An osteopath and an orthopedist are both medical professionals who specialize in the musculoskeletal system, but there are key differences between the two.
An osteopath is a type of holistic healthcare provider who focuses on treating the body as a whole, rather than just targeting specific symptoms. They believe that the body has the ability to heal itself and use manual therapy techniques such as manipulation and massage to promote healing. Osteopaths also consider factors such as diet, exercise, and mental health when treating patients.
On the other hand, an orthopedist is a medical doctor who specializes in the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of musculoskeletal disorders and injuries. They often use a combination of surgical and non-surgical treatments to address problems such as fractures, arthritis, and sports injuries. Orthopedists typically work with patients who have acute or chronic conditions that require medical intervention.
In summary, the main difference between an osteopath and an orthopedist is their approach to healthcare. Osteopaths focus on holistic care and manual therapy techniques, while orthopedists specialize in the medical and surgical treatment of musculoskeletal conditions. Patients should choose the type of provider based on their individual needs and preferences.
Why are osteopaths better than chiropractors?
Differences. The primary difference between chiropractors and osteopaths is the degree they hold. An osteopath holds a medical degree and has the same medical rights as any M.D., including the right to prescribe medication. Chiropractors hold a Doctorate of Chiropractic degree and cannot write prescriptions.

Why choose an osteopath?
The key to osteopathy is the importance of treating the patient as an individual and not just the injury or condition. OsteopathsOsteopathsOsteopaths attempt to diagnose and treat what was originally called “the osteopathic lesion”, but which is now named “somatic dysfunction”, by manipulating a person’s bones and muscles. Osteopathic Manipulative Treatment (OMT) techniques are most commonly used to treat back pain and other musculoskeletal issues.https://en.wikipedia.org › wiki › OsteopathyOsteopathy – Wikipedia spend time getting to know their patients so that they can understand their unique set of circumstances and other factors which may be playing a part in their conditions.

Why are osteopathic doctors better?
Osteopathic medicine is a “whole person” approach to medicine—treating the entire person rather than just the symptoms. With a focus on preventive health care, Doctors of Osteopathic Medicine (DOs) help patients develop attitudes and lifestyles that don’t just fight illness, but help prevent it, too.

What is difference between orthopedic and orthopedist?
The only difference between the two words is in fact their spelling.
What not to do after ulnar nerve surgery?
Allow your arm to heal. Don’t push, pull, or lift anything heavy until your doctor says it’s okay to do so. This will depend on the type of surgery you had. You may drive when you are fully able to use your arm.
How do I know if I need ulnar nerve transposition?
The ulnar nerve transposition procedure is usually performed on patients whose ulnar nerve is compressed near their medial epicondyle inside the elbow. This compressing of the ulnar nerve can cause pain, tingling, or numbness in the small and ring fingers and forearm.
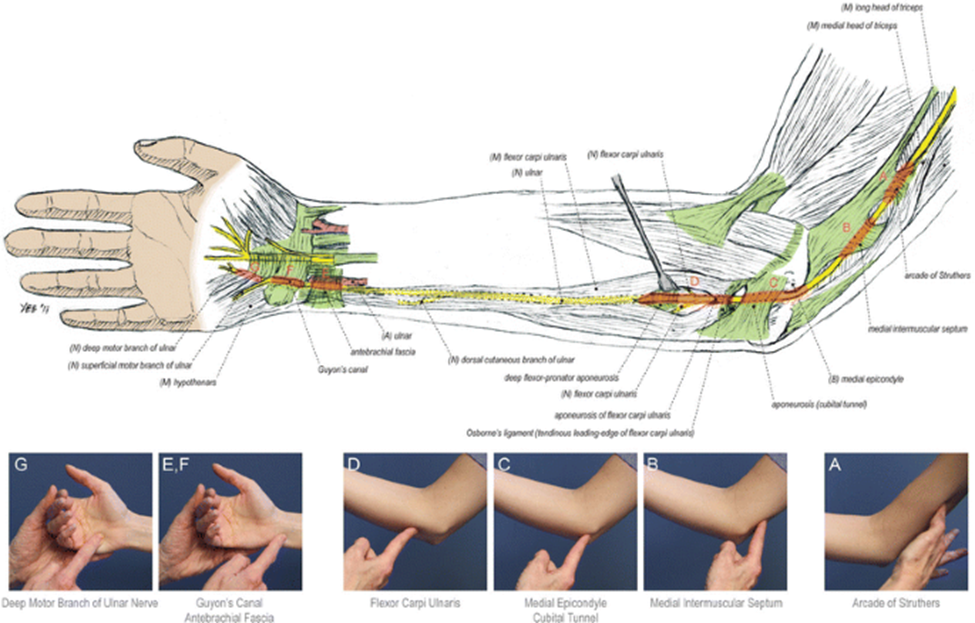
How do I know if I damaged my ulnar nerve?
Weakness, loss of coordination of the fingers. Claw-like deformity of the hand and wrist. Pain, numbness, decreased sensation, tingling, or burning sensation in the areas controlled by the nerve.
How long will I be off work after ulnar nerve surgery?
After surgery, people who work at a job requiring physical activity should use the affected arm or elbow only for occasional work during the first few weeks after the procedure. People who work in an office can typically return to work a day or two after surgery.
When should you get ulnar nerve surgery?
If ulnar nerve compression does not improve with nonsurgical treatments, or if the condition causes persistent pain and numbness, your doctor may recommend surgery.



