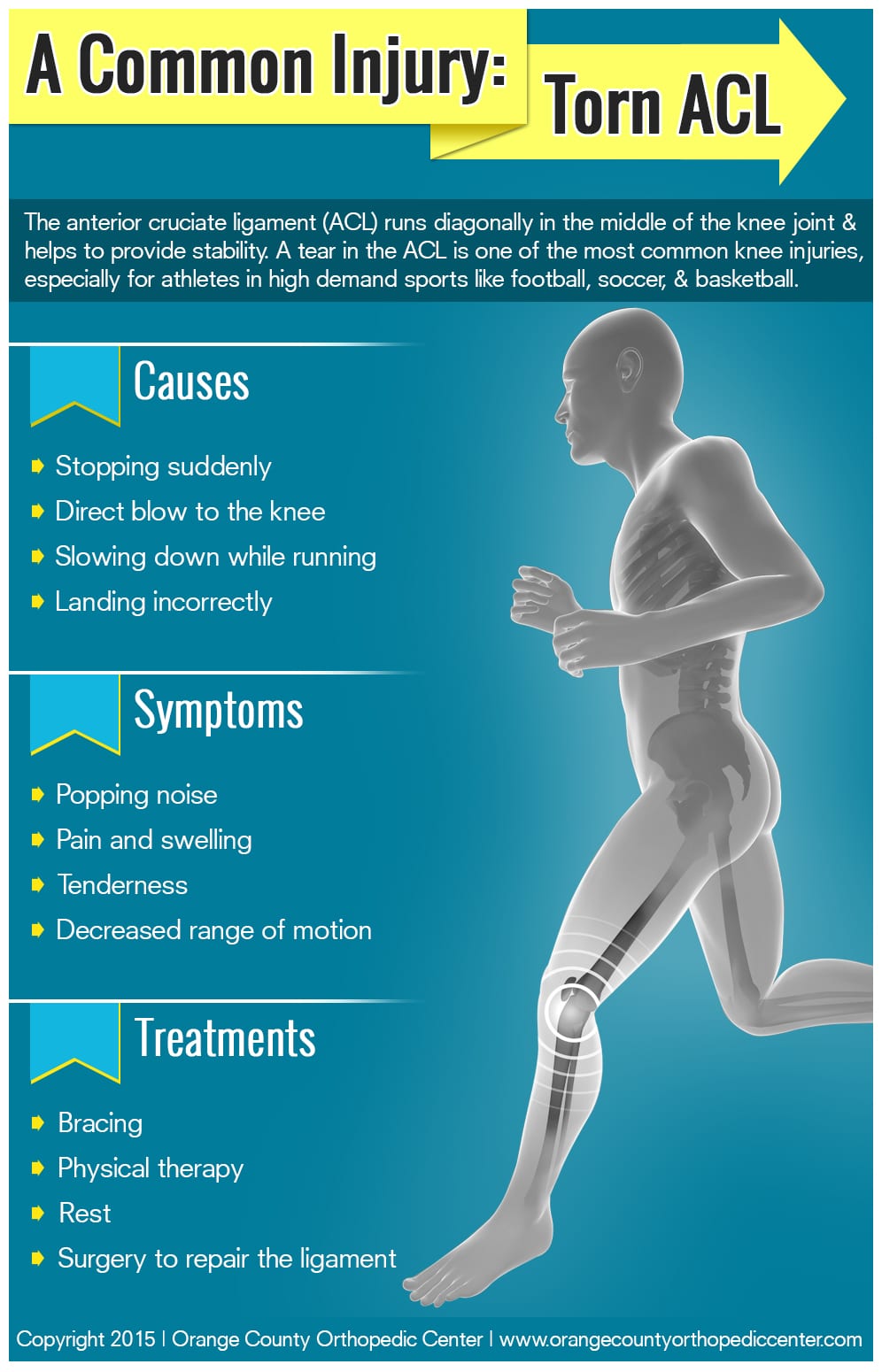
Determining whether an ACL (Anterior Cruciate Ligament) is torn or sprained requires a comprehensive evaluation by a medical professional. The ACL is a crucial ligament in the knee joint, responsible for providing stability and preventing excessive forward movement of the shin bone.
When an ACL injury occurs, individuals typically experience a distinct popping sound or sensation, followed by immediate pain and swelling in the knee. A torn ACL often results from sudden pivoting or twisting motions, such as those commonly observed in sports like soccer, basketball, or skiing.
