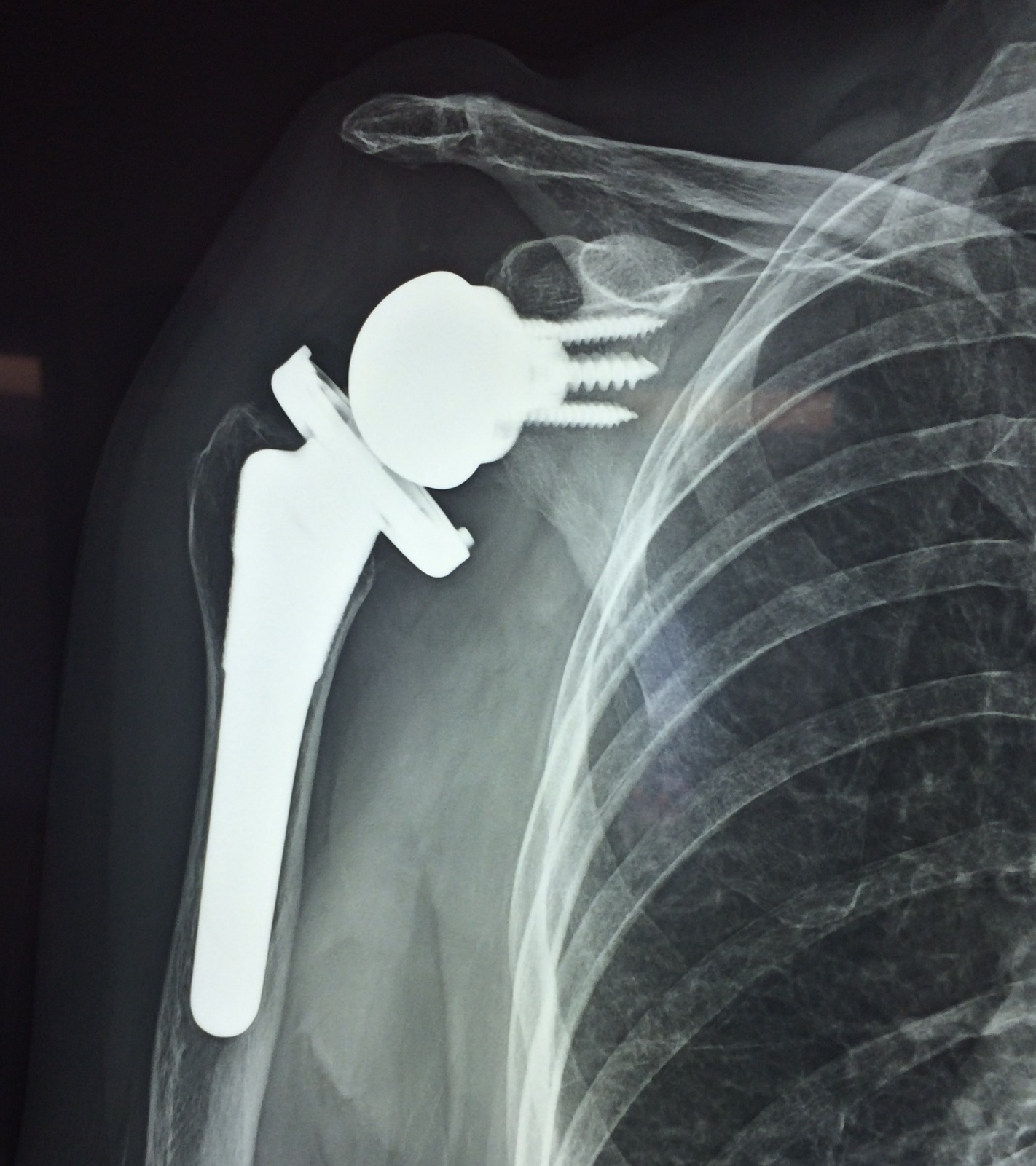
Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is a condition that occurs when the tendon that supports the arch of the foot becomes inflamed or torn, leading to pain, swelling, and difficulty walking. Treatment for this condition typically involves a combination of non-surgical and surgical interventions.
