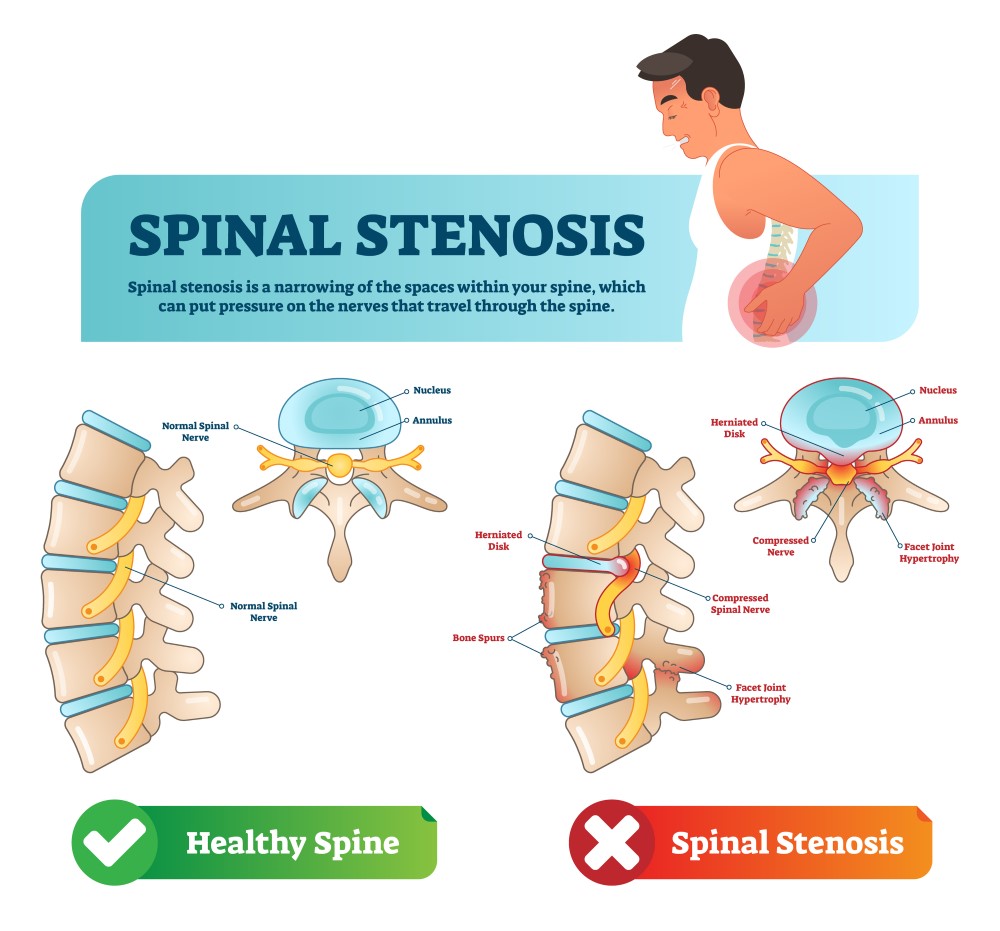
Spinal stenosis is a condition in which the spinal canal narrows, putting pressure on the spinal cord and nerves. The progression of spinal stenosis can vary from person to person, but in general, it tends to progress slowly over time. However, in some cases, spinal stenosis can progress more rapidly, leading to more severe symptoms and potentially causing complications.
The rate at which spinal stenosis progresses depends on various factors, including the underlying cause of the condition, the individual’s overall health, and the presence of any risk factors. For example, degenerative changes in the spine, such as herniated discs or bone spurs, can contribute to the progression of spinal stenosis. In some cases, a sudden injury or trauma to the spine can also accelerate the progression of the condition.
Symptoms of spinal stenosis can include pain, numbness, weakness, and tingling in the affected area of the body. As the condition progresses, these symptoms may worsen and impact daily activities. In severe cases, spinal stenosis can lead to complications such as difficulty walking, loss of bladder or bowel control, and even paralysis.
Early diagnosis and treatment of spinal stenosis are key to managing the condition and preventing further progression. Treatment options may include medications, physical therapy, steroid injections, and in some cases, surgery. It is important for individuals with spinal stenosis to work closely with their healthcare provider to develop an appropriate treatment plan and monitor the progression of the condition.
Will I end up in a wheelchair with spinal stenosis?
The symptoms are often so gradual, that patients seek medical attention very late in the course of this condition. Patients may be so disabled and weak that they require the use of a wheelchair for mobility. In rare instances, severe spinal stenosis can cause paraplegia and/or bowel/bladder incontinence.
What is considered severe spinal stenosis?
Stenosis is considered severe when it causes loss of certain functions or disabilities, or when other treatment options have failed to relieve symptoms. You should consult an expert neurosurgeon to assess your symptoms.
Can spinal stenosis develop quickly?
For most people, symptoms develop and progress slowly over a period of time, and some people may not have any symptoms. The symptoms you experience depend on the location of the narrowing in your spine. Symptoms of spinal stenosis in the lower back can include: Pain in the lower back.Nov 1, 2023

How do I know if my spinal stenosis is severe?
More serious symptoms that need prompt attention include: Difficulty or poor balance when walking. Worsening numbness and weakness of your limb. Problems controlling urine or bowel movements.

How to tell the difference between hip joint and muscle pain?
Problems within the hip joint itself tend to result in pain on the inside of the hip or the groin. Hip pain on the outside of the hip, upper thigh or outer buttock is usually caused by problems with muscles, ligaments, tendons and other soft tissues that surround the hip joint.
How do I know if my hip pain is muscle or joint?
Problems within the hip joint itself tend to result in pain on the inside of the hip or the groin. Hip pain on the outside of the hip, upper thigh or outer buttock is usually caused by problems with muscles, ligaments, tendons and other soft tissues that surround the hip joint.

Why does my hip hurt when I sit but not when I walk?
Many people experience hip pain while sitting. A variety of factors, including poor posture, improper seating, sitting for prolonged periods, or sitting in a way that puts pressure on the hips, may cause hip pain. Potential medical causes include autoimmune conditions and pinched nerves.
Why does my hip hurt when I sit but not walk?
Typically, the top causes of hip pain while sitting include arthritis, hip bursitis, tendinitis, lupus and piriformis syndrome. If left untreated, many of these conditions can cause permanent joint damage. Therefore, it is important to take action immediately through the physical therapy treatments mentioned below.
How do I know if my hip pain is muscle or bone?
Problems within the hip joint itself tend to result in pain on the inside of the hip or the groin. Hip pain on the outside of the hip, upper thigh or outer buttock is usually caused by problems with muscles, ligaments, tendons and other soft tissues that surround the hip joint.



