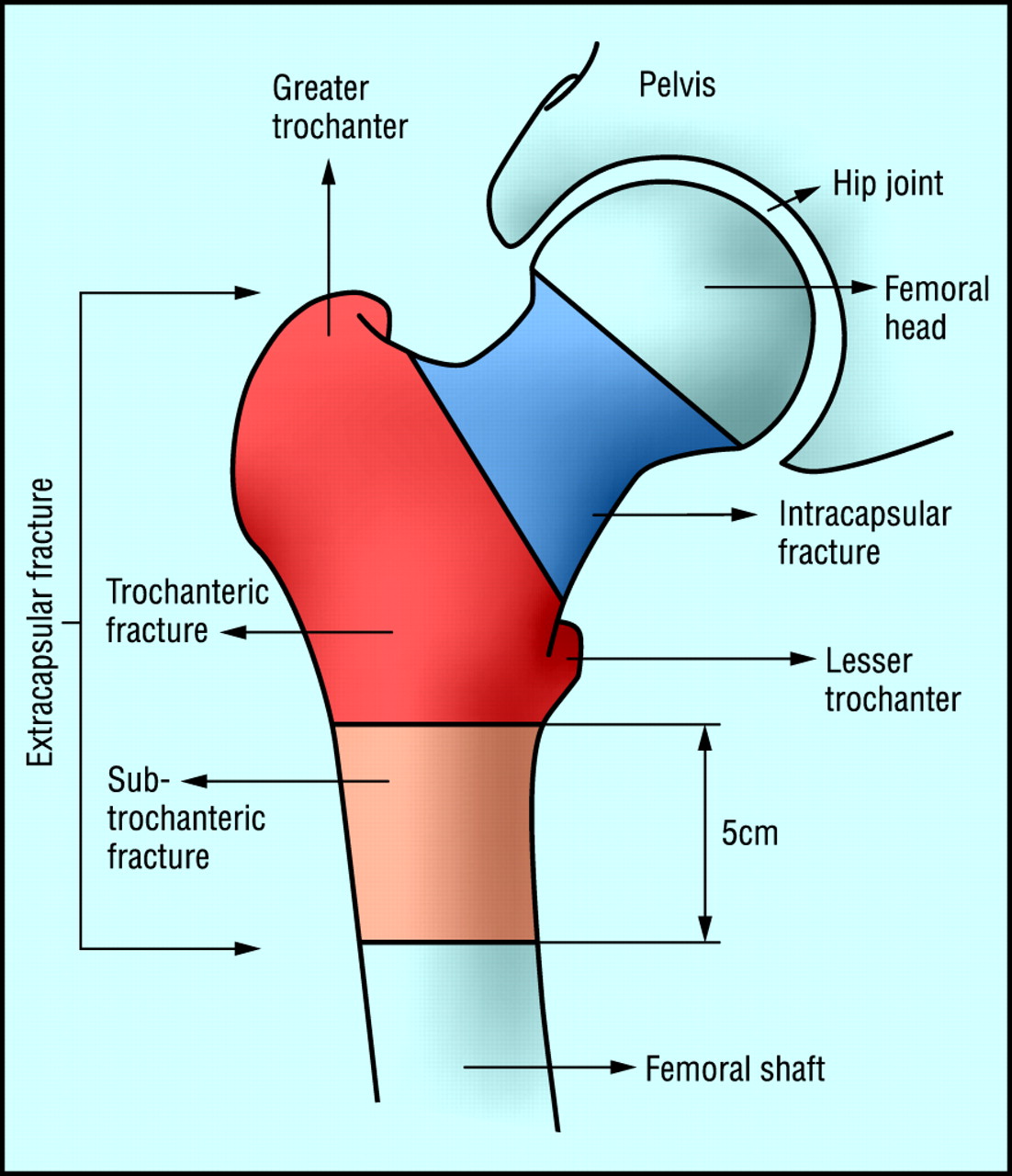
A subcapital femur fracture refers to a fracture that occurs just below the head of the femur, where it connects to the hip joint. This type of fracture can have a range of complications, which may significantly impact the patient’s overall health and mobility.
