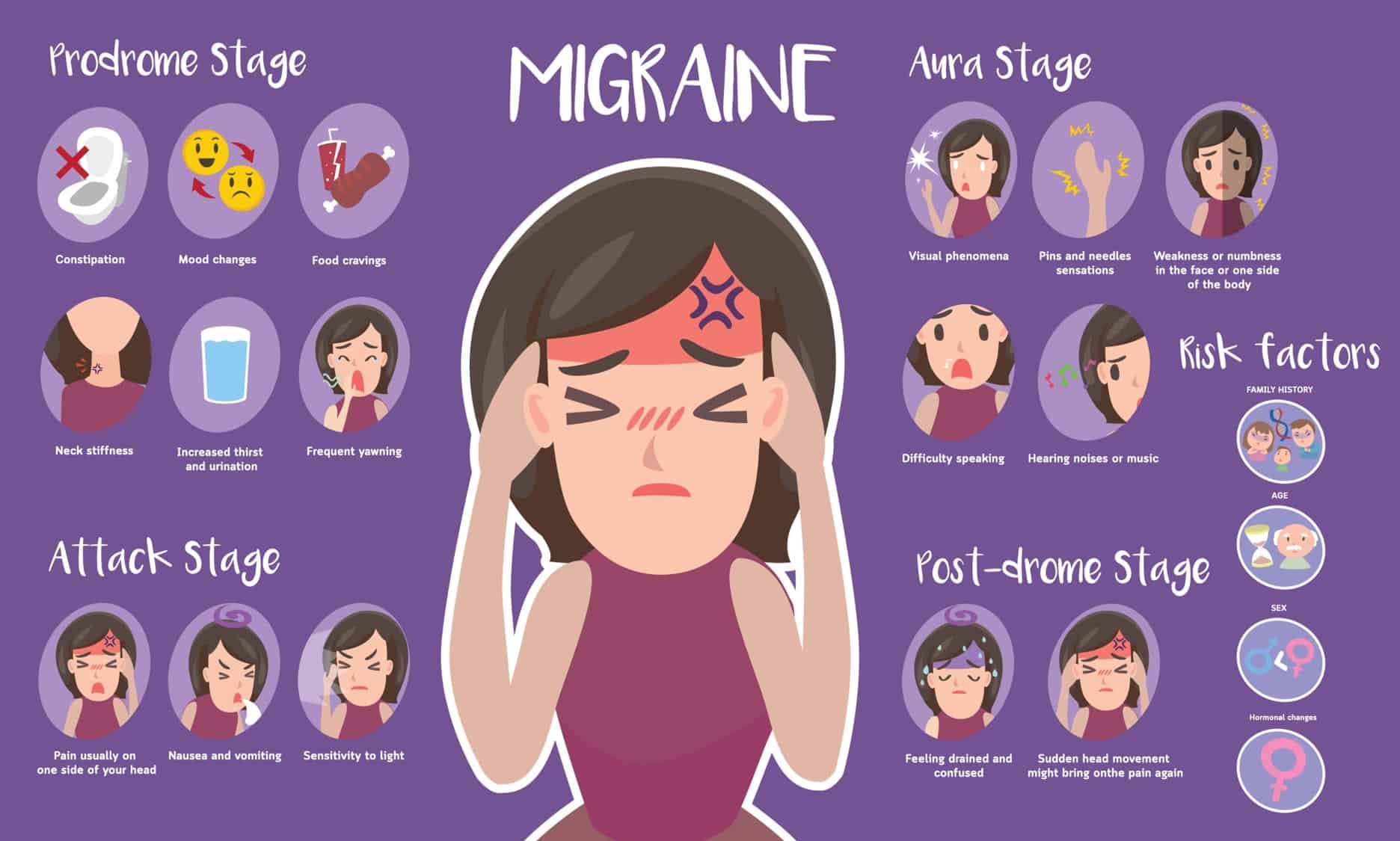
Migraine headaches and stress headaches are two common types of headaches that can have similar symptoms, making it challenging to differentiate between them. However, there are some key factors that can help identify whether a headache is due to a migraine or stress.
Migraine headaches are often accompanied by pulsating or throbbing pain on one side of the head. The pain can range from moderate to severe and may worsen with physical activity. Additionally, individuals with migraines often experience specific symptoms known as aura, which can include visual disturbances such as seeing flashing lights or zigzag patterns.
On the other hand, stress headaches typically present as a dull, constant ache on both sides of the head. This type of headache is often described as a tight band or pressure around the forehead or back of the head. Stress headaches are commonly triggered by stressful situations, anxiety, or tension, and can be milder in intensity compared to migraines.
Another important distinction is the presence of additional symptoms. Migraines are frequently associated with nausea, vomiting, and increased sensitivity to light and sound. People experiencing a migraine attack may also find relief by resting in a dark, quiet room. In contrast, stress headaches rarely cause such symptoms and can typically be relieved with over-the-counter pain medications.
It is worth mentioning that some individuals may experience both migraine and stress headaches simultaneously, making it even more challenging to differentiate between the two. In these cases, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
In conclusion, distinguishing between migraine and stress headaches relies on various factors, including the location and nature of the pain, accompanying symptoms, triggers, and response to treatment. Despite their similarities, understanding these differences can help individuals manage their headaches more effectively and seek the most appropriate care.
What can be mistaken for a migraine?
– Anxiety Disorder.
– Tension Headaches.
– Stroke.
– Meniere’s Disease.
– Epilepsy.
– Post-Concussion Syndrome.
– Medication Overuse Headaches.
– Sinus Infections.
What does a migraine headache feel like?
A migraine feels like a throbbing or pounding pain that tends to be worse on one side of the head. You may also have symptoms like nausea, vomiting, numbness, chills, and sensitivity to light or sound. A migraine can typically last anywhere from 6 hours to 2 days.
.png?1657263685)
What is migraine misdiagnosed as?
Sphenoid sinusitis, specifically, can often be misdiagnosed as migraine, because it features periorbital pain, nausea, and vomiting but rarely has nasal discharge or postnasal drip. Among myriad other symptoms, Lyme disease can often feature headache, with migraine semiology appearing most frequently.
What is the difference between a headache and migraine?
People who have tension headaches often complain of a band of pain across their forehead, or pressure on either side of the head. The pain is tiring, but not as severe as migraine. Migraine, on the other hand, usually hurts worse on one side of the head.

Is it bad to ice for too long after surgery?
We may prevent the body’s natural release of IGF-1 and, therefore, delay the start of the healing and recovery process. A prolonged period of cold on the skin will lead to a reduction of the blood flow, resulting in tissue death or even permanent nerve damage[22].

How long is too long to hold ice?
Do not apply ice for longer than 15 to 20 minutes at a time, and do not fall asleep with the ice on your skin. Commercial cold packs are too heavy and bulky for use on or around the eye.
What happens if you ice for more than 20 minutes?
Greater than 20 minutes of icing can cause reactive vasodilation, or widening, of the vessels as the body tries to make sure the tissues get the blood supply they need. Studies have also shown 30 to 40 minutes in between icing sessions are needed to counter this reaction.
How much ice is too much after surgery?
You should continue a regular and consistent icing program as long you experience symptoms. Remember, ice is “your friend” after any orthopaedic injury or surgery. In order to maximize the benefit of the ice treatments, you must ice the affected area at least four times a day, 15-20 minutes at a time.

Can you ice too much after knee surgery?
recommended using cryotherapy for no more than 30 minutes at a time to reduce the risk of complications [20].


