Performing a physical assessment on a child requires a specific approach to ensure accuracy and comfort. Start by introducing yourself to the child and their parent or guardian, explaining the process in a simple and reassuring way. Begin by observing the child’s general appearance, noting any signs of distress or discomfort. Then, assess their vital signs including temperature, heart rate, and respiratory rate.
Next, examine the child’s skin, checking for any abnormalities, rashes, or bruises. Move on to inspect their head and neck, including the eyes, ears, nose, and throat. Evaluate their chest and lungs by listening to their breathing with a stethoscope.
Continue the assessment by examining their heart, abdomen, and extremities, checking for any tenderness or swelling. Lastly, conclude by assessing the child’s neurological status, including their level of consciousness, muscle strength, and reflexes.
Throughout the assessment, communicate clearly with the child, using age-appropriate language and providing positive reinforcement. Maintain a calm and patient demeanor to help put the child at ease. Remember to respect the child’s privacy and autonomy throughout the examination. By following these steps, healthcare providers can ensure a thorough and accurate physical assessment of a child.
What does a child’s physical consist of?
The doctor will take a medical and family history and do a physical exam. During the visit, your child’s blood pressure, vision, and hearing will be checked. Your child may be screened for anemia, tuberculosis, or high cholesterol. The doctor might also ask about your child’s sleep, exercise, and eating habits.

How do you examine a pediatric patient?
Observe the child under ideal circumstances, for example, while in mother’s lap and leave the more painful and uncomfortable parts of the examination until last, for example, throat and ears. Vital Signs: Record vital signs which include temperature, pulse, respiratory rate, and blood pressure (arm and legs).
What is physical assessment of a child?
In addition to diagnosing disease, pediatric assessment should involve identification of malnutrition, immunization status, level of development, screening for 4 Ds (Defects at birth, Deficiencies, Diseases and Developmental Delay including Disability), hearing and visual assessment and detection of child abuse.

What is a physical exam for a child?
The doctor will take a medical and family history and do a physical exam. During the visit, your child’s blood pressure, vision, and hearing will be checked. Your child may be screened for anemia, tuberculosis, or high cholesterol. The doctor might also ask about your child’s sleep, exercise, and eating habits.
Can kyphoplasty be redone?
Due to technical constraints, placing an additional kyphoplasty after one has already been accomplished may be technically dangerous and a simpler less costly vertebroplasty technique may be beneficial.
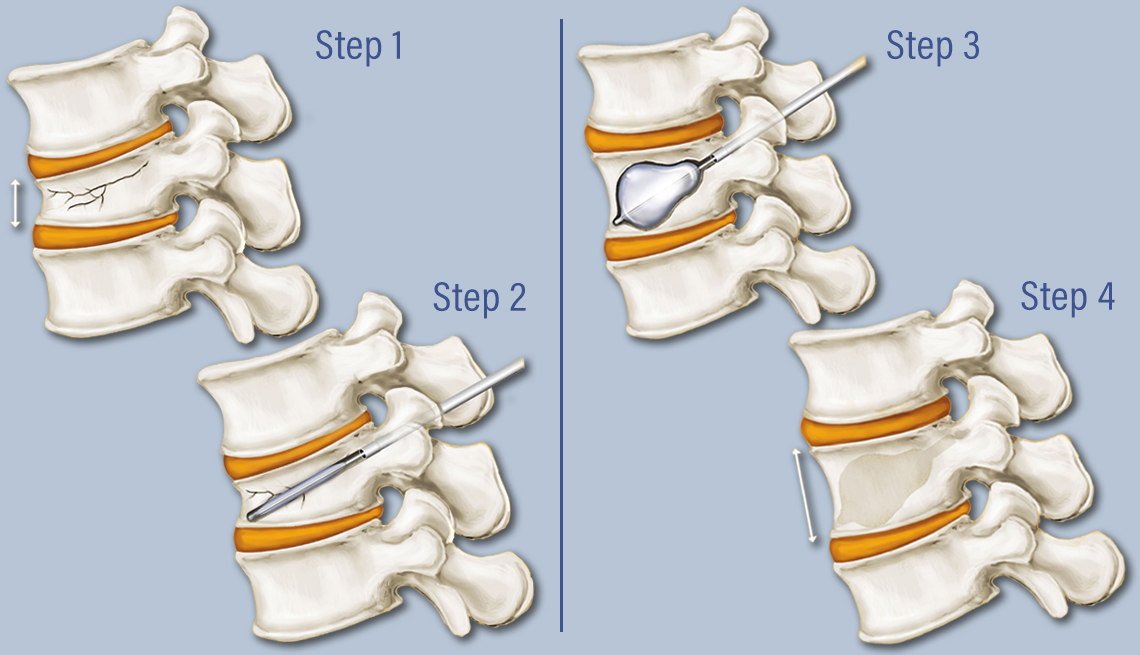
How long does a kyphoplasty last?
The entire procedure usually takes less than an hour. If more than one vertebra requires treatment, the procedure may take longer.
Why does my back still hurt after kyphoplasty?
In some cases, kyphoplasty either fails to relieve the pain or results in worse pain or other symptoms. For example, if bone cement leaks onto a nerve root or the spinal cord, it could potentially cause worsened symptoms of pain, tingling, numbness, and/or weakness.
What happens when kyphoplasty doesn’t work?
In some cases, kyphoplasty either fails to relieve the pain or results in worse pain or other symptoms. For example, if bone cement leaks onto a nerve root or the spinal cord, it could potentially cause worsened symptoms of pain, tingling, numbness, and/or weakness. Pulmonary embolism.
What are the drawbacks of kyphoplasty?
Potential Complications of Kyphoplasty Some general surgical risks apply to kyphoplasty, including infection, excessive bleeding, and/or a negative reaction to anesthesia. Other risks that are more specific to the kyphoplasty procedure include: Bone cement leakage.


