Scoliosis is a condition characterized by an abnormal curvature of the spine. There are three main types of scoliosis: congenital scoliosis, idiopathic scoliosis, and neuromuscular scoliosis.
Congenital scoliosis is present at birth and is caused by abnormal spinal development in the womb. This type of scoliosis is relatively rare and can be the result of genetic factors or environmental influences during pregnancy. The severity of congenital scoliosis can vary greatly and often requires early intervention to prevent further progression of the spinal curvature.
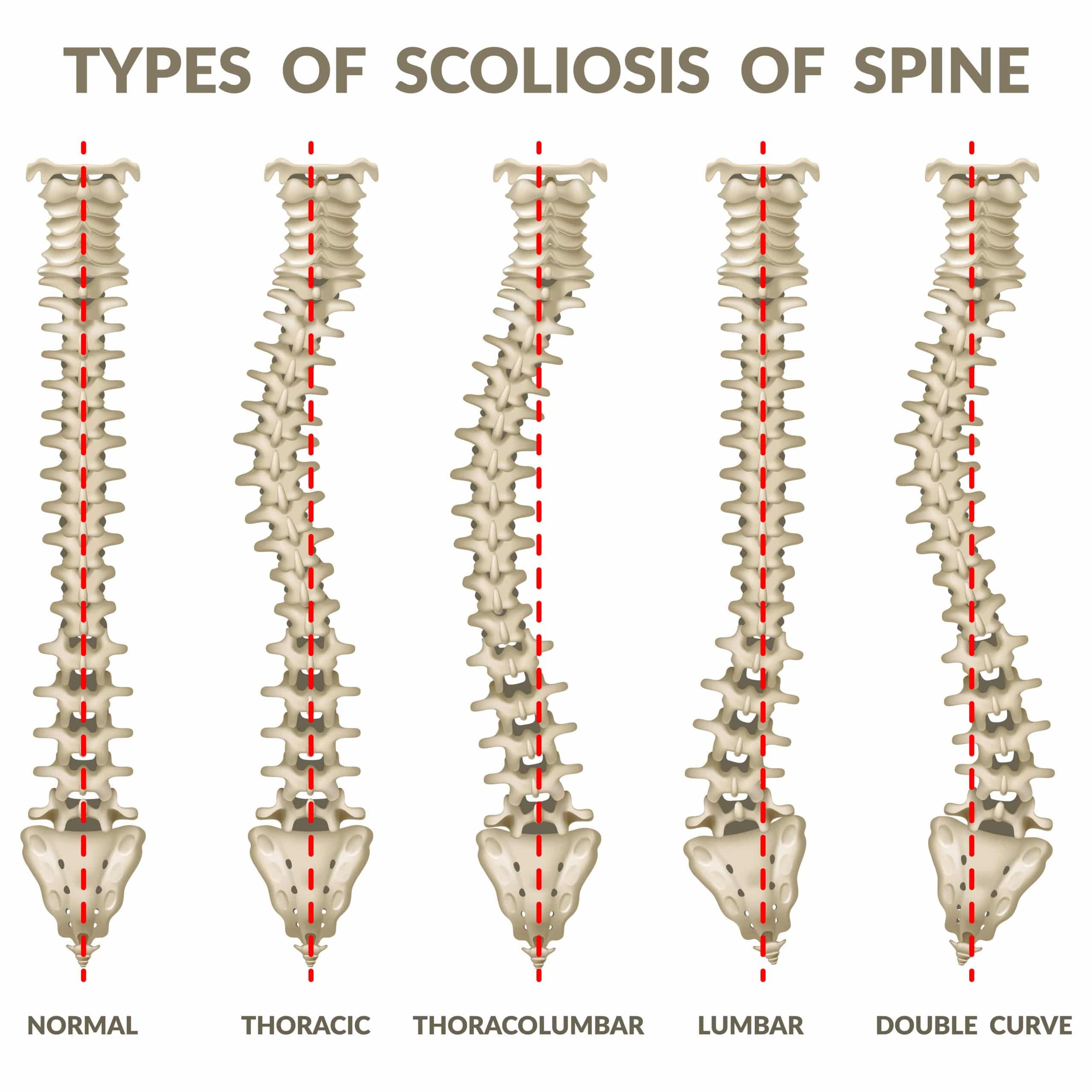
Idiopathic scoliosis is the most common type and accounts for approximately 80% of all scoliosis cases. It typically develops during adolescence and has no known cause. Idiopathic scoliosis can be classified into three age groups: infantile, juvenile, and adolescent. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial in managing the condition and preventing potential complications.
Neuromuscular scoliosis occurs as a secondary symptom of an underlying neurological or muscular disorder. Conditions such as cerebral palsy, muscular dystrophy, and spinal cord injuries can lead to muscle imbalances and abnormal spinal growth, resulting in scoliosis. The severity of neuromuscular scoliosis can vary depending on the underlying disorder and may require specialized treatment to address both the spinal curvature and primary condition.
Diagnosing scoliosis typically involves a physical examination, medical history review, and imaging tests such as X-rays or MRI scans. Treatment options for scoliosis vary depending on the severity and progression of the condition. Mild cases may only require observation and regular monitoring, while more severe cases may necessitate bracing or surgery to correct the spinal curvature.
In conclusion, scoliosis is a complex condition with three main types: congenital, idiopathic, and neuromuscular. Each type requires specific diagnostic and treatment approaches to effectively manage the condition and improve the patient’s quality of life. Early detection and intervention play a crucial role in preventing further progression of scoliosis and minimizing potential complications.
What medical conditions cause scoliosis?
Scoliosis is a sideways curvature of the spine that most often is diagnosed in adolescents. While scoliosis can occur in people with conditions such as cerebral palsy and muscular dystrophy, the cause of most childhood scoliosis is not known. Most cases of scoliosis are mild, but some curves worsen as children grow.
What is the difference between scoliosis and levoscoliosis?
People who develop scoliosis after puberty have adult scoliosis. Levoscoliosis is the name for scoliosis that makes your spine curve to the left. Dextroscoliosis is scoliosis that makes your spine curve to the right. Most people who have mild levoscoliosis or mild dextroscoliosis don’t need treatment.
What position should I sleep in for levoscoliosis?
Levoscoliosis is considered atypical because most scoliotic curves bend to the right, away from the heart, but levoscoliosis curves bends to the left, towards the heart. The best sleeping position for someone with levoscoliosis is sleeping flat on the back.
What diseases cause levoscoliosis?
It is often associated with vertebral anomalies or malformations. Neuromuscular: Levoscoliosis can develop as a secondary condition to certain neuromuscular disorders, such as cerebral palsy, muscular dystrophy, or spinal cord injuries.