Chronic pain is a prevalent and debilitating condition affecting individuals worldwide. When it comes to managing chronic pain, the first-line treatment is often non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). In a recent article, the authors explore the efficacy, safety, and current guidelines regarding the use of NSAIDs in chronic pain management.
NSAIDs are a class of medications commonly used for their analgesic (pain-relieving) and anti-inflammatory properties. These drugs work by inhibiting the production of prostaglandins, which are responsible for causing pain and inflammation in the body. NSAIDs have shown efficacy in managing various chronic pain conditions, including osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and musculoskeletal pain.
Despite their widespread use, it is important to consider the potential risks and side effects associated with NSAID use. Long-term use of NSAIDs can lead to gastrointestinal complications such as ulcers, bleeding, and perforation. Additionally, NSAIDs have been associated with increased cardiovascular risks, including high blood pressure and heart attack. Therefore, the authors argue that healthcare professionals should carefully evaluate the benefits versus risks before prescribing NSAIDs for chronic pain management.
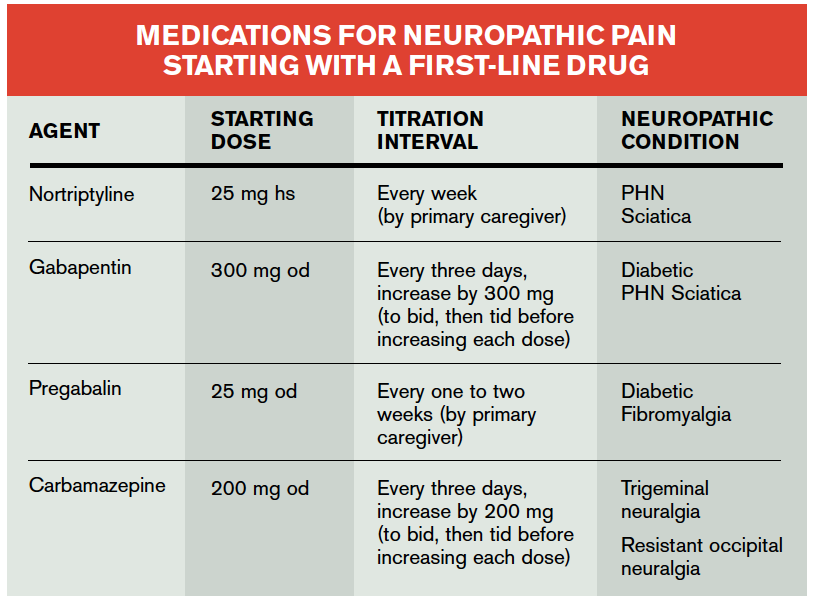
Furthermore, the article highlights the existing guidelines for the optimal use of NSAIDs in chronic pain. These guidelines suggest starting with the lowest effective dose and monitoring patients for adverse effects regularly. In cases where NSAIDs are contraindicated or ineffective, other pain management options such as opioids, antidepressants, or anticonvulsants may be considered.
In conclusion, NSAIDs are considered the first-line treatment for chronic pain due to their analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties. However, healthcare professionals should proceed with caution when prescribing NSAIDs, considering the potential risks involved. Regular monitoring and adherence to guidelines are essential for ensuring the safe and effective use of NSAIDs in chronic pain management. Further research and advancements in this field are necessary to explore alternative treatment options and promote better outcomes for individuals suffering from chronic pain.
What are the long term effects of untreated chronic pain?
Chronic pain leads to significantly decreased quality of life, reduced productivity, lost wages, worsening of chronic disease, and psychiatric disorders such as depression, anxiety, and substance abuse disorders. Patients with chronic pain are also at a significantly increased risk for suicide and suicidal ideation.
What is the standard treatment for chronic pain?
Medical management of chronic pain, including medicine management: Over-the-counter (OTC) medicines may include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), aspirin, or acetaminophen. Prescription pain medicines, including opioids, may be needed to provide stronger pain relief than aspirin.
What is the first line medication for pain crisis?
Topical nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are safe and effective for treating acute pain. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, acetaminophen, or a combination is an effective initial treatment approach for acute pain syndromes. Medication selection should be based on minimizing risks for the specific patient.