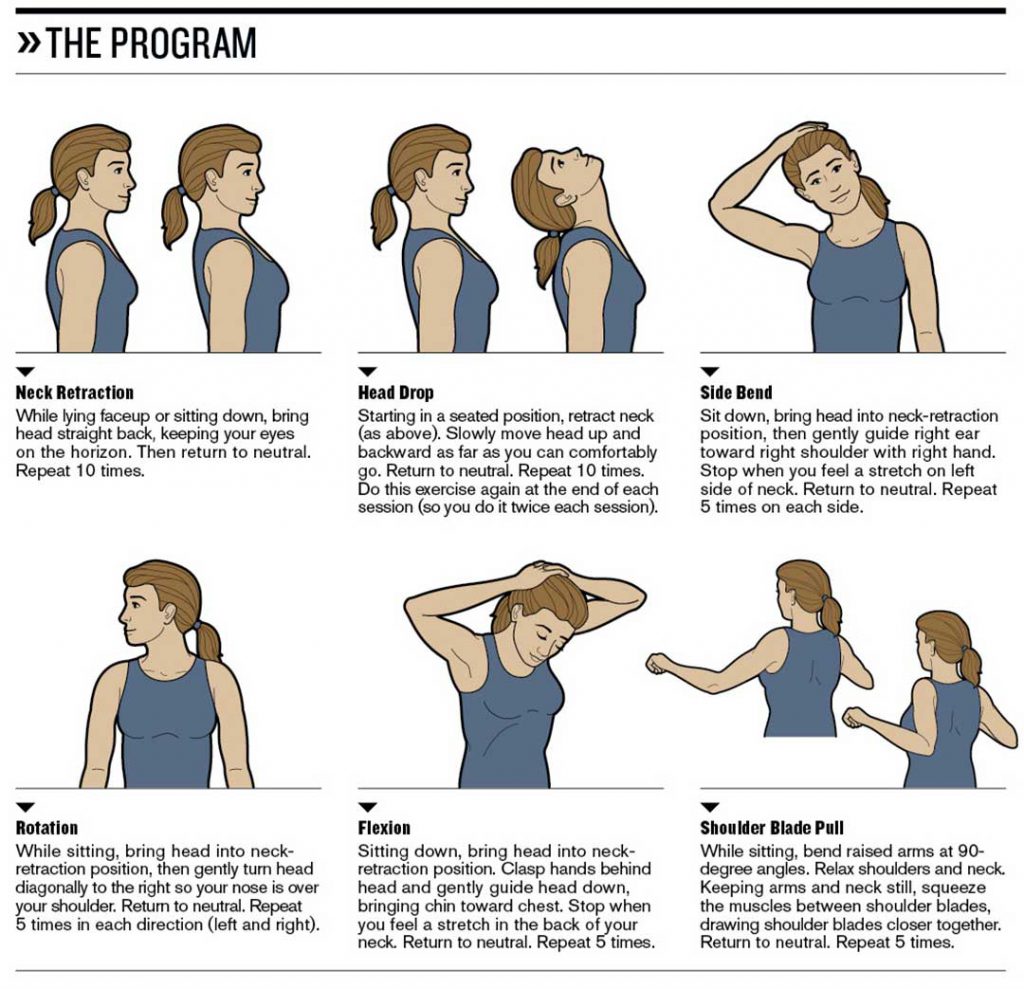
Non-surgical treatments may include rest, ice, compression, and elevation to reduce pain and swelling. Physical therapy exercises can help strengthen the muscles around the tendon and improve flexibility. Orthotic devices, such as arch supports or braces, may also be recommended to provide additional support to the foot and alleviate symptoms.
In cases where non-surgical treatments are not effective, surgery may be necessary to repair or reconstruct the damaged tendon. This may involve removing inflamed tissue, transferring a tendon from another part of the body, or fusing the bones in the foot to stabilize the arch.
Overall, the most effective treatment for posterior tibial tendon dysfunction will depend on the severity of the condition and the individual’s specific symptoms. It is important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best course of action for managing this condition and preventing further complications.
Can I walk with posterior tibial tendonitis?
The early stages of posterior tibial tendinitis will allow you to walk with only mild pain. However, your symptoms will worsen as your condition progresses, leading to difficulty moving the affected foot. Reduce the use of your painful foot to give the tendons enough time to heal.Dec 8, 2021
What is posterior tibial tendon dysfunction?
Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction (PTTD) is a condition caused by changes in the tendon, impairing its ability to support the arch. This results in flattening of the foot. PTTD is often called adult acquired flatfoot because it is the most common type of flatfoot developed during adulthood.
What is stage 4 posterior tibial tendonitis?
Stage IV PTTDPTTDPosterior tibial tendon dysfunction (PTTD) represents an acquired, progressive disease of the foot and ankle that is seen commonly in middle-aged patients. It is the most common cause of adult acquired flatfoot deformity. Treatments involve conservative and surgical options depending on the severity of the disease.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov › books › NBK542160Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction – StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf is the most challenging of the posterior tibial tendon deficiencies. The combination of a flattened longitudinal arch and a tilted ankle make successful management unpredictable.
How do you test for Tib post?
X-ray and MRI can confirm diagnosis, help stage disease and assist in preoperative planning. The disease as an entity is under-recognized, and early stages of the disease can be misdiagnosed, but prompt treatment can prevent deformity and need for surgery.
How much is DOT physical in Michigan?
How much does a DOT physical cost in Michigan? The average cost of a DOT physical in Michigan ranges between $10 to $50 with insurance and between $50-$200 without insurance.

How much does a NYS DOT physical cost?
What is the cost of DOT or CDL physical examination for uninsured people? If you do not have a medical insurance the physical exam is $100(credit)… $88(cash).
Where do I send my DOT medical card in NY?
How to submit a Medical Certificate to the Medical Certification Unit. Email: [email protected] Put your first and last name in the subject line. In the event that you need to confirm receipt of your e-mailed medical certificate, DMV will track it using the information in the subject line.
How much does a DOT physical cost in New York State?
$85 DOT Medical Exams in NYC Our DOT Medical Examiners can submit your certification to the Department of Motor Vehicles during the same visit.