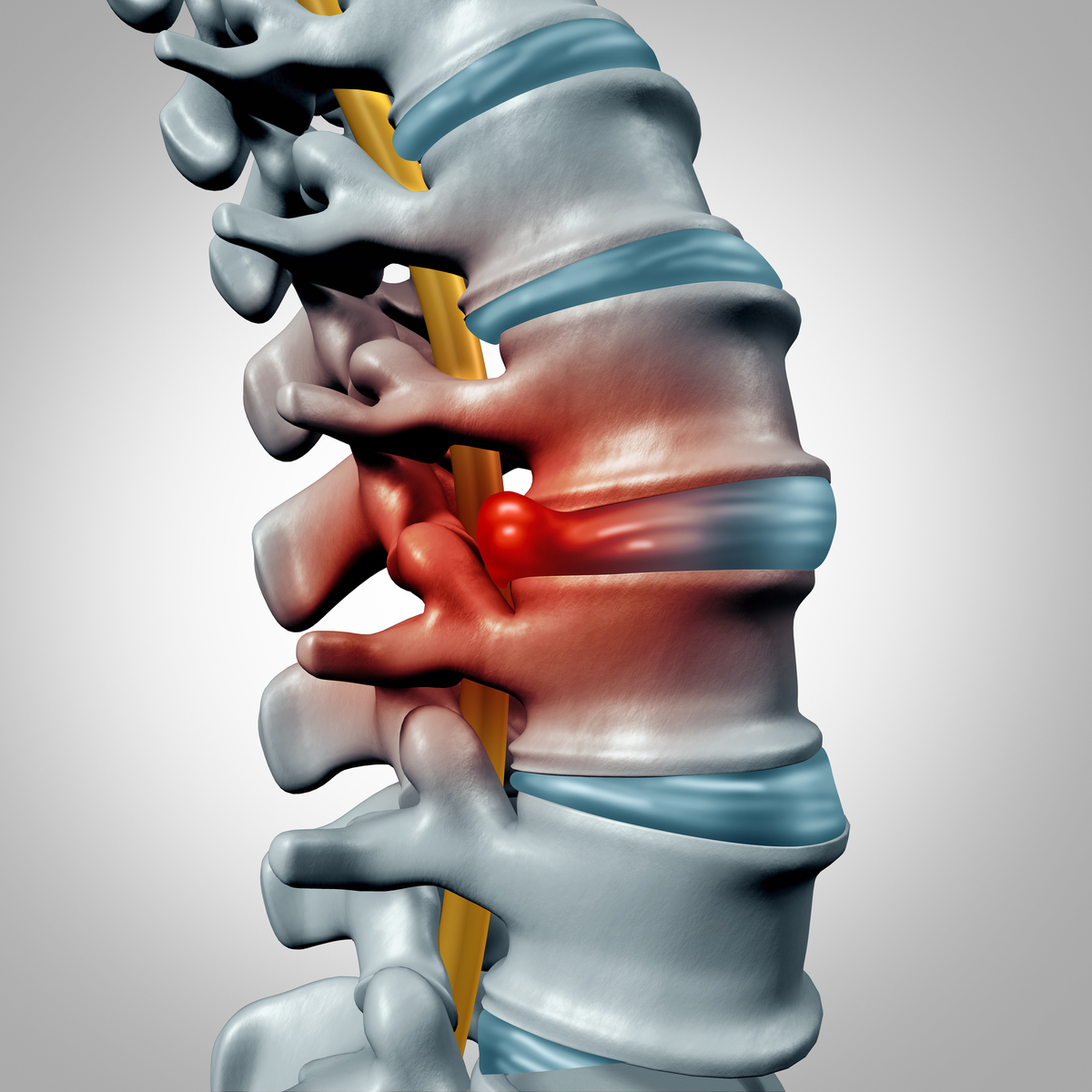
A bulging disc, also known as a herniated disc, is a common spinal condition that can cause significant discomfort and pain. It occurs when the soft inner portion of a disc protrudes through the outer layer and irritates nearby nerves. Understanding what aggravates a bulging disc is essential for managing and preventing further damage.
Several factors can contribute to the aggravation of a bulging disc. One of the primary causes is repetitive or improper movements, such as lifting heavy objects using incorrect technique or twisting while carrying a heavy load. These actions put excessive strain on the spine, leading to disc displacement and potential bulging.
