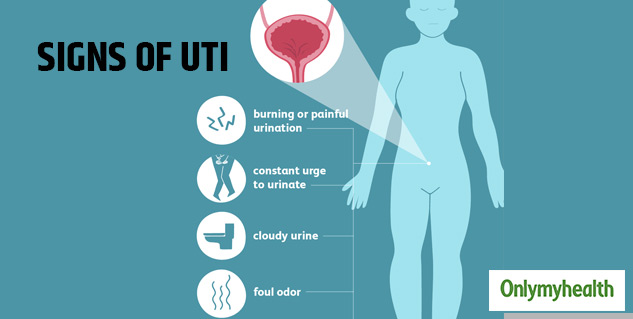
A urinary tract infection (UTI) occurs when harmful bacteria enter and multiply in the urinary system, causing inflammation and discomfort. If left untreated, a UTI can potentially spread to the kidneys, leading to more severe complications. But how can one determine if the infection has indeed reached the kidneys?
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of a kidney infection is crucial for early detection and prompt treatment. While the initial symptoms of a UTI involve the lower urinary system, such as frequent and painful urination, a kidney infection manifests with additional symptoms. These may include fever, back pain, side pain, chills, fatigue, and even nausea or vomiting.
When a UTI progresses to the kidneys, the severity and intensity of symptoms tend to increase. The infection can cause the kidneys to become swollen and inflamed, affecting their normal functioning. As a result, individuals may experience more intense pain and discomfort in the lower back, sides, or groin. In some cases, the pain may radiate to the abdomen or even the thighs.
Other indicators of a kidney infection include cloudy or bloody urine, a strong and persistent urge to urinate, and occasionally, difficulty passing urine. It is important to note that these symptoms may not always be present, and individuals may exhibit differing combinations of them.
If there is a suspicion of a kidney infection, it is crucial to seek medical attention promptly. A healthcare professional will evaluate the symptoms, conduct a physical examination, and may order further tests, such as urine and blood tests, to confirm the diagnosis and determine the appropriate course of treatment.
In conclusion, detecting whether a UTI has spread to the kidneys requires attentiveness to symptoms. Increased pain in the back, sides, or groin, along with additional signs such as fever and chills, indicate the possibility of a kidney infection. Seeking medical attention and undergoing the necessary tests are essential for proper diagnosis and timely treatment.
How long does it take for a UTI to turn into a kidney infection?
A kidney infection usually starts out as a urinary tract infection (UTI) that affects the bladder. There’s no rule for how long it takes a UTI to spread from your bladder to your kidneys. For a mild kidney infection, treatment can last 7 to 14 days.
Where does your back hurt with a UTI?
A UTI causes inflammation in the lining of your urinary tract. The inflammation may cause the following problems: Pain in your flank, abdomen, pelvic area or lower back. Pressure in the lower part of your pelvis.Apr 6, 2023
Can a UTI cause back pain on one side?
A urinary tract infection is a very common type of infection in your urinary system. It can involve any part of your urinary system. Bacteria — especially E. coli — are the most common cause of UTIs. Symptoms include needing to pee often, pain while peeing and pain in your side or lower back.Apr 6, 2023

What are 3 symptoms of a UTI?
– Pain or burning while urinating.
– Frequent urination.
– Feeling the need to urinate despite having an empty bladder.
– Bloody urine.
– Pressure or cramping in the groin or lower abdomen.
Does medical California cover urgent care?
If you are outside the L.A. Care service area, but inside the United States, you do not need pre-approval to get urgent care. Go to the nearest urgent care facility. Medi-CalMedi-CalThe California Medical Assistance Program (Medi-Cal or MediCal) is the California implementation of the federal Medicaid program serving low-income individuals, including families, seniors, persons with disabilities, children in foster care, pregnant women, and childless adults with incomes below 138% of federal …https://en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Medi-CalMedi-Cal – Wikipedia does not cover urgent care services outside the United States.
Where do UCLA students go for urgent care?
Students can access local UCLA Health Immediate Cares to address their urgent medical concerns with a UCLA Health Physician when same-day appointments have filled at The Ashe Center. UCLA Health Immediate Care visits are subject to applicable copays and coinsurances for services rendered.
Does UCLA have a clinic?
UCLA OUTPATIENT CLINICS Our clinics provide medical services to patients in a variety of specialties, including: AIDS, gastroenterology, gynecology, ophthalmology, endocrinology, geriatrics, neurology, orthopedics, otolaryngology, psychiatry, rheumatology, and urology.
Does Medi-Cal cover copays?
Medi- Cal may pay for any co-pays or deductibles you accrue under your private health insurance coverage, Medicare Part A (in-patient hospital), Medicare Part B (out-patient services, including specialty care and lab tests), Veterans Insurance, Tricare or any other public or private insurance plan that allows for such …