To diagnose an ACL injury, a healthcare provider assesses multiple factors. Initially, they discuss the patient’s medical history, specifically focusing on the details of the injury and the symptoms experienced. A physical examination follows, including various knee tests to assess stability, movement range, and joint tenderness. These tests may involve analyzing the Lachman test, Pivot Shift test, or anterior drawer test, which evaluate the looseness of the ACL and the integrity of the knee joint.
Imaging techniques such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) help to confirm the diagnosis by providing detailed images of the knee’s internal structures. An MRI can precisely identify a torn or sprained ACL, as well as assess potential damage to other ligaments or structures in the joint.
In some cases, a sprained ACL may heal with conservative treatment, including physical therapy and bracing to stabilize the knee. However, a completely torn ACL typically requires surgical intervention, especially for individuals who plan to engage in activities that demand knee stability.
In conclusion, the diagnosis of a torn or sprained ACL entails a comprehensive examination by a healthcare professional. The signs and symptoms, combined with physical tests and imaging studies, enable an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan tailored to each individual’s circumstances.
Can a sprained ACL heal on its own?
A torn ACL can’t heal on its own, but it’s possible to live with it (especially if you have a low-grade tear). But if you’re an athlete or want to return to physical activity, you’ll need surgery to repair your ACL. Most people choose to have an ACL tear surgically repaired.Aug 2, 2023

Can you walk on a sprained ACL?
The short answer is yes. After the pain and swelling subsides and if there is no other injury to your knee, you may be able to walk in straight lines, go up and down stairs and even potentially jog in a straight line. The ACL (anterior cruciate ligament) is an important ligament that provides stability to the knee.
How do you test if your ACL is torn?
– Pull the tibia forward towards you to assess how much motion there is. – If the ACL is intact, there should be very little motion with a “firm” end feel. – If there is an ACL injury, there might be excessive motion and an “empty” end feel (no catch limiting forwards translation.Nov 8, 2018
How serious is a sprained ACL?
ACL Sprains While patients will experience symptoms, they can usually be treated without surgery. This type of ACL sprain occurs when the fibers of the ligament are stretched, but a tear does not exist. For the most part, the knee will remain stable.
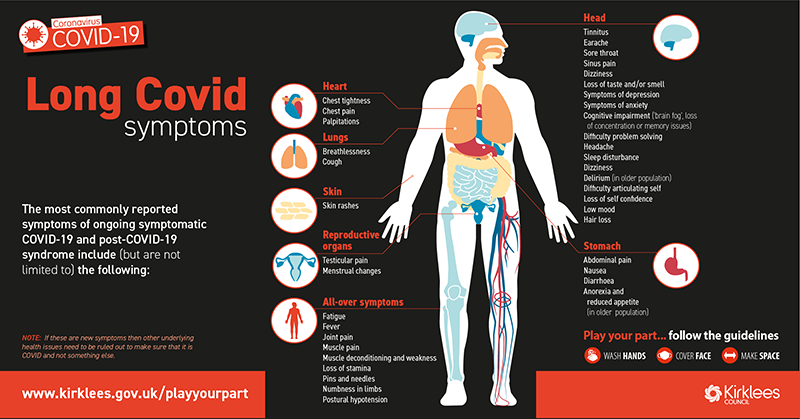
What are the symptoms of long COVID?
The symptoms, such as chronic pain, brain fog, shortness of breath, chest pain, and intense fatigue, can be debilitating. Severe cases of Long COVID can even affect the body’s organs. But imaging tests don’t always show the origins of those symptoms.
Where is the COVID headache located?
This variety often takes center stage in the forehead, cheeks, and nose regions. Bending forward or lying down can exacerbate these headaches, and they may arrive hand in hand with congestion and facial pressure. Attributes of Sinus Headaches Associated with COVID-19: Location: Forehead, cheeks, and nose.
Can long COVID cause migraines?
And migraine-like headaches are being tracked as the most common symptom of long COVID, says Dr. Matthew Robbins, Associate Professor of Neurology and Associate Attending Neurologist at Weill Cornell Medicine.
On what day do Covid symptoms peak?
Symptoms peak: Around 3-5 days after you start to feel sick, symptoms of COVID peak. This is when you’re more likely to have fever, muscle aches, and headache. Losing your sense of smell and taste with COVID is less common now.
Are migraines a side effect of long COVID?
And migraine-like headaches are being tracked as the most common symptom of long COVID, says Dr. Matthew Robbins, Associate Professor of Neurology and Associate Attending Neurologist at Weill Cornell Medicine.