Additionally, poor posture plays a significant role in irritating a bulging disc. Sitting or standing for prolonged periods with improper spinal alignment can increase pressure on the discs, leading to their bulging. It is important to maintain good posture and regularly change positions while sitting or standing to reduce the risk of aggravating the condition.
Lifestyle choices also play a role in aggravating a bulging disc. Being overweight or obese can put extra pressure on the spine, increasing the likelihood of disc herniation. Smoking, on the other hand, can deteriorate the structure and health of discs, making them more prone to bulging.
Furthermore, certain activities can aggravate a bulging disc. High-impact sports, such as football or gymnastics, can exert excessive pressure on the spine, increasing the risk of disc herniation. Similarly, jobs that involve heavy lifting, repetitive motions, or prolonged sitting or standing can contribute to the aggravation of a bulging disc.
To prevent the aggravation of a bulging disc, it is crucial to adopt healthy habits. Maintaining a proper posture, regularly exercising to strengthen the core and back muscles, and maintaining a healthy weight are key preventive measures. Additionally, practicing proper lifting techniques, taking regular breaks during prolonged activities, and avoiding activities that involve repetitive or high-impact movements can also help reduce the risk of aggravating a bulging disc.
In conclusion, several factors can aggravate a bulging disc, including repetitive or improper movements, poor posture, lifestyle choices, and certain activities. Understanding and addressing these factors through lifestyle modifications and appropriate preventive measures can help manage the condition and prevent further damage.
What should you not do with bulging discs?
– Avoid lifting heavy objects or bending at the waist at any time.
– Avoid wearing high-heeled shoes. …
– Focus on workouts that strengthen your abdomen and core muscles. …
– Avoid smoking as it weakens your disks.
– Practice good posture while sitting, standing, and walking.
Is walking good for a bulging disc?
Generally speaking—as long as they’re performed correctly—core and back exercises are beneficial for bulging discs, as are activities like walking, elliptical exercise, swimming, and riding a stationary or regular bike.
What should you not do with a bulging disc?
– Avoid lifting heavy objects or bending at the waist at any time.
– Avoid wearing high-heeled shoes. …
– Focus on workouts that strengthen your abdomen and core muscles. …
– Avoid smoking as it weakens your disks.
– Practice good posture while sitting, standing, and walking.
What makes a bulging disc worse?
If the repeated forward bending stress continues, or the improper body mechanics continue, very often the inner disc material will continue to push backwards, causing the disc bulgedisc bulgeA disc protrusion is a medical condition that can occur in some vertebrates, including humans, in which the outermost layers of the anulus fibrosus of the intervertebral discs of the spine are intact but bulge when one or more of the discs are under pressure.https://en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Disc_protrusionDisc protrusion – Wikipedia to worsen, to herniate, progressing into the spinal canal and towards the spinal cord.

What is the best Medicare package?
– Best Overall: AARP/UnitedHealthcare.
– Lowest Cost: Cigna.
– Great for Nationwide Coverage: Humana.
– Best for Additional Drug Coverage in the Gap: Aetna.
– Best for Patient Quality and Customer Satisfaction: Kaiser Permanente.
How do I know which Medicare plan is best for me?
– Overall coverage cost.
– Additional benefits, like hearing, vision and travel coverage.
– Medicare Part D coverage for medicines.
– Staying with your current doctor or switching providers.
– Possible perks like gym memberships and additional services.
What is the difference between a doctor and a physician?
A physician is someone who has earned a doctoral degree (PHD) in medicine. These individuals are specialized in one area of medicine, such as cardiology or pediatrics, and completed a medical residency in that field. A doctor refers to anyone having earned a PHD in any number of fields.Nov 8, 2021
What is the difference between a doctor and a primary care physician?
People sometimes use “primary care physician” and “general practitioner” interchangeably. These two terms are not synonymous, however. A primary care physician is the doctor you see for regular check-ups. Your primary care physician may be an internistinternistA therapist is a person who offers any kinds of therapy. Therapists are trained professionals in the field of any types of services like psychologists, social workers, counsellors, etc. They are helpful in counseling individuals for various mental and physical issues.https://en.wikipedia.org › wiki › TherapistTherapist – Wikipedia, a family practitioner, or another type of doctor.