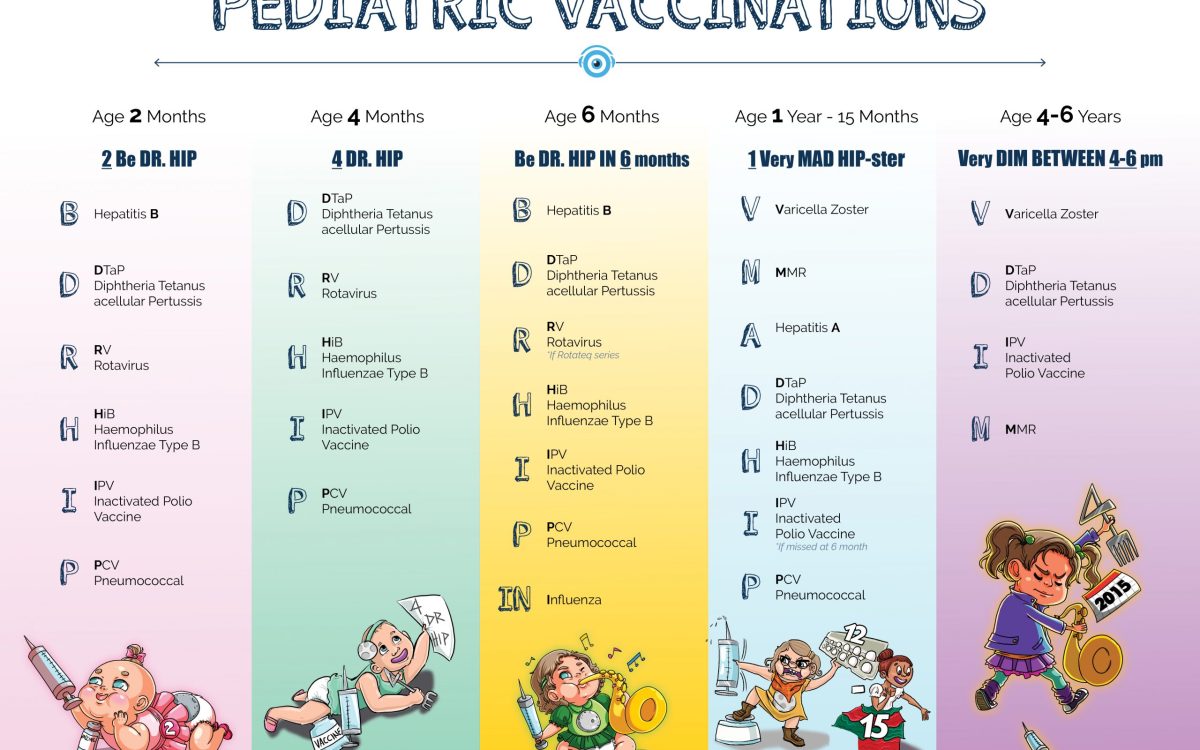
It is important for individuals to follow the recommended immunization schedule provided by healthcare professionals. This schedule ensures that individuals receive the necessary vaccines at the right time to build immunity and protect against diseases.
Immunization also plays a vital role in creating herd immunity, which occurs when a large percentage of the population is immune to a disease, reducing the spread of infectious diseases and protecting those who are unable to be vaccinated, such as infants and individuals with compromised immune systems.
In conclusion, immunization is a safe and effective way to prevent serious diseases and protect public health. By staying up to date with vaccinations, individuals can contribute to a healthier and more resilient community.
What makes vaccines so important?
Vaccines help your body create protective antibodies—proteins that help it fight off infections. By getting vaccinated, you can protect yourself and also avoid spreading preventable diseases to other people in your community.
What is the most effective vaccine of all time?
Smallpox vaccination with vaccinia virus is the most famous example of a highly effective vaccine and at the time when people were faced with smallpox outbreaks, this vaccine was associated with each of these characteristics that led to the implementation of a successful vaccine.
Which vaccines last a lifetime?
Measles is an example of a stable virus that is unlikely to replicate, so scientists could predict that immunity would last a long time, which it does.” Smallpox and polio, highly contagious viruses that were almost eradicated through vaccination, are also stable with low mutation rates.