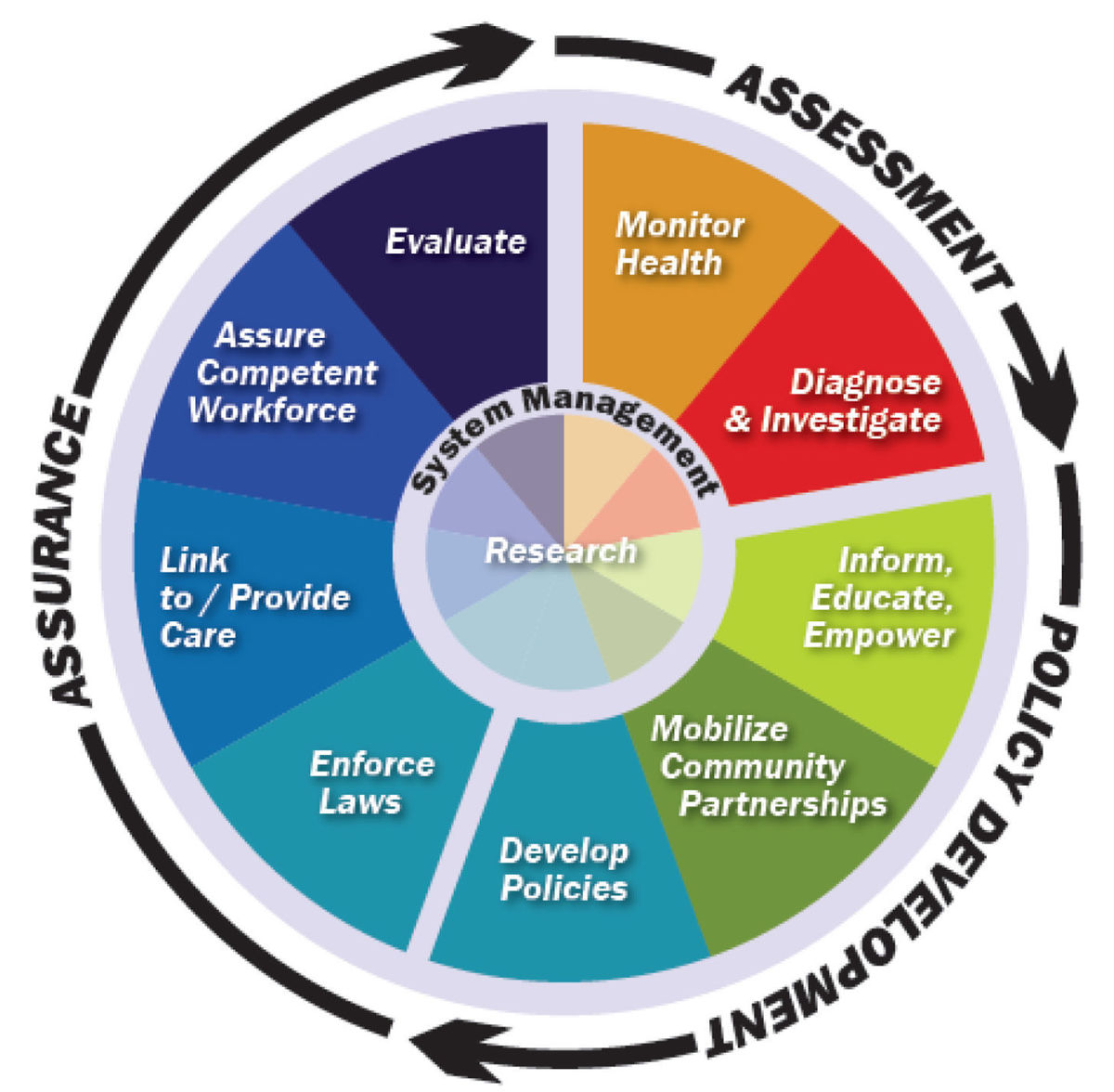
Public health ethics are principles that guide the actions and decisions of public health practitioners in promoting and protecting the well-being of populations. The 7 ethics of public health include:
1. Respect for persons: This principle emphasizes the importance of treating individuals with dignity and ensuring their autonomy in decision-making related to their health.
2. Beneficence: Public health practitioners have a responsibility to promote the well-being of populations and prevent harm by maximizing the benefits and minimizing risks.
3. Non-maleficence: The principle of non-maleficence requires public health practitioners to avoid causing harm to individuals and populations in their efforts to promote health.
4. Justice: Public health actions should be fair and equitable, taking into consideration the needs and rights of all individuals and populations.
5. Proportionality: Interventions and policies implemented in public health should be proportionate to the risks and benefits involved, ensuring that the response is neither excessive nor insufficient.
6. Transparency: Public health practitioners should be transparent in their decision-making process, providing clear and accurate information to the public.
7. Accountability: Public health practitioners should be accountable for their actions and decisions, ensuring that they are responsible for the consequences of their work.
Overall, these ethics provide a framework for ethical decision-making in public health, guiding practitioners in their efforts to promote and protect the health of populations while respecting individual rights and values.
What are the 7 principles of ethics in research?
– Social and clinical value.
– Scientific validity.
– Fair subject selection.
– Favorable risk-benefit ratio.
– Independent review.
– Informed consent.
– Respect for potential and enrolled subjects.
What are the 3 P’s of public health?
The 3Ps of public health (prevention, promotion, and protection) are essential in the context of food safety as well. #prevention refers to taking measures to prevent foodborne illnesses from occurring in the first place.
What are the principles of public health?
Public health principles are fundamental guidelines and practices aimed at improving the well-being of communities and preventing health problems. In simple terms, these principles include things like promoting good hygiene, ensuring clean water, preventing diseases, and encouraging healthy lifestyles.
How do you explain public health?
Public health is the science of protecting and improving the health of people and their communities. This work is achieved by promoting healthy lifestyles, researching disease and injury prevention, and detecting, preventing and responding to infectious diseases.