Title: Can an Epidural Make Things Worse? An Overview
Epidurals, a commonly used approach for pain relief during childbirth and other medical procedures, have shown both benefits and potential drawbacks. This article aims to provide a concise summary of the potential risks and complications associated with epidurals, focusing on their potential to worsen certain outcomes.
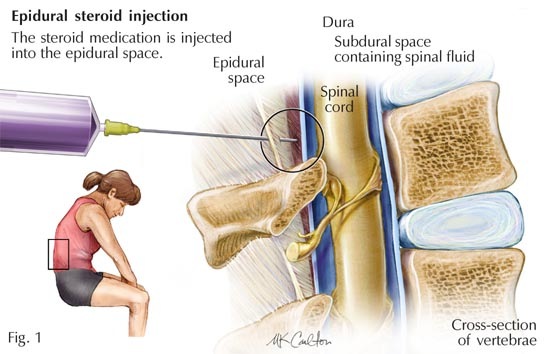
Epidurals work by delivering pain medication directly into the epidural space surrounding the spinal cord. While they are highly effective in managing labor pain, there are a few considerations to keep in mind. Firstly, epidurals may slow down labor, potentially leading to the need for additional interventions such as labor-inducing drugs or even a cesarean section. Research indicates that epidurals can extend the duration of the first stage of labor and increase the likelihood of instrumental deliveries. However, it’s important to note that these findings are not conclusive and can vary among individuals.
Another potential drawback is the effect of epidurals on maternal blood pressure. Some studies suggest that epidurals can cause a drop in blood pressure, leading to dizziness or fainting. Special precautions are taken to monitor and manage blood pressure during and after administration of the epidural.
In rare cases, epidurals may cause nerve damage, although the incidence of this complication is exceedingly low. Occasionally, some women may experience headaches, backaches, or soreness at the injection site after receiving an epidural. These side effects are typically temporary and resolve spontaneously within a short period.
It is worth noting that this article does not cover all potential risks and benefits of epidurals comprehensively. The decision to choose an epidural for pain management should be made after a thorough discussion between the healthcare provider and the patient. It is important to consider individual needs, medical history, and preferences, taking into account both the potential benefits and risks associated with epidural administration.
In conclusion, epidurals offer effective pain relief during labor, but they are not without potential risks or drawbacks. Understanding the possibilities of slowed labor progression, blood pressure changes, and rare complications can help individuals make informed choices regarding pain management during childbirth. Open and honest communication with healthcare professionals is crucial in ensuring the safety and well-being of both the mother and the baby.
What problems do epidurals cause?
Risks and side effects of an epidural Epidurals are usually safe, but there’s a small risk of side effects and complications, including: low blood pressure, which can make you feel lightheaded or nauseous. temporary loss of bladder control. itchy skin.
What is the major adverse side effect of epidural anesthesia?
Risks and side effects of an epidural low blood pressure, which can make you feel lightheaded or nauseous. temporary loss of bladder control. itchy skin. feeling sick.
What are 2 risks side effects of an epidural?
– low blood pressure, which can make you feel lightheaded or nauseous.
– temporary loss of bladder control.
– itchy skin.
– feeling sick.
– headaches.
– nerve damage.
What is the most common complication of an epidural injection?
Temporary nerve damage Nerve damage can cause loss of feeling or movement in parts of your lower body. The most common symptom is a small, numb area with normal movement and strength. This usually gets better after a few days or weeks, but can sometimes take months.

How do I know if my pain is from my kidney?
In comparison, kidney pain is typically located higher on your back and it often feels deeper. Most of the time, kidney pain symptoms occur under your ribs, to the right or left of your spine. Kidney pain may also radiate to other areas, such as your abdomen or groin.
How can you tell the difference between muscle pain and kidney pain?
Kidney pain is often felt on one side, under the rib cage, in the middle part of the back. Some people refer to this area as the “flank.” Type of pain: Kidney pain comes from a deeper place than the muscles. This means it usually doesn’t get worse with lifting, twisting, or bending like muscle pain does.Jan 6, 2023

How do you know the difference between muscle pain and kidney pain?
Kidney pain is often felt on one side, under the rib cage, in the middle part of the back. Some people refer to this area as the “flank.” Type of pain: Kidney pain comes from a deeper place than the muscles. This means it usually doesn’t get worse with lifting, twisting, or bending like muscle pain does.Jan 6, 2023
What does it feel like when your kidneys hurt?
What does kidney pain feel like? Kidney pain often feels like a dull ache that gets worse if someone gently presses on that area. While it is more common to feel kidney pain on only one side, some health problems may affect both kidneys and cause pain on both sides of your back.
What can be mistaken for kidney pain?
– shingles.
– cancer of the spine.
– infection.
– cauda equina syndrome affecting the base of the spinal cord.
– abdominal aortic aneurysm.
– endometriosis.