Walking is a mild physical activity that is often recommended for people suffering from sciatica. Sciatica is a condition characterized by pain that radiates along the pathway of the sciatic nerve, which runs from the lower back through the hips and down each leg. This pain is typically caused by compression or irritation of the sciatic nerve roots in the lower spine.
Engaging in regular walking can have several benefits for individuals with sciatica. First and foremost, walking helps promote blood circulation and oxygen flow, which can potentially reduce inflammation and alleviate pain. It also strengthens the muscles in the lower back, buttocks, and legs, providing more support to the spine and reducing pressure on the affected nerves.
Walking is a low-impact exercise that places minimal strain on the joints, making it a suitable option for individuals with sciatica-related mobility issues. It can be easily incorporated into daily routines and adjusted to personal fitness levels, ensuring a safe and sustainable exercise routine.
Furthermore, walking helps maintain a healthy body weight, which is important for preventing and managing sciatica. Excess weight can put additional pressure on the spine, aggravating the symptoms of sciatica. Regular walking can help individuals maintain a healthy weight and reduce the risk of developing or exacerbating the condition.
While walking can offer relief for sciatica, it is crucial to approach it gradually and listen to your body. Start with shorter walks and gradually increase the duration as tolerance improves. It is important to maintain proper posture while walking and wear supportive footwear to minimize strain on the spine.
In conclusion, walking can be a beneficial activity for individuals dealing with sciatica. It helps improve blood circulation, strengthens muscles, supports weight management, and promotes overall well-being. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any exercise program to ensure it is appropriate for your specific condition.
How do you Unpinch a sciatic nerve?
How do I get my sciatic nerve to stop hurting fast?
– Cold packs. Place a cold pack on the painful area for up to 20 minutes several times a day. …
– Hot packs. After 2 to 3 days, apply heat to the areas that hurt. …
– Stretching. Stretching exercises for the low back might provide some relief. …
– Medications.
How long does it take for sciatic nerve pain to go away?
Sciatica is where the sciatic nerve, which runs from your lower back to your feet, is irritated or compressed. It usually gets better in 4 to 6 weeks but can last longer.
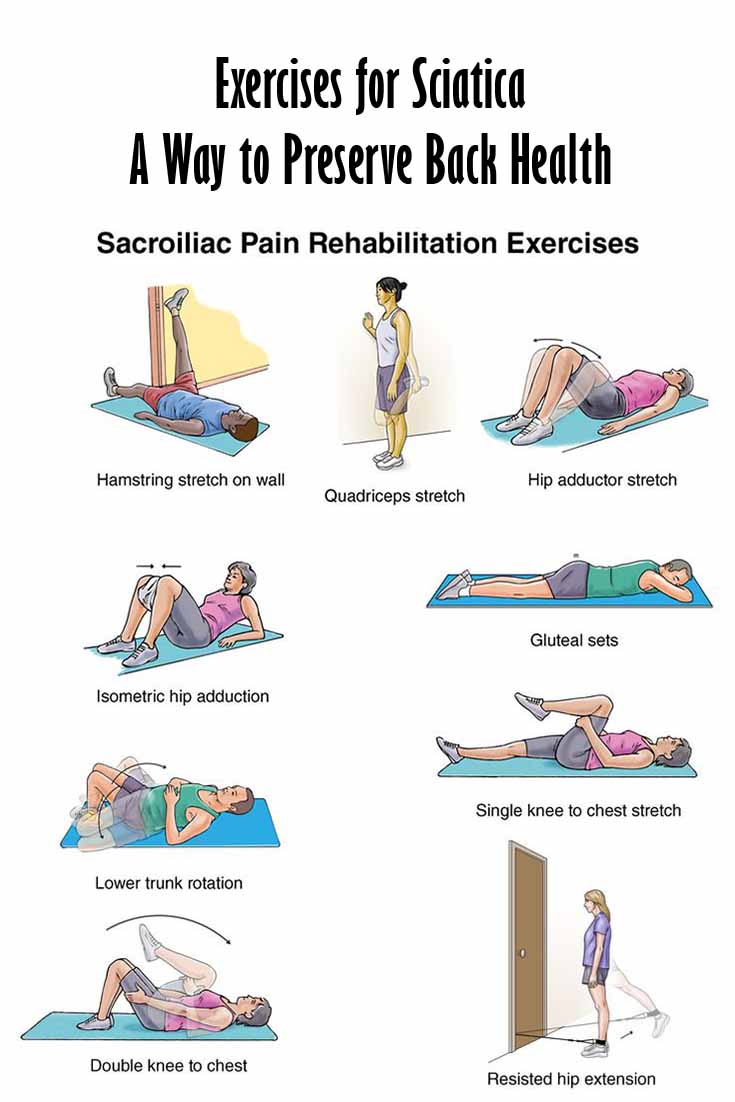
What is the best exercise for sciatic nerve pain?
– Lie on your back with your legs extended. Try not to arch your back.
– Slowly bring one knee toward your chest and grasp it with your hands (behind or on top of the knee).
– Pull on the knee gently until you feel a mild stretch in your lower spine and hip.
– Hold 5 to 30 seconds. Lower slowly.
When does a herniated disc become serious?
The most serious complication from a herniated disc is the development of the cauda equina syndrome. This results when a very large fragment of disc material is ruptured into the spinal canal in the area where the nerves that control the bowels and bladder travel before they leave the spine.
How do I know if my herniated disc is severe?
Seek emergency medical attention if you have: Worsening symptoms. Pain, numbness or weakness can increase to the point that they hamper your daily activities. Bladder or bowel dysfunction.
What are the 5 stages of herniated disc?
– Stage 1: Disc Compression. …
– Stage 2: Bulging Disc. …
– Stage 3: Disc Protrusion. …
– Stage 4: Herniated Disc.
What does disc reherniation feel like?
For example, if the sciatic nerve is affected again by remaining disc material from the initial herniation, you will likely notice pain, numbness, tingling sensations, and general muscle weakness in your lower body. A common indication is pain that is mostly felt in one leg.
How do you know if disc is re herniated?
An imaging study in the form of an MRI is used to diagnose re-herniation. MRI studies with gadolinium may be used to differentiate between scar tissue and re-herniation. Other imaging studies such as an X-ray and a CT scan are more commonly used to visualize the bony anatomy of the patient.