One major complication of a subcapital femur fracture is the potential for avascular necrosis. This occurs when the blood supply to the bone is compromised due to the fracture, leading to cell death and the bone’s inability to repair itself. Avascular necrosis can result in long-term pain, limited mobility, and even the need for joint replacement surgery.
Another complication is the risk of nonunion or delayed union. Nonunion refers to the failure of the fractured bone ends to heal together, while delayed union indicates a prolonged healing time. These complications can require additional surgery or prolonged immobilization, leading to extended recovery periods and potential complications such as infection or blood clots.
Additionally, subcapital femur fractures can lead to the development of deep vein thrombosis (DVT). DVT occurs when blood clots form in the veins deep within the body, particularly in the legs. If these clots break loose and travel to the lungs, they can cause a potentially life-threatening condition known as a pulmonary embolism.
Patients with subcapital femur fractures are also at risk of complications related to immobility. Prolonged bed rest or limited mobility can lead to muscle weakness, joint stiffness, pressure sores, and respiratory complications such as pneumonia.
Furthermore, there is a higher risk of falls and subsequent fractures in the elderly population, who are more prone to subcapital femur fractures. This can further complicate the recovery process and increase the overall morbidity and mortality rates.
In conclusion, subcapital femur fractures can be associated with various complications that can significantly affect a patient’s physical function, quality of life, and overall recovery. Proper management, including surgical intervention, physical therapy, and preventive measures, is crucial in minimizing these complications and optimizing outcomes for patients with this type of fracture.
What serious complication can result from a femoral neck fracture?
– Avascular necrosis increased risk factor with increased initial displacement and failure to obtain an anatomical reduction[13]
– Nonunion.
– Dislocation increased with total hip arthroplasty surgery.
What is life expectancy after hip fracture?
According to a 2019 study in Acta Orthopaedica, the one-year mortality after a hip fracture is 21% for those whose fracture is surgically repaired. If the fracture is not repaired, the one-year mortality is about 70%.
Is a broken hip life changing?
