An otolaryngologist, commonly referred to as an ENT specialist, is a medical doctor who specializes in treating conditions related to the ears, nose, and throat. These physicians are trained to diagnose and manage a wide range of disorders, including hearing loss, sinus infections, tonsillitis, and vocal cord issues. Otolaryngologists undergo extensive training in both medical and surgical techniques to effectively address the diverse needs of their patients.
The term “ENT” stands for Ear, Nose, and Throat, which is a more colloquial way of referring to this medical specialty. The use of “ENT” is often seen in the context of common language or marketing, while “otolaryngologist” is the official title used in medical settings. Both terms, however, refer to the same type of medical professional who has expertise in treating disorders of the head and neck.
In conclusion, an otolaryngologist and an ENT specialist are essentially the same thing. They are medical doctors who specialize in diagnosing and treating conditions related to the ears, nose, and throat. Whether they are referred to as an otolaryngologist or an ENT, these specialists play a crucial role in helping patients maintain optimal health and function in these important areas of the body.
What are the symptoms of ear, nose, and throat infection?
– Ear infections can cause earache, wax or discharge, hearing loss and balance problems.
– Nose infections are likely to cause a runny or blocked nose and sneezing. …
– Throat infections can cause a sore or scratchy throat and pain or difficulty swallowing.
What is an ear nose and throat specialist concerned with?
Whether you call them ear, nose, and throat doctors; ENTs; or otolaryngologists, these doctors specialize in those parts of your body, as well as the head and neck. If you have issues with your sinuses, allergies, sleep apnea, throat, lumps, or more, this is who to call.
What is a common condition in ENT?
Most Common ENT Problems That We See: Dysphagia (Difficulty Swallowing) Ear Infection (Otitis Media) Gastric Reflux. Hearing Aids.

Which condition would an otolaryngologist treat?
What do otolaryngologists treat? Ear: Otolaryngologists are trained in the medical and surgical treatment of hearing loss, ear infections, balance disorders, ear noise (tinnitus), nerve pain, and facial and cranial nerve disorders. They also manage congenital (birth) disorders of the outer and inner ear.
How long does a TB test last?
How long is the test valid? A negative test is valid for 2 years and must not expire at any time during the semester. If you have submitted a copy of a negative test to us previously and do not know if it has expired, contact us to find out.
Can I book TB test online?
Booking a “Quantiferon-TB Gold (TB Test) near me” or a “TB test near me” is easy using LabFinder. Just choose your location and enter your insurance information to find the closest Quantiferon-TB Gold (TB Test) near you.
How many years is a TB test good for?
If you have a negative skin test, you need a repeat test at least once every four years. If you have a documented positive skin test, you must have an initial chest X-ray. After that, you still need to be screened every four years.
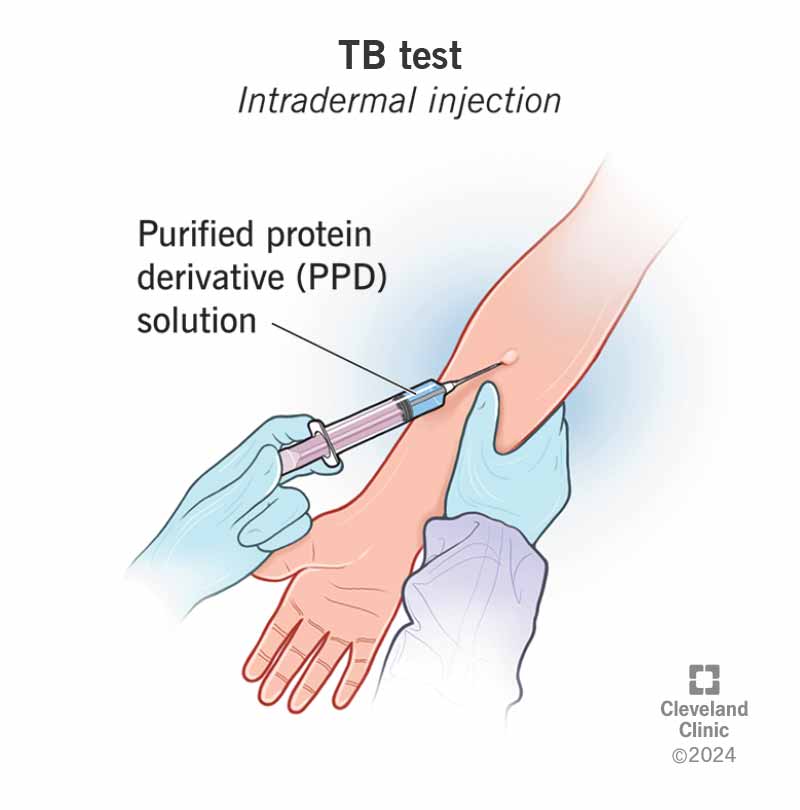
What is in the tuberculosis test?
The TB skin test is performed by injecting a small amount of fluid (called tuberculintuberculinTuberculin, also known as purified protein derivative, is a combination of proteins that are used in the diagnosis of tuberculosis. This use is referred to as the tuberculin skin test and is recommended only for those at high risk.https://en.wikipedia.org › wiki › TuberculinTuberculin – Wikipedia) into the skin on the lower part of the arm. A person given the tuberculin skin test must return within 48 to 72 hours to have a trained health care worker look for a reaction on the arm.
How long is a TB test good for teachers?
Repeat risk assessments should occur every four years (unless otherwise required) to identify any additional risk factors, and TB testing based on the results of the TB risk assessment. Re- testing should only be done in persons who previously tested negative, and have new risk factors since the last assessment.May 6, 2020