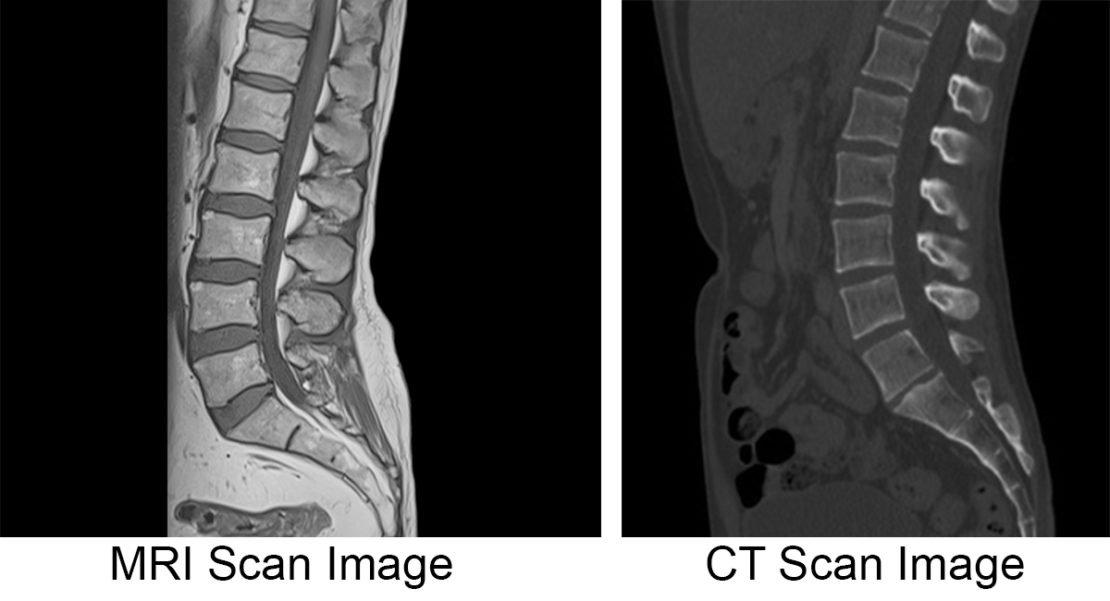
When it comes to diagnosing disc herniation, the decision between getting an MRI or a CT scan can be a bit challenging. Both imaging tests provide detailed pictures of the spine and can help in identifying disc herniation, but there are some key differences that should be considered.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is often preferred in cases of suspected disc herniation. It uses a strong magnetic field and radio waves to produce images, allowing for a comprehensive view of the soft tissues, including the intervertebral discs. This makes it effective at detecting herniated discs accurately, visualizing the extent of the injury, and assessing potential nerve compression. In addition, an MRI can also reveal other spinal conditions that may contribute to the symptoms.
On the other hand, a Computed Tomography (CT) scan uses X-ray technology to create detailed cross-sectional images of the body. While it is less preferred for disc herniation diagnosis due to the limited soft tissue visualization, it can still detect herniated discs and provide valuable information about the bones, such as fractures or bone spurs. CT scans are particularly useful when there is a concern for spinal instability or when a patient cannot undergo an MRI due to metal implants or claustrophobia.
Ultimately, the choice between an MRI and a CT scan should be based on the specific circumstances of each individual case. Factors like the nature and severity of symptoms, the presence of metal implants, and the patient’s personal preferences should be taken into account. Consulting with a healthcare professional, preferably a spine specialist, can help in making an informed decision and selecting the most appropriate imaging test for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment planning.
What scan is done for a herniated disc?
MRI scan is the best non-invasive test available to find herniated and bulging discs and annular tears. Because the spatial resolution of spinal anatomy can be defined to 0.5mm with an MRI scan, doctors can identify with over 95% accuracy the herniated discs in the spine.

Does a herniated disc show up on CT scan?
Because of their availability, CT scans are still used for diagnosis of disc herniations. MRI may, however, be superior in its specificity. In taking into account the subjective complaint and orthopedic and neurological findings, a disk herniation can often be diagnosed without a CT scan or MRI.
What is the best scan for a herniated disc?
MRI scan is the best non-invasive test available to find herniated and bulging discs and annular tears. Because the spatial resolution of spinal anatomy can be defined to 0.5mm with an MRI scan, doctors can identify with over 95% accuracy the herniated discs in the spine.
Is MRI better than CT for herniated disc?
Because of their availability, CT scans are still used for diagnosis of disc herniations. MRI may, however, be superior in its specificity. In taking into account the subjective complaint and orthopedic and neurological findings, a disk herniation can often be diagnosed without a CT scan or MRI.