A hip fracture can be life-changing. Many older people don’t regain full mobility or independence after a hip fracture. Some people need a cane or walker to get around. Other people may need full-time care.
What are 3 major post op complications for a femur fracture?
– Infection.
– Bleeding.
– Nerve damage.
– Blood clots.
– Fat embolism.
– Healing of the fractured bone in an abnormal alignment.
– Irritation of the overlying tissue from the hardware.
– Complications from anesthesia.
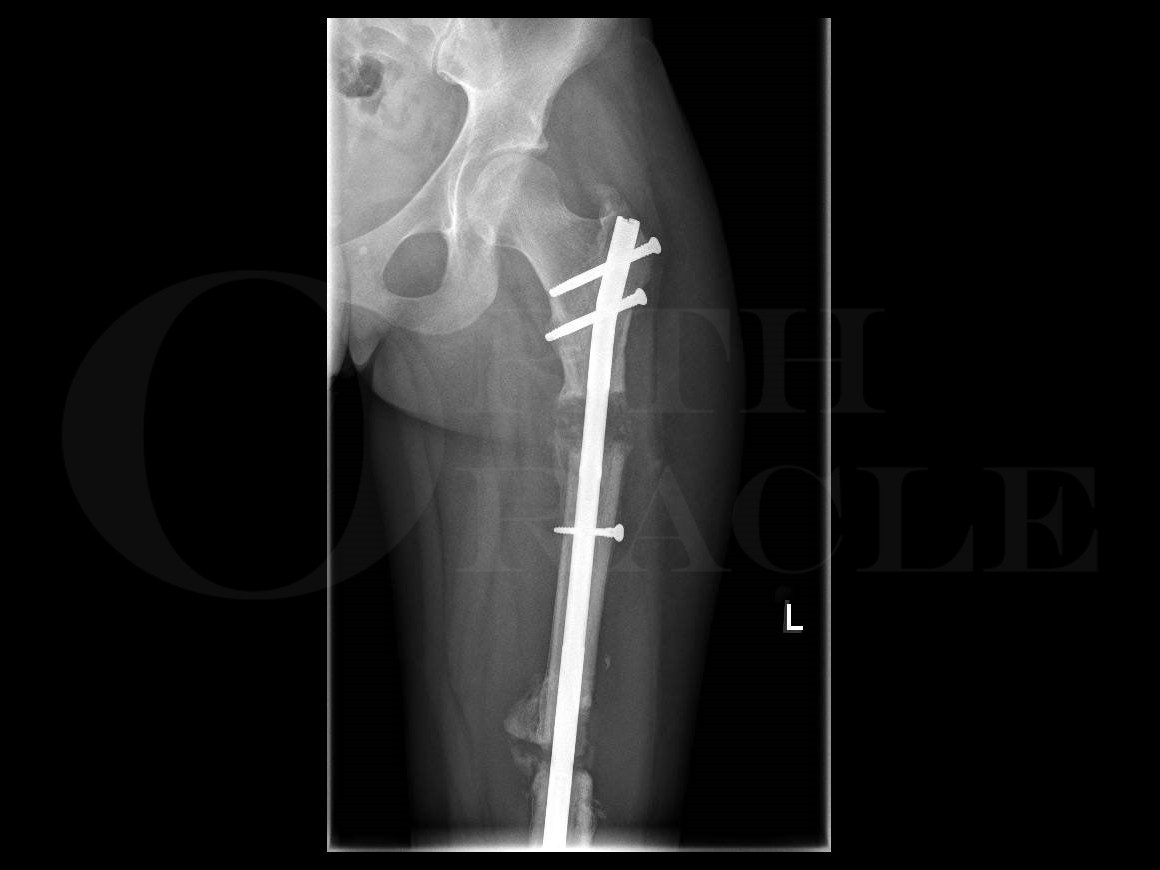
What is the ICD-10 code for S72 14?
2024 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code S72. 14: Intertrochanteric fracture of femur.
What is the ICD-10 code for unspecified injury of right hip?
2024 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code S79. 911A: Unspecified injury of right hip, initial encounter.
What is the ICD-10 code for hip strain unspecified?
2024 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code S76. 019A: Strain of muscle, fascia and tendon of unspecified hip, initial encounter.
What is the ICD-10 code for S72 143D?
Displaced intertrochantericintertrochantericThe intertrochanteric line is a line upon the anterior aspect of the proximal end of the femur, extending between the lesser trochanter and the greater trochanter. It is a rough, variable ridge.https://en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Intertrochanteric_lineIntertrochanteric line – Wikipedia fracture of unspecified femur, subsequent encounter for closed fracture with routine healing. S72. 143D is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is a closed intertrochanteric fracture of the right femur?
Intertrochanteric fractures are defined as extracapsular fracturesextracapsular fracturesAn extracapsular fracture is a bone fracture near a joint but still located outside the joint capsule. Examples of extracapsular fractures are intertrochanteric and subtrochanteric hip fractures.https://en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Extracapsular_fractureExtracapsular fracture – Wikipedia of the proximal femur that occur between the greater and lesser trochanterlesser trochanterIn human anatomy, the lesser trochanter is a conical, posteromedial, bony projection from the shaft of the femur. it serves as the principal insertion site of the iliopsoas muscle. Lesser trochanter. Left hip-joint, opened by removing the floor of the acetabulum from within the pelvis.https://en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Lesser_trochanterLesser trochanter – Wikipedia. The intertrochanteric aspect of the femur is located between the greater and lesser trochanters and is composed of dense trabecular bone.Aug 